Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DFCBGNVHMB, Tyjmf
Uploaded by
Devraj0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pagek,jhutyfgcvb
Original Title
dfcbgnvhmb,tyjmf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentk,jhutyfgcvb
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageDFCBGNVHMB, Tyjmf
Uploaded by
Devrajk,jhutyfgcvb
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Transparent Bridges:
A bridge is a device that operates at the Data Link Layer of the OSI model. It
selectively forwards frames based on an examination of the Data Link Layer addresses in
the frames. Any device that fits this description is acting as a transparent bridge.
This definition has an important implication: A bridge doesn't care what upper layer protocols
are being used. A bridge will forward packets correctly whether they are NetWare, TCP/IP,
AppleTalk, or even DECnet. As long as the bridge has the right kind of NIC, it can forward
properly. Because of this quality, bridges are said to be protocol independent.
The Concept Of Transparency:
When a NIC (Network Interface Card) receives a valid packet, the normal behavior is for
the NIC to check to see if the Destination DLC Address in the packet is one that it has been
configured to recognize. If the destination DLC Address is one that the NIC has been
configured to recognize, then the packet is passed up to the next higher layer of processing.
Bridges, on the other hand, listen to the network in promiscuous mode, meaning that they
accept all packets, regardless of the packets' addressing. On a side note, this promiscuous
mode is the same thing that allows your network analyzer to capture all the packets going
across the network. The bridge then looks up each packet's Destination DLC Address in its
internal tables to find out which port the Destination NIC is attached to. Finally, it forwards
the packet onto only the necessary port. In the case of a broadcast message, the bridge
forwards the packet onto every port except the port that the packet came in on. Promiscuous
listening is the key to the bridge's transparent operation. Since the bridge effectively "hears"
all packets that are transmitted, it can decide whether forwarding is necessary without any
special behavior from the individual stations.
Transparent Bridging Behavior:
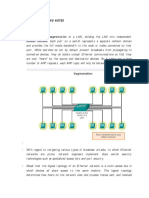
Consider a simple network consisting of a four-port transparent bridge with five stations
attached to it. The ports on the bridge shall be numbered one through four, with Station A
and Station B on port 1, no station on port 2, Station C on port 3, and Station D and Station
E on port 4.
You might also like
- Networking Hardware and TopologiesDocument56 pagesNetworking Hardware and Topologiesskam zacNo ratings yet
- It Sec NotesDocument74 pagesIt Sec NotesShamima AkhterNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyFrom EverandIntroduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument36 pagesComputer NetworksSameer NandanNo ratings yet
- Networking Coursework. G5.1Document13 pagesNetworking Coursework. G5.1mbaziira eddyNo ratings yet
- TCP/IP: Network+ Protocols And Campus LAN Switching FundamentalsFrom EverandTCP/IP: Network+ Protocols And Campus LAN Switching FundamentalsNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Midsems 17074004Document8 pagesComputer Networks Midsems 17074004Kumar shivamNo ratings yet
- Functions of Network Layer Routing TableDocument4 pagesFunctions of Network Layer Routing TableAkshay VNo ratings yet
- CCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedDocument20 pagesCCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedVibrant PublishersNo ratings yet
- D PDFDocument29 pagesD PDFokienaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Computer Network: Local Area NetworksDocument19 pagesAdvanced Computer Network: Local Area NetworksAkram TahaNo ratings yet
- Viva VoceDocument5 pagesViva VocesathishNo ratings yet
- Computer Network GateDocument5 pagesComputer Network GateJayaprasannaNo ratings yet
- 5-Repeaters - Hubs - Switches - Bridges-Routers-19-01-2024Document46 pages5-Repeaters - Hubs - Switches - Bridges-Routers-19-01-2024vedhatrioathi100No ratings yet
- Unit5 OracleDocument16 pagesUnit5 Oraclemarshmallow12211221No ratings yet
- Viva Questions Ec8563Document6 pagesViva Questions Ec8563iyyanarNo ratings yet
- ComputerNetworks Chapter19Document23 pagesComputerNetworks Chapter19JIGSNo ratings yet
- Link LayerDocument58 pagesLink LayerrajindermmathNo ratings yet
- NCS Unit 4 - LAN TechnologyDocument16 pagesNCS Unit 4 - LAN Technologynanobala15No ratings yet
- 5.3 Computer Network Bridge: Types of Bridges Fixed Point BridgeDocument3 pages5.3 Computer Network Bridge: Types of Bridges Fixed Point BridgePramod Kumar ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Adeel Ahmed Roll No Bsem-F18-156 DCN Section A Submitted To Sir Arif Assignment 3 DCN DEAD LINE Friday 11:59PMDocument4 pagesAdeel Ahmed Roll No Bsem-F18-156 DCN Section A Submitted To Sir Arif Assignment 3 DCN DEAD LINE Friday 11:59PMUmer HafeezNo ratings yet
- Ochapter 5 Communication From Host To HostDocument9 pagesOchapter 5 Communication From Host To HostOmar Alejandro Ortiz GranadosNo ratings yet
- OSI Layer ModelDocument22 pagesOSI Layer ModelshaikNo ratings yet
- CN Unit-4 NotesDocument24 pagesCN Unit-4 Notessivakanthvaddi61No ratings yet
- Exp 1Document25 pagesExp 19185 KrisNo ratings yet
- CCNA R&S Practical EbookDocument78 pagesCCNA R&S Practical EbookParvinderSinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five EditedDocument26 pagesChapter Five EditedAklilu AyeleNo ratings yet
- Network Layer ProtocolsDocument5 pagesNetwork Layer ProtocolsSemir HamidNo ratings yet
- Cat 1 Exam Notes - CN Unit 2Document46 pagesCat 1 Exam Notes - CN Unit 2Deepan surya RajNo ratings yet
- Model KTU QP With AnswerDocument13 pagesModel KTU QP With AnswerAвнιѕнєк SVNo ratings yet
- Suvarna ReportDocument3 pagesSuvarna ReportSiddharth DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- LAN TechnologiesDocument4 pagesLAN TechnologiesCCNAResourcesNo ratings yet
- CN Ass 3 SolnDocument10 pagesCN Ass 3 SolnNoobs RageNo ratings yet
- T3 Modulele 8-10Document40 pagesT3 Modulele 8-10Adrian Constantin StanNo ratings yet
- Cns Practical 4Document10 pagesCns Practical 4How to download AnythingNo ratings yet
- The Switch Book by Rich Seifert-NotesDocument51 pagesThe Switch Book by Rich Seifert-NotesharinijNo ratings yet
- sc250 04 11Document41 pagessc250 04 11D2p6 D2p6No ratings yet
- The Bits and Bytes of Computer NetworkingDocument23 pagesThe Bits and Bytes of Computer NetworkingAshish SinghNo ratings yet
- 11.protocolimplementation 131206143607 Phpapp02Document48 pages11.protocolimplementation 131206143607 Phpapp02sujithavNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Source RoutingDocument5 pagesDynamic Source Routingpriyatoshdwivedi2010No ratings yet
- Test8 10Document34 pagesTest8 10dirawiw454No ratings yet
- Packet SwitchingDocument4 pagesPacket SwitchingAnkit BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Network PacketDocument7 pagesNetwork Packetempeeno1No ratings yet
- sc250 04 12Document44 pagessc250 04 12D2p6 D2p6No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document42 pagesChapter 5Bezabh AbebawNo ratings yet
- 6.0.1 Welcome 6.0.1.1 Chapter 6: Network LayerDocument39 pages6.0.1 Welcome 6.0.1.1 Chapter 6: Network Layercamys18No ratings yet
- $RVAMY8ZDocument36 pages$RVAMY8Zzyrgeon100% (1)
- Notes of Computer NetworkDocument4 pagesNotes of Computer Networkhet shahNo ratings yet
- CCNET Handbook - Good Summary For Networking IdeasDocument42 pagesCCNET Handbook - Good Summary For Networking IdeasAnas ElgaudNo ratings yet
- CS306 - Mod - 6 CNS/ Computer Network NotesDocument6 pagesCS306 - Mod - 6 CNS/ Computer Network NotesTauseef khanNo ratings yet
- CS 601 Data Communication Latest File Spring 2021Document111 pagesCS 601 Data Communication Latest File Spring 2021mc210202582 MUEEN HASANNo ratings yet
- Repeater: Physical Layer OSI ModelDocument4 pagesRepeater: Physical Layer OSI Modeljhony jonNo ratings yet
- Toward Reliable Data Delivery For Highly Dynamic MobileDocument42 pagesToward Reliable Data Delivery For Highly Dynamic MobileprincegirishNo ratings yet
- 5 OSI Network LayerDocument34 pages5 OSI Network Layerapi-3837822100% (1)
- Routing&Switching NotesDocument66 pagesRouting&Switching NotesMalxy55 DNo ratings yet
- CCNA Chapters 8-10Document29 pagesCCNA Chapters 8-10FatjonNo ratings yet
- IRCAR: Improved Reputation Based Context-Aware Routing Algorithm For Delay Tolerant NetworkDocument4 pagesIRCAR: Improved Reputation Based Context-Aware Routing Algorithm For Delay Tolerant Network87aditya87No ratings yet
- New Doc 3Document23 pagesNew Doc 3DevrajNo ratings yet
- Game Theory Is A Set of Mathematical Tools To Study The Interactive Decision Problems Between The Nodes in A Communication NetworkDocument4 pagesGame Theory Is A Set of Mathematical Tools To Study The Interactive Decision Problems Between The Nodes in A Communication NetworkDevrajNo ratings yet
- Tapas BrochureDocument2 pagesTapas BrochureDevrajNo ratings yet
- Transparent BridgesDocument1 pageTransparent BridgesDevrajNo ratings yet
- English (C)Document8 pagesEnglish (C)Anurag Saxena NetizenNo ratings yet
- GS IDocument4 pagesGS IDeepak Martian TomarNo ratings yet
- Water and Diamond ParadoxDocument19 pagesWater and Diamond ParadoxDevraj100% (1)
- Imprt 2Document52 pagesImprt 2DevrajNo ratings yet
- EE Lec5 3august2016Document9 pagesEE Lec5 3august2016DevrajNo ratings yet
- IAS SyllabusDocument4 pagesIAS SyllabusDevrajNo ratings yet
- IAS SyllabusDocument4 pagesIAS SyllabusDevrajNo ratings yet
- IAS SyllabusDocument4 pagesIAS SyllabusDevrajNo ratings yet
- Hacking Network Protocols: Complete Guide about Hacking, Scripting and Security of Computer Systems and Networks.From EverandHacking Network Protocols: Complete Guide about Hacking, Scripting and Security of Computer Systems and Networks.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Set Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNFrom EverandSet Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Concise Guide to OTN optical transport networksFrom EverandConcise Guide to OTN optical transport networksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Evaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsFrom EverandEvaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsFrom EverandMicrosoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsNo ratings yet
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamFrom EverandAWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionFrom EverandThe Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- PHP BLUEPRINT: An Essential Beginners Guide to Learn the Realms of PHP From A-ZFrom EverandPHP BLUEPRINT: An Essential Beginners Guide to Learn the Realms of PHP From A-ZNo ratings yet
- Alcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsFrom EverandAlcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsNo ratings yet
- Designing and Building Security Operations CenterFrom EverandDesigning and Building Security Operations CenterRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (3)
- Computer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityFrom EverandComputer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Mastering Linux Security and Hardening - Second Edition: Protect your Linux systems from intruders, malware attacks, and other cyber threats, 2nd EditionFrom EverandMastering Linux Security and Hardening - Second Edition: Protect your Linux systems from intruders, malware attacks, and other cyber threats, 2nd EditionNo ratings yet
- Software-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachFrom EverandSoftware-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamFrom EverandAWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamNo ratings yet
- FTTx Networks: Technology Implementation and OperationFrom EverandFTTx Networks: Technology Implementation and OperationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Computer Networking: The Complete Guide to Understanding Wireless Technology, Network Security, Computer Architecture and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCNA and CCENT)From EverandComputer Networking: The Complete Guide to Understanding Wireless Technology, Network Security, Computer Architecture and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCNA and CCENT)No ratings yet
- ITIL 4: Digital and IT strategy: Reference and study guideFrom EverandITIL 4: Digital and IT strategy: Reference and study guideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)