GMI
GERMAN MALAYSIAN INSTITUTE
FINAL YEAR PROJECT
DOCUMENTATION HANDBOOK
Diploma Final Year Project Documentation
Guidelines
Training
for
Ad v a n c e d
T e c h n o l o gy
�[FINAL YEAR PROJECT DOCUMENTATION
HANDBOOK]
GMI
GERMAN MALAYSIAN INSTITUTE
GMI has the right to change the Final Year Project Documentation Handbook if it deems
necessary.
5th Edition, September 2014
Updated May 2015
All rights reserved.
No part of this book may be reproduced in any form or any means without written permission
from
German-Malaysian Institute.
GERMAN-MALAYSIAN INSTITUTE
�TABLE OF CONTENTS
Contents
1.0
Page
Sequence of Project Report
1.1
Verification of Project Report
1.2
Title Page
1.3
Oath
1.4
Dedication
1.5
Acknowledgements
1.6
Abstract
1.7
Table of Contents
1.8
List of Tables
1.9
List of Figures
1.10
List of Symbols / Abbreviation
1.11
List of Appendix
1.12
Chapters and Sub-chapters
1.13
Citing Sources of Information
1.14
Appendix
1.15
Bibliography
1.2
Format of Project Report
1.3
Final Year Project Documentation Assessment
Appendix A - P
10 - 27
�1.0
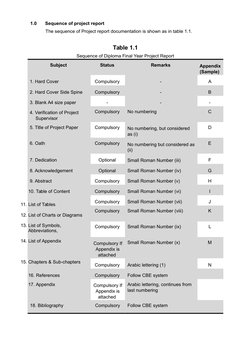
Sequence of project report
The sequence of Project report documentation is shown as in table 1.1.
Table 1.1
Sequence of Diploma Final Year Project Report
Subject
Status
Remarks
Appendix
(Sample)
1. Hard Cover
Compulsory
2. Hard Cover Side Spine
Compulsory
3. Blank A4 size paper
4. Verification of Project
Supervisor
Compulsory
No numbering
5. Title of Project Paper
Compulsory
No numbering, but considered
as (i)
6. Oath
Compulsory
No numbering but considered as
(ii)
7. Dedication
Optional
Small Roman Number (iii)
8. Acknowledgement
Optional
Small Roman Number (iv)
Compulsory
Small Roman Number (v)
Compulsory
Small Roman Number (vi)
Compulsory
Small Roman Number (vii)
Compulsory
Small Roman Number (viii)
Compulsory
Small Roman Number (ix)
Compulsory If
Appendix is
attached
Small Roman Number (x)
Compulsory
Arabic lettering (1)
16. References
Compulsory
Follow CBE system
17. Appendix
Compulsory If
Appendix is
attached
Arabic lettering, continues from
last numbering
9. Abstract
10. Table of Content
11. List of Tables
12. List of Charts or Diagrams
13. List of Symbols,
Abbreviations,
14. List of Appendix
15. Chapters & Sub-chapters
18. Bibliography
Compulsory
Follow CBE system
�1.1
Verification of Project Paper
The project report has to be verified by your supervisor upon completion.
1.2 Title Page
The title page serves several purposes. It should include:
Title of your final year project.
Name of group members submitting the report.
Date on which the project and report were completed.
Name of your project supervisor/s.
1.3
Oath
The oath statement is an affirmation of your project authenticity/genuineness.
1.4 Dedication
Dedication statement should be simple and in a paragraph only. Dedication should not
consist of numbers, charts or pictures.
1.5 Acknowledgements
The purpose of this page is to acknowledge the people who have assisted you in
finding the sources for your project / report.
1.6 Abstract
An abstract allows the reader something that can be read rather quickly. The
descriptive abstract provides an introduction, purpose of study, approach and design,
results and analysis and highlight the findings achievement. The abstract shall be
precise, simple, written in one paragraph and not more than 300 words.
1.7 Table of Contents
The table of contents is designed to help readers find the sections of the report, which
interest them. It should be a complete and accurate listing of the main and minor
topics covered in the proposal
1.8 List of Tables
A list of tables is needed when a report contains several tables. It must be clear and
informative.
�1.9 List of Figures
This is needed when a report contains several figures. It must be clear and
informative.
1.10
List of Symbols / Abbreviation
All the symbols and abbreviation used shall be listed for list of symbols.
1.11 List of Appendix
The table of content of all appendices in the report shall be placed here.
appendices shall be tagged.
All
1.12 Chapters and Sub-chapters
The project report should have the following chapters as follows:
Chapter 1: Introduction
Chapter 2: Feasibility Studies
Chapter 3: Project Methodology
Chapter 4: Project Implementation
Chapter 5: Findings and Analysis
Chapter 6: Conclusion
Details of what is expected in each chapter are in:
Appendix O : Industrial Electronics
Appendix P
: Production Technology
1.13 Citing sources of information
When a student refers to, or quotes from, another writers work, he / she must
acknowledge them. Failure to document your sources is called plagiarism.
For the sciences the CBE system is used for documenting sources.
The CBE system recognizes two different systems for citing sources as shown below.
You must be consistent and only use ONE system in your report.
System 1
Superscript numbers are used in the body of the report to identify and designate
entries on the bibliography page. Entries on the bibliography page are listed
according to the order in which they appear in the body of the report and not in
alphabetical order.
.. this confusion is only due to the practical method of measuring mass 1
�System 2
The authors name and year of publication are given in brackets following the
information being cited and the entries in the bibliography page are alphabetized
according to the last name of the author.
... this confusion is only due to the practical method of measuring mass..(Majumdar
2002)
Students are advised to refer to The Writers Guide to Research and
Documentation by Kirk Rasmussen for further information on citing sources.
1.14 Appendix
Under this section, the student should enhance his /her explanation with additional
information without disturbing the flow of the reader. The additional information
includes tables, figures, charts, programming codes etc.
For Industrial Electronics, the following should be placed in this section:
Gantt chart (containing both planned and actual task duration)
Task List according to weeks (this is embedded in the Gantt
chart)
Reviewed Task Lists (this is embedded in the Gantt chart)
Project Progress Report
Measurement data
Troubleshooting procedures (this part of the Quality Plan in
Chapter 4)
Vendor data
List of standards and codes of practice (this part of the Quality
Plan in Chapter 4)
Other relevant information
For Production Technology, the following should be placed in this section:
Detailed drawings (this is part of Chapter 3)
Measurement data (this is part of Chapter 3)
Tasks lists
Project progress report
Vendor data
Cost data (this is part of Chapter 3)
Lists of standards and codes of practice (this part of the Quality Plan in
Chapter 4)
Other relevant information
�1.15 Bibliography
A bibliography is a separate page at the end of the document. This page consists of
the list of all the references used in writing the report.
The CBE system uses the following format:
Authors(s). Year. Title. Place of Publication: publisher name.
Example:
1. Majumdar S R . 2002 . Oil Hydraulic Systems . New Delhi : Tata Press
2. Aquino M and Oates F. 1995. Positive Communication Rules. Brisbane: Independent Press.
Students are advised to refer to The Writers Guide to Research and
Documentation by Kirk Rasmussen for further information on citing sources.
1.2
Format of Project Report
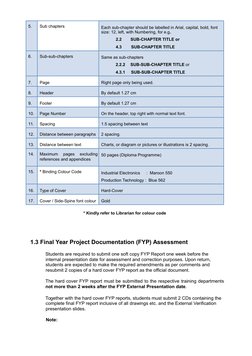
The format of project report is summarized in Table 1.4.
Table 1.4
Format of Project Report
No.
Subject
Remark
1.
Paper
White A4 size paper weighing 80 grams each
2.
Borders
Left = 3.5cm, Right = 2.5 cm, Bottom = 2.5cm, Top =2.5cm
3.
Normal Text Font
Set to Arial, font size: 11
4.
Chapters
Each chapter should be labelled in Arial, capital, bold, font size:
14, centre,
For e.g. CHAPTER II or CHAPTER IV
�5.
6.
Sub chapters
Each sub-chapter should be labelled in Arial, capital, bold, font
size: 12, left, with Numbering, for e.g.
Sub-sub-chapters
2.2
SUB-CHAPTER TITLE or
4.3
SUB-CHAPTER TITLE
Same as sub-chapters
2.2.2
SUB-SUB-CHAPTER TITLE or
4.3.1
SUB-SUB-CHAPTER TITLE
7.
Page
Right page only being used.
8.
Header
By default 1.27 cm
9.
Footer
By default 1.27 cm
10.
Page Number
On the header, top right with normal text font.
11.
Spacing
1.5 spacing between text
12.
Distance between paragraphs
2 spacing.
13.
Distance between text
Charts, or diagram or pictures or illustrations is 2 spacing.
14.
Maximum pages excluding 50 pages (Diploma Programme)
references and appendices
15.
* Binding Colour Code
Industrial Electronics
: Maroon 550
Production Technology : Blue 562
16.
Type of Cover
Hard-Cover
17.
Cover / Side-Spine font colour
Gold
* Kindly refer to Librarian for colour code
1.3 Final Year Project Documentation (FYP) Assessment
Students are required to submit one soft copy FYP Report one week before the
internal presentation date for assessment and correction purposes. Upon return,
students are expected to make the required amendments as per comments and
resubmit 2 copies of a hard cover FYP report as the official document.
The hard cover FYP report must be submitted to the respective training departments
not more than 2 weeks after the FYP External Presentation date.
Together with the hard cover FYP reports, students must submit 2 CDs containing the
complete final FYP report inclusive of all drawings etc. and the External Verification
presentation slides.
Note:
�GMI reserves the right to withhold students result until the two hard cover
copies of the FYP report and two CDs are submitted.
Failure to submit according to the deadline will also
jeopardise your graduation date
APPENDIX A
�[FINAL YEAR PROJECT DOCUMENTATION
HANDBOOK
APPENDIX B
GERMAN-MALAYSIAN INSTITUTE
1
| 18 0
German Malaysian Institute
�[FINAL YEAR PROJECT DOCUMENTATION
HANDBOOK
APPENDIX C
I / We * hereby declare that the project paper or thesis has been read and
I / we * have the opinion that the project paper is appropriate in terms of scope coverage
and quality for awarding an Industrial Diploma in .
Signature
Name of Supervisor I
Date
Signature
Name of Supervisor II
Date
GERMAN-MALAYSIAN INSTITUTE
1
1
�[FINAL YEAR PROJECT DOCUMENTATION
HANDBOOK
* Please delete or add where applicable.
APPENDIX D
GERMAN-MALAYSIAN INSTITUTE
1
2
�[FINAL YEAR PROJECT DOCUMENTATION
HANDBOOK
GERMAN-MALAYSIAN INSTITUTE
1
3
�[FINAL YEAR PROJECT DOCUMENTATION
HANDBOOK
APPENDIX E
I / We hereby declare that this project paper is authentic and the group members are
Signature
Name of Group Member
Signature
Name of Group Member
Signature
Name of Group Member
Signature
Name of Group Member
Date
GERMAN-MALAYSIAN INSTITUTE
1
| 14 4
German Malaysian Institute
�[FINAL YEAR PROJECT DOCUMENTATION
HANDBOOK
APPENDIX F
DEDICATION
I would like to dedicate this project report to ( student to write their own
dedication ).
APPENDIX G
Top Margin (2.5 cm)
2.5 cm
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
4 Spacing
1.27 cm
Start writing your acknowledgement here.
GERMAN-MALAYSIAN INSTITUTE
1
5
�[FINAL YEAR PROJECT DOCUMENTATION
HANDBOOK
Left Margin
3.5 cm
Right Margin
2.5 cm
Bottom Margin (2.5 cm)
APPENDIX H
Top Margin (2.5 cm)
2.5 cm
ABSTRACT
4 Spacing
1.27 cm
Start writing your abstract here.
GERMAN-MALAYSIAN INSTITUTE
1
6
�[FINAL YEAR PROJECT DOCUMENTATION
HANDBOOK
Left Margin
3.5 cm
Right Margin
2.5 cm
Bottom Margin (2.5 cm)
APPENDIX I
Top Margin (2.5 cm)
2.5 cm
TABLE OF CONTENT
4 Spacing
CHAPTER
CONTENT
PAGE NUMBER
CHAPTER 1
Introduction
1.1 Introduction
1.2 Background Theory
1.3 System Layout
10
CHAPTER 2
Title
2.1 Sub-title 1
13
GERMAN-MALAYSIAN INSTITUTE
1
7
�[FINAL YEAR PROJECT DOCUMENTATION
HANDBOOK
2.2 Sub-title 2
Left Margin
3.5 cm
15
2.3 Sub-title 3
17
2.4 Sub-title 4
19
Right Margin
2.5 cm
APPENDIX J
Top Margin (2.5 cm)
2.5 cm
LIST OF TABLES
Bottom Margin (2.5 cm)
4 Spacing
TABLE
TITLE
1.1
1.2
Sequence of Project Report
Format of Project Report
1
2
1.3
Measurement of Torque
Left Margin
3.5 cm
PAGE NUMBER
Right Margin
2.5 cm
GERMAN-MALAYSIAN INSTITUTE
1
8
�[FINAL YEAR PROJECT DOCUMENTATION
HANDBOOK
Bottom Margin (2.5 cm)
APPENDIX K
Top Margin (2.5 cm)
2.5 cm
LIST OF DIAGRAMS
4 Spacing
Left Margin
3.5 cm
DIAGRAMS
CONTENT
PAGE NUMBER
1.1
Block Diagram of Closed
Loop Speed Control
1.2
Torque versus Speed
Curve of an Introduction
Motor
1.3
Flow Chart of Step 1
11
Right Margin
2.5 cm
GERMAN-MALAYSIAN INSTITUTE
1
9
�[FINAL YEAR PROJECT DOCUMENTATION
HANDBOOK
Bottom Margin (2.5 cm)
APPENDIX L
Top Margin (2.5 cm)
2.5 cm
LIST OF SYMBOLS AND ABBREVIATIONS
4 Spacing
Left Margin
3.5 cm
D,d
Diameter
Gravity
Toque delivered at shaft
P1
Power to be delivered to shaft
P2
Power output
Ra
Armature resistance
Right Margin
2.5 cm
GERMAN-MALAYSIAN INSTITUTE
2
0
�[FINAL YEAR PROJECT DOCUMENTATION
HANDBOOK
Bottom Margin (2.5 cm)
APPENDIX M
Top Margin (2.5 cm)
2.5 cm
LIST OF APPENDIX
4 Spacing
APPENDIX
TITLE
Sample Verification of
Project
80
Sample Verification of
Project Supervisor
81
Sample Verification of
Department
82
Sample Title Page of
Project
83
E
Left Margin
3.5 cm F
PAGE NUMBER
Sample of Oath
Right Margin
2.5 cm
P1
Power to be delivered to shaft
P2
Power output
Ra
Armature resistance
GERMAN-MALAYSIAN INSTITUTE
2
1
�[FINAL YEAR PROJECT DOCUMENTATION
HANDBOOK
Bottom Margin (2.5 cm)
APPENDIX N
Top Margin (2.5 cm)
2.5 cm
CHAPTER II
2 spacing
Title of Chapter II
2 spacing
The start of the text begins here. Paragraph format should
be First Line Indent of 1.27 cm (by default using MS Word). The
spacing between the text lines should be 1.5 spacing.
2 spacing
2.1 SUB-CHAPTER
1 spacing
The start of the text begins here. Paragraph format should
be First Line Indent of 1.27 cm (by default using MS Word). The
spacing between the text lines should be 1.5 spacing.
2 spacing
2.1.1 SUB-SUB-CHAPTER
1 spacing
The start of the text begins here. Paragraph format should be First Line
Indent of 1.27 cm (by default using MS Word). The spacing between the text
Left Spacing
lines should be 1.5 spacing.
GERMAN-MALAYSIAN INSTITUTE
2
2
�[FINAL YEAR PROJECT DOCUMENTATION
HANDBOOK
3.5 cm
2.5 cm
Right Spacing
Bottom Margin (2.5 cm)
APPENDIX O
Industrial Electronics: Details for Project Report.
Student is encouraged to enhance his/her explanation with tables, figures or charts for
clarity.
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
1.1
PROJECT BACKGROUND
The project background must comprise of related information/data obtained from
reliable sources, eg. website, and must be re-written (paraphrased) from it being a
general idea to narrowing it down thus, deriving to the corresponding problem
statement.
1.2
PROBLEM STATEMENT
The problem statement, usually one or a maximum of two only, must be a
continuation of the general statement derived/constructed from the previous project
background.
1.3
PROJECT OBJECTIVES
The project objectives must answer the problem statement(s) by tagging each
objective with a specialization niche.
The number of objectives should be
approximately between 4 to 6; depending on the complexity of the project.
Upon completion of this project, students should be able :
To design and construct an automated system of the xxx machine using (a
technology related to the programme)
To monitor and control the process with the implementation of PLC
CHAPTER 2: FEASIBILITY STUDIES
GERMAN-MALAYSIAN INSTITUTE
2
3
�[FINAL YEAR PROJECT DOCUMENTATION
HANDBOOK
Feasibility Studies to include both primary and secondary sources. The former must
include at least one interview with an SME or industrialist; and an observation at
industry/an experiment or a market research.
The latter must include reliable
sources from print and electronic media. All sources of information must be correctly
referenced, eg. using the APA 6th edition of reference guide from Curtin University of
Technology, Australia.
CHAPTER 3: PROJECT METHODOLOGY
3.1
PROJECT SPECIFICATION
This section covers the project as a whole and is presented in a table. Topics to be
included are :
3.2
Project title
Power supply
Raw input
Output
Production rate
Dimension, etc.
PROJECT FEATURES
State and explain the extra features, functions, capabilities, application, etc. of the
project as compared to a normal/existing machine eg. WinCC etc.
3.3
CONTROL STRATEGIES (PIC & Mecha only) + SIGNAL FLOW DIAGRAM (PIC
only) and DATA FLOW DIAGRAM (EIT & NWS only)
3.4
SYSTEM LAYOUT (all other specialized areas) / NETWORK LAYOUT (NWS only)
This section includes :
Piping & Instrument Diagram or Machine Layout Diagram (assembly
drawing, isometric and orthographic views in 1st angle perspective)
Electronics/Electrical/Pneumatics, PLC, and Instrument Loop Diagram
Hook-up Diagram (how the instrument or component is being
installed) with standard format template
GERMAN-MALAYSIAN INSTITUTE
2
4
�[FINAL YEAR PROJECT DOCUMENTATION
HANDBOOK
3.5
PROJECT COSTING
This section includes costing for the entire project comprising material, fabrication,
standard parts, etc. Product cost should be inclusive of material, labour, machine
rental, secondary process, delivery costs, etc.
3.6
SAFETY
This comprises various safety requirements and safety features. Security features
for
NWS only.
CHAPTER 4: PROJECT IMPLEMENTATION
4.1
PROCESS PLAN
Explain the operation of the system and project sequence supported by related block
diagrams/flowcharts. All explanations should be made with reference to the P&ID or
machine assembly.
4.2
QUALITY PLAN
Present a quality plan detailing how quality is to be checked and maintained during
your
project implementation.
4.3
PROJECT SCHEDULE
This section includes explanation on main tasks phases, milestones and justified
delays (if any) while meeting the deadline. Provide contingency plans in ensuring that the
project runs smoothly.
CHAPTER 5: FINDINGS AND ANALYSIS
5.1
COMMISSIONING AND TESTING
This
section
should
include
procedures
and
problems
encountered
and
countermeasures (only technical problems and countermeasures are allowed).
5.2
RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Present results of testing (at least 5 trial-runs) using tables, graphs, etc.
CHAPTER 6: CONCLUSION
6.1
CONCLUSION
GERMAN-MALAYSIAN INSTITUTE
2
5
�[FINAL YEAR PROJECT DOCUMENTATION
HANDBOOK
State whether project objectives have been achieved.
achieved,
6.2
If they have not been
provide explanation why.
RECOMMENDATIONS
Provide between 2 to 3 technical recommendations on improvement or upgrading of
the
system.
APPENDIX P
Production Technology: Details for Project Report.
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
1.1
PROJECT BACKGROUND
The project background must comprise of related information/data obtained from
reliable sources, eg. website, and must be re-written (paraphrased) from it being a
general idea to narrowing it down thus, deriving to the corresponding problem
statement.
1.2
PROBLEM STATEMENT
The problem statement, usually one or a maximum of two only, must be a
continuation of the general statement derived/constructed from the previous project
background.
1.3
PROJECT OBJECTIVES
The project objectives must answer the problem statement(s) by tagging each
objective with a specialization niche.
The number of objectives should be
approximately between 4 to 6; depending on the complexity of the project.
Upon completion of this project, students should be able :
To design and construct an automated system of the xxx machine using (a
technology related to the programme)
To monitor and control the process with the implementation of PLC
GERMAN-MALAYSIAN INSTITUTE
2
6
�[FINAL YEAR PROJECT DOCUMENTATION
HANDBOOK
CHAPTER 2: FEASIBILITY STUDIES
Feasibility Studies to include both primary and secondary sources. The former must
include at least one interview with an SME or industrialist; and an observation at
industry/an experiment or a market research.
The latter must include reliable
sources from print and electronic media. All sources of information must be correctly
referenced, eg. using the APA 6th edition of reference guide from Curtin University of
Technology, Australia.
CHAPTER 3: PROJECT METHODOLOGY
3.1
PROJECT SPECIFICATION
This section covers the project as a whole and is presented in a table. Topics to be
included are :
3.2
Project title
Material
Machining process and sub-processes
Production rate
Dimension, etc.
PROJECT FEATURES
State and explain the extra features, functions, capabilities, application, etc. of the
project as compared to a normal/existing die, mould, machining process, product
design specifications (PDS) and analysis, eg. new machining pathway, new material, etc.
3.3
STRIP LAYOUT (TDT only) / MOULD CONCEPT (MoT only) / JIGS & FIXTURES
(CPT only) / SKETCHES + ERGONOMICS TABLE (PDM only)
This section should include drawings (orthographic, isometric, 3D, sectional, etc.)
based on the respective industrial standards.
Product explanation comprising
product function, advantages and reasons for choosing this design must also be
included with reference to similar findings in Feasibility Studies.
3.4
CALCULATIONS / TECHNICAL DRAWINGS
GERMAN-MALAYSIAN INSTITUTE
2
7
�[FINAL YEAR PROJECT DOCUMENTATION
HANDBOOK
For Die calculations include cutting and bending forces, spring selection, etc.
For Mould calculations include shot capacity, shrinkage, clamp force, runner and
gate
size, etc.
This section includes :
Piping & Instrument Diagram or Machine Layout Diagram (assembly
drawing, isometric and orthographic views in 1st angle perspective)
Electronics/Electrical/Pneumatics, PLC, and Instrument Loop Diagram
Hook-up Diagram (how the instrument or component is being
installed) with standard format template
3.5
PROJECT COSTING
This section includes costing for the entire project comprising material, fabrication,
standard parts, etc. Product cost should be inclusive of material, labour, machine
rental, secondary process, delivery costs, etc.
Product Manufacturing Cost (CPT only)
3.6
SAFETY
This comprises various safety requirements and safety features.
CHAPTER 4: PROJECT IMPLEMENTATION
4.1
PROCESS PLAN
Explain the overall process plan for the project and for each of the component
fabricated. Include individual process plan sheet in the Appendix.
4.2
QUALITY PLAN & CHECKING
Present a quality plan detailing how quality is to be checked and maintained during
your
project implementation. Provide records of measurement checks done, specifically
for
critical assembly components.
4.3
PROJECT SCHEDULE
GERMAN-MALAYSIAN INSTITUTE
2
8
�[FINAL YEAR PROJECT DOCUMENTATION
HANDBOOK
This section includes explanation on main tasks phases, milestones and justified
delays (if any) while meeting the deadline. Provide contingency plans in ensuring that the
project runs smoothly.
CHAPTER 5: FINDINGS AND ANALYSIS
5.1
COMMISSIONING AND TESTING
This
section
should
include
procedures
and
problems
encountered
and
countermeasures (only technical problems and countermeasures are allowed).
5.2
RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Present results of testing (at least 100 pieces produced TDT and MOT only; from at
least 5 trial-runs PDM only; and one piece produced CPT only) using tables,
graphs,
etc.
CHAPTER 6: CONCLUSION
6.1
CONCLUSION
State whether project objectives have been achieved.
achieved,
6.2
If they have not been
provide explanation why.
RECOMMENDATIONS
Provide between 2 to 3 technical recommendations on improvement or upgrading of
the
system.
GERMAN-MALAYSIAN INSTITUTE
2
| 32 9
German Malaysian Institute

![[FINAL YEAR PROJECT DOCUMENTATION
HANDBOOK]
GMI
GERMAN MALAYSIAN INSTITUTE
GMI has the right to change the Final Year Pro](https://screenshots.scribd.com/Scribd/252_100_85/356/327069022/2.jpeg)