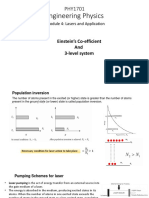
Molecular Geometry & Polarity Example
Problems
Remember!... Step 1: Draw the Lewis structure, Step 2: Draw the 3D
molecular structure w/ VSEPR rules,
Step 3: Use symmetry to determine if the molecule is polar or nonpolar.
Click on the molecule's name to see the answer, but first try to do it yourself!
1. SF5Cl - Sulfur Monochloride
Pentafluoride
2. SOF4 Sulfur Monoxide
Tetrafluoride
3. SF6 - Sulfur Hexafluoride
4. SF4 - Sulfur Tetrafluoride
5. ICl5 - Iodine Pentachloride
6. PCl5 - Phosphorus Pentachloride
7. XeCl2 - Xenon Dichloride
8. XeF4 - Xenon Tetrafluoride
9. AlCl3 - Aluminum Trichloride
10. CS2 - Carbon Disulfide
11. BeI2 - Beryllium Diiodide
12. SeF6 - Selenium Hexafluoride
13. AsF5 - Arsenic Pentafluoride
14. NOCl - Nitrosyl Chloride
15. PO(OH)3 - Phosphoric Acid
16. SO2Cl2 - Sulfuryl Chloride
17. NOCl - Nitrosyl Bromide
18. BrF3 - Bromine
Trifluoride
19. ClF5 - Chlorine
Pentafluoride
20. BCl3 - Boron Trichloride
21. SiH4 - Silicon
Tetrahydride
22. BeBr2 - Beryllium
Dibromide
23. PF5 - Phosphorus
Pentafluoride
24. BrF5 - Bromine
Pentafluoride
25. CH2O - Formaldehyde
26. NH2Cl - Chloramine
27. CH4 - Methane
28. SO2 - Sulfur Dioxide
29. AlF3 - Aluminum
Trifluoride
30. NH3 - Ammonia
31. SeH2 - Hydrogen
Selenide
32. XeO3 - Xenon Trioxide
33. H2O - Water
34. CO2 - Carbon Dioxide
35. SCl2 - Sulfur Dichloride
36. NO2F - Nitryl Fluoride
37. CSe2 - Carbon Diselenide
38. IF5 - Iodine Pentafluoride
39. ClF3 - Chlorine Trifluoride
40. SF5Cl - Sulfur Pentafluoride
Monochloride
41. PF3Cl2 - Phosphorus Trifluoride
Dichloride
42. POCl3 - Phosphoryl Chloride
43. CCl4 - Carbon Tetrachloride
44. PF2Cl3 - Phosphorus Difluoride
Trichloride
45. GeH4 - Germanium Tetrahydride
46. AlBr3 - Aluminum Tribromide
47. BeCl2 - Beryllium Dichloride
48. IBr3 - Iodine Tribromide
49. SO3 - Sulfur Trioxide
50. PCl3 - Phosphorus Trichloride
51. BeF2 - Beryllium Difluoride
52. BF3 - Boron Trifluoride
�1. SF5Cl - Sulfur Monochloride Pentafluoride
First Draw the Lewis Dot Structure:
Electron geometry: octahedral. Hybridization: sp3d2
Next Draw the 3D structure based on VSEPR rules:
Click and drag the molecle to rotate it.
Decision:
The molecular geometry of SF5Cl is octahedral and the charge distribution
on the central atom is asymmetric; the dipoles do not "cancel out".
Therefore SF5Cl is polar.
2. SOF4 Sulfur Monoxide Tetrafluoride
SOF4 - Sulfur Monoxide Tetrafluoride:
First draw the lewis structure:
Electron geometry: trigonal bipyramidal. Hybridization: sp 3d
Second determine the 3D molecular geometry with VSEPR rules:
Click and drag the molecle to rotate it.
Decision:
The molecular geometry of SOF4 is trigonal bipyramidal with asymmetric
charge distribution around the central atom.
Therefore SOF4 is polar.
3. SF6 - Sulfur Hexafluoride
SF6 - Sulfur Hexafluoride:
First draw the Lewis Structure:
Electron geometry: octahedral. Hybridization: sp3d2
Then draw the 3D structure using VSEPR rules:
Click and drag the molecle to rotate it.
�Decision:
The molecular geometry of SF6 is octahedral with a symmetric charge
distribution around the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is nonpolar.
4. SF4 - Sulfur Tetrafluoride
SF4 :
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: trigonal bipyramidal. Hybridization: sp 3d
Next draw the 3D structure using VSPER rules:
Decision:
The geometry of SF4 is seesaw with an asymmetric electron region
distribution around the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is polar.
5. ICl5 - Iodine Pentachloride
ICl5 : First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: octahedral. Hybridization: sp3d2
Then construct the 3D geometry using VSEPR rules:
Decision:
The molecular geometry of ICl5 is square pyramid with an asymmetric
electron region distribution.
Therefore this molecule is polar.
6. PCl5 - Phosphorus Pentachloride
Phosphorus Pentachloride - PCl5 :
First determine the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: trigonal bipyramidal. Hybridization: sp 3d
Next determine the 3D molecular geometry with VSPER rules:
Decision:
�The molecular geometry of PCl5 is trigonal bipyramid with symmetric
electron region distribution around the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is nonpolar.
7. XeCl2 - Xenon Dichloride
Xenon dichloride - XeCl2 :
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: trigonal bipyramidal. Hybridization: sp 3d
Next determine the 3D molecular geometry using VSEPR rules:
Decision:
The molecular geometry of XeCl2 is linear with symmetric electron region
distribution.
Therefore this molecule is nonpolar.
8. XeF4 - Xenon Tetrafluoride
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: octahedral. Hybridization: sp3d2
Next draw the 3D Molecular geometry using VSEPR rules:
Decision:
The geometry of XeF4 is square planar with symmetric electron region
distribution.
Therefore this molecule is nonpolar.
9. AlCl3 - Aluminum Trichloride
AlCl3 :
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: Trigonal planar. Hybridization: sp 2
�Next draw the 3D molecular geometry using VSEPR rules:
Decision:
The molecular geometry of AlCl3 is trigonal planar with symmetric electron
region distribution.
Therefore this molecule is nonpolar.
10. CS2 - Carbon Disulfide
CS2 - Carbon Disulfide:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: linear. Hybridization: sp
Next draw the 3D molecular geometry using VSEPR rules:
Decision:
The molecular geometry of CS2 is linear with symmetric electron region
distribution around the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is nonpolar.
11. BeI2 - Beryllium Diiodide
BeI2 - Beryllium Diiodide:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: linear. Hybridization: sp
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Decision:
The molecular geometry of BeI2 is linear with symmetric charge
distribution on the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is nonpolar.
12. SeF6 - Selenium Hexafluoride
SeF6 - Selenium Hexafluoride:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: octahedral. Hybridization: sp3d2
�Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Decision:
The molecular geometry of SeF6 is octahedral with symmetric charge
distribution on the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is nonpolar.
13. AsF5 - Arsenic Pentafluoride
AsF5 - Arsenic Pentafluoride:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: trigonal bipyramidal. Hybridization: sp 3d
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Decision:
The molecular geometry of AsF5 is trigonal bipyramidal with symmetric
charge distribution on the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is nonpolar.
14. NOCl - Nitrosyl Chloride
NOCl - Nitrosyl Chloride:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: trigonal planar. Hybridization: sp 2
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Decision:
The molecular geometry of NOCl is bent (or angular) with an asymmetric
charge distribution on the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is polar.
15. PO(OH)3 - Phosphoric Acid
PO(OH)3 - Phosphoric acid - also H3PO4 :
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
�Electron geometry: tetrahedral. Hybridization: sp3
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Decision:
The molecular geometry of PO(OH)3 is tetrahedral with asymmetric charge
distribution on the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is polar.
16. SO2Cl2 - Sulfuryl Chloride
SO2Cl2 - Sulfuryl Chloride:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: tetrahedral. Hybridization: sp3
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Decision:
The molecular geometry of SO2Cl2 is tetrahedral with an asymmetric
charge distribution on the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is polar.
17. NOCl - Nitrosyl Bromide
NOBr Nitrosyl Bromide:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: trigonal planar. Hybridization: sp 2
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Decision:
�The molecular geometry of NOBr is bent (or angular) with asymmetric
charge distribution on the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is polar.
18. BrF3 - Bromine Trifluoride
BrF3 Bromine Trifluoride:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: trigonal bipyramidal. Hybridization: sp 3d
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Decision:
The molecular geometry of BrF3 is T-shaped with asymmetric charge
distribution about the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is polar.
19. ClF5 - Chlorine Pentafluoride
ClF5 Chlorine Pentafluoride:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: octahedral. Hybridization: sp3d2
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Decision:
The molecular geometry of ClF5 is square pyramidal with asymmetric
charge distribution around the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is polar.
20. BCl3 - Boron Trichloride
BCl3 - Boron Trichloride:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: trigonal planar. Hybridization: sp 2
�Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Decision:
The molecular geometry of BCl3 is trigonal planar with symmetric charge
distribution around the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is nonpolar.
21. SiH4 - Silicon Tetrahydride
SiH4 - Silicon Tetrahydride, better known as Silane:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: tetrahedral. Hybridization: sp3
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Decision:
The molecular geometry of SiH4 is tetrahedral with symmetric charge
distribution around the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is non-polar.
22. BeBr2 - Beryllium Dibromide
BeBr2 - Beryllium Dibromide:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: linear. Hybridization: sp
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Decision:
The molecular geometry of BeBr2 is linear with symmetric charge
distribution on the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is non-polar.
23. PF5 - Phosphorus Pentafluoride
PF5 - Phosphorus Pentafluoride:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
�Electron geometry: trigonal bipyramidal. Hybridization: sp 3d
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Decision:
The molecular geometry of PF5 is trigonal bipyramidal with symmetric
charge distribution.
Therefore this molecule is nonpolar.
24. BrF5 - Bromine Pentafluoride
BrF5 - Bromine Pentafluoride:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: octahedral. Hybridization: sp3d2
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Decision:
The molecular geometry of BrF5 is square pyramidal with asymmetric
charge distribution on the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is polar.
25. CH2O - Formaldehyde
CH2O - Formaldehyde:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: trigonal planar. Hybridization: sp 2
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Decision:
The molecular geometry of CH2O is trigonal planar with asymmetric charge
�distribution.
Therefore this molecule is polar.
26. NH2Cl - Chloramine
NH2Cl - Chloramine:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: tetrahedral. Hybridization: sp3
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Decision:
The molecular geometry of NH2Cl is trigonal pyramidal with asymmetric
charge distribution on the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is polar.
27. CH4 - Methane
CH4 - Methane:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: tetrahedral. Hybridization: sp3
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Decision:
The molecular geometry of methane - CH4 - is tetrahedral with symmetric
charge distribution on the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is non-polar.
28. SO2 - Sulfur Dioxide
SO2 - Sulfur Dioxide:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: trigonal planar. Hybridization: sp 2
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Decision:
�The molecular geometry of SO2 is bent (approx. 120 degrees) with
asymmetric charge distribution on the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is polar.
29. AlF3 - Aluminum Trifluoride
AlF3 - Aluminum Trifluoride:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: trigonal planar. Hybridization: sp 2
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Decision:
The molecular geometry of AlF3 is trigonal planar with a symmetric charge
distribution on the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is non-polar.
30. NH3 - Ammonia
NH3 - Ammonia:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: tetrahedral. Hybridization: sp3
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
The molecular geometry of NH3 is trigonal pyramidal with asymmetric
charge distribution on the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is polar.
31. SeH2 - Hydrogen Selenide
SeH2 - Hydrogen Selenide:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: tetrahedral. Hybridization: sp3
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Decision:
�The molecular geometry of SeH2 is bent with asymmetric charge
distribution on the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is polar.
32. XeO3 - Xenon Trioxide
XeO3 - Xenon Trioxide:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: tetrahedral. Hybridization: sp3
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Decision:
The molecular geometry of XeO3 is trigonal pyramidal with asymmetric
charge distribution on the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is polar.
33. H2O - Water
H2O - Water:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: tetrahedral. Hybridization: sp3
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Decision:
The molecular geometry of H2O is bent (approx 108 degrees) with
asymmetric charge distribution about the central oxygen atom.
Therefore this molecule is polar.
In fact water is one of the most polar molecules there are, and a
good illustration of why using VSEPR rules along with
electronegativity is important!
34. CO2 - Carbon Dioxide
CO2 - Carbon Dioxide:
First draw the lewis structure of CO2, Carbon dioxide:
Electron geometry: linear. Hybridization: sp
Then draw the 3D structure with VSEPR rules:
�Decision:
The molecular geometry of CO2 is linear with symmetric charge
distribution about the carbon atom.
Therefore CO2 is non-polar.
35. SCl2 - Sulfur Dichloride
SCl2 - Sulfur Dichloride:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
The molecular geometry of SCl2 is bent with asymmetric charge
distribution around the central atom.
Therefore SCl2 is polar.
36. NO2F - Nitryl Fluoride
NO2F - Nitryl Fluoride:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: trigonal planar. Hybridization: sp 2
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Decision:
The molecular geometry of NO2F is trigonal planar with asymmetric charge
distribution on the central atom.
Therefore NO2F is polar.
37. CSe2 - Carbon Diselenide
CSe2 - Carbon Diselenide:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: linear. Hybridization: sp
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Decision:
The molecular geometry of CSe2 is linear with symmetric charge
�distribution on the central atom.
Therefore CSe2 is non-polar.
38. IF5 - Iodine Pentafluoride
IF5 - Iodine Pentafluoride:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: octahedral. Hybridization: sp3d2
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Click and drag the molecle to rotate it.
Decision:
The molecular geometry of IF5 is square pyramidal with asymmetric charge
distribution on the central atom.
Therefore IF5 is polar.
39. ClF3 - Chlorine Trifluoride
ClF3 - Chlorine Trifluoride:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: trigonal bipyramidal. Hybridization: sp 3d
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Click and drag the molecle to rotate it.
Decision:
The molecular geometry of ClF3 is T-shaped with asymmetric charge
distribution around the central atom.
Therefore ClF3 is polar.
40. SF5Cl - Sulfur Pentafluoride Monochloride
SF5Cl - Sulfur Pentafluoride Monochloride:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
�Electron geometry: octahedral. Hybridization: sp3d2
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Click and drag the molecle to rotate it.
Decision:
The molecular geometry of SF5Cl is octahedral with asymmetric charge
distribution on the central atom.
Therefore SF5Cl is polar.
41. PF3Cl2 - Phosphorus Trifluoride Dichloride
PF3Cl2 - Phosphorus Trifluoride Dichloride:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: trigonal bipyramidal. Hybridization: sp 3d
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Don't put the chlorine atoms directly across from each other;
the fluorine atoms are more electronegative than chlorine and will
repel each other more strongly.
Click and drag the molecle to rotate it.
Decision:
The molecular geometry of PF3Cl2 is trigonal bipyramidal with asymmetric
charge distribution on the central atom.
Therefore PF3Cl2 is polar.
42. POCl3 - Phosphoryl Chloride
POCl3 - Phosphoryl Chloride: First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Click and drag the molecle to rotate it.
Decision:
The molecular geometry of POCl3 is tetrahedral with asymmetric charge
distribution around the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is polar.
43. CCl4 - Carbon Tetrachloride
�CCl4 - Carbon Tetrachloride:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: tetrahedral. Hybridization: sp3
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Click and drag the molecule to rotate it.
Decision:
The molecular geometry of CCl4 is tetrahedral with symmetric charge
distribution around the central atom.
Therefore CCl4 is nonpolar.
44. PF2Cl3 - Phosphorus Difluoride Trichloride
PF2Cl3 - Phosphorus Difluoride Trichloride:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: trigonal bipyramidal. Hybridization: sp 3d
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Click and drag the molecule to rotate it.
Decision:
The molecular geometry of PF2Cl3 is trigonal bipyramidal with symmetric
charge distribution around the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is nonpolar.
45. GeH4 - Germanium Tetrahydride
GeH4 - Germanium Tetrahydride (Germane):
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: tetrahedral. Hybridization: sp3
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
�Click and drag the molecule to rotate it.
Decision:
The molecular geometry of GeH4 is tetrahedral with a symmetric charge
distribution.
Therefore this molecule is nonpolar.
46. AlBr3 - Aluminum Tribromide
AlBr3 - Aluminum Tribromide:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: trigonal planar. Hybridization: sp 2
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Click and drag the molecle to rotate it.
Decision:
The molecular geometry of AlBr3 is trigonal planar with symmetric charge
distribution around the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is nonpolar.
47. BeCl2 - Beryllium Dichloride
BeCl2 - Beryllium Dichloride:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: linear. Hybridization: sp
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Click and drag the molecle to rotate it.
Decision:
The molecular geometry of BeCl2 is linear with symmetric charge
distribution around the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is nonpolar.
48. IBr3 - Iodine Tribromide
IBr3 - Iodine Tribromide:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
�Electron geometry: trigonal bipyramidal. Hybridization: sp 3d
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Click and drag the molecle to rotate it.
Decision:
The molecular geometry of Br3 is T-shaped with an asymmetric charge
distribution on the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is polar.
49. SO3 - Sulfur Trioxide
SO3 - Sulfur Trioxide:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: trigonal planar. Hybridization: sp 2
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Click and drag the molecle to rotate it.
Decision:
The molecular geometry of SO3 is trigonal planar with symmetric charge
distribution on the central atom.
Therefore SO3 is nonpolar.
50. PCl3 - Phosphorus Trichloride
PCl3 - Phosphorus Trichloride:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: tetrahedral. Hybridization: sp3
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Click and drag the molecle to rotate it.
Decision:
The molecular geometry of PCl3 is trigonal pyramidal with asymmetric
charge distribution on the central atom.
Therefore this molecule is polar.
51. BeF2 - Beryllium Difluoride
�BeF2 Beryllium Difluoride:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: linear. Hybridization: sp
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Click and drag the molecle to rotate it.
Decision:
The molecular geometry of BeF2 is linear with symmetric charge
distribution on the central atom.
Therefore BeF2 is nonpolar.
52. BF3 - Boron Trifluoride
BF3 - Boron Trifluoride:
First draw the Lewis dot structure:
Electron geometry: trigonal planar. Hybridization: sp 2
Then draw the 3D molecular structure using VSEPR rules:
Click and drag the molecle to rotate it.
Decision:
The molecular geometry of BF3 is trigonal planar with symmetric charge
distribution on the central atom.
Therefore BF3 is nonpolar.