Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mitsubishi 4N13, 4N14 Engines PDF
Mitsubishi 4N13, 4N14 Engines PDF
Uploaded by
Ra AranzasoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mitsubishi 4N13, 4N14 Engines PDF
Mitsubishi 4N13, 4N14 Engines PDF
Uploaded by
Ra AranzasoCopyright:
Available Formats
MITSUBISHI 4N13, 4N14 ENGINES
COMMON RAIL SYSTEM (CRS)
Issued : November 2010
Applicable Vehicle :
Vehicle Manufacturer
Vehicle Name
LANCER
MITSUBISHI
ASX
OUTLANDER
50000023E
2010 DENSO CORPORATION
All rights reserved. This material may not be reproduced
or copied, in whole or in part, without the written
permission of DENSO Corporation.
Table of Contents
Operation Section
1. PRODUCT APPLICATION INFORMATION
1.1
Outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
1.2
Applicable Vehicles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
1.3
System Component Part Numbers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
2. SUPPLY PUMP
2.1
Outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
2.2
Suction Control Valve (SCV) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
2.3
Fuel Temperature Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
3. RAIL
3.1
Outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
3.2
Rail Pressure Sensor (Pc Sensor). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
3.3
Pressure Limiter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
4. INJECTOR
4.1
Outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-9
5. OPERATION OF CONTROL SYSTEM COMPONENTS
5.1
Engine Control System Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-11
5.2
Engine Electronic Control Unit (ECU) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-12
5.3
Sensor Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-13
6. FUEL INJECTION CONTROL
6.1
Outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-15
6.2
Fuel Injection Quantity Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-15
6.3
Other Controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-17
7. OTHER SYSTEMS
7.1
Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-19
7.2
Fuel Filter with Filter Clog Switch, In-Tank Pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-20
8. DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTC)
8.1
Codes Shown in the Table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-21
8.2
DTC Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-21
9. CONTROL SYSTEM COMPONENTS
9.1
Engine ECU External Wiring Diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-26
9.2
ECU Connector Terminal Layouts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-30
Operation Section
1 1
1. PRODUCT APPLICATION INFORMATION
1.1 Outline
This section describes the Common Rail System (CRS) newly introduced for the 4N13 engine equipped in
the MITSUBISHI ASX and LANCER (from March 2010), as well as the CRS newly introduced for the 4N14
engine equipped in the MITSUBISHI OUTLANDER (from July 2010). The 4N13 and 4N14 engines conform
to the European emission standards stipulated in the "EURO 5" regulations.
For CRS basics, refer to "COMMON RAIL SYSTEM SERVICE MANUAL - OPERATION (Doc ID:
00400534EA)."
Features
Maximum injection pressure increased to 200 MPa.
Equipped with G3 type injectors.
Equipped with fuel filter with filter clog switch (made by DENSO), and an in-tank pump (made by another
company.)
1.2 Applicable Vehicles
Vehicle Manufacturer
Vehicle Name
Engine Model
LANCER
4N13
ASX
MITSUBISHI
Destination
OUTLANDER
Europe
Line Off Period
March 2010
4N14
July 2010
1.3 System Component Part Numbers
4N13 Engine (LANCER, ASX)
DENSO
Manufacturer
Part Name
Part Name
Supply Pump
294000-099#
1460A043
Injector
295050-012#
1465A323
Rail
095440-142#
1465A304
275700-080#
1860B624
275700-081#
1860A625
275700-082#
1860A626
275800-972#
1860B179
079800-929#
1865A156
Mass Air Flow (MAF) Meter
197400-5200
1525A021
Diesel Throttle
197920-008#
1450A139
Part Name
Engine ECU
Manifold Absolute Pressure
(MAP) Sensor
Remarks
For the LANCER
For the ASX
For the ASX
Operation Section
1 2
DENSO
Manufacturer
Part Name
Part Name
265600-233#
1587A038
265600-234#
1587A039
265600-235#
1587A040
104990-170#
1865A184
139700-106#
8657A091
Fuel Filter with Filter Clog Switch
186320-003#
1770A179
Air Cleaner
014140-241#
1500A271
Inter-Cooler
127100-371#
1530A093
DENSO
Manufacturer
Part Name
Part Name
Supply Pump
294000-099#
1460A043
Injector
295050-034#
1465A353
Rail
095440-142#
1465A304
Engine ECU
275800-972#
1860B179
079800-929#
1865A156
Mass Air Flow (MAF) Meter
197400-5200
1525A021
Diesel Throttle
197920-008#
1450A139
Differential Pressure Sensor
104990-170#
1865A184
139700-106#
8657A091
Fuel Filter with Filter Clog Switch
186320-003#
1770A179
Air Cleaner
014140-241#
1500A271
Part Name
Exhaust Gas Temperature
Sensor
Differential Pressure Sensor
Electric-Vacuum Regulating
Valve (E-VRV)
Remarks
For the LANCER
For the LANCER
4N14 Engine (OUTLANDER)
Part Name
Manifold Absolute Pressure
(MAP) Sensor
Electric-Vacuum Regulating
Valve (E-VRV)
Remarks
Operation Section
1 3
2. SUPPLY PUMP
2.1 Outline
The supply pump equipped with the 4N13 and 4N14 engines is compliant with pressures up to 200 MPa.
The supply pump uses an SV3 type Suction Control Valve (SCV.)
1 4
Operation Section
2.2 Suction Control Valve (SCV)
When the solenoid in the SCV is not energized, the return spring pushes against the needle valve,
completely opening the fuel passage and supplying fuel to the plungers. (Total quantity suctioned
Total
quantity discharged)
When the solenoid in the SCV is energized, the armature pushes the needle valve, compressing the return
spring and closing the fuel passage.
The solenoid is actuated ON and OFF by duty ratio control. Fuel is supplied in an amount corresponding to
the open surface area of the passage in response to the duty ratio. The fuel is then discharged by the
plungers.
(1) Duty ratio control
The engine ECU outputs sawtooth wave signals with a constant frequency. The current value is the
effective (average) value of these signals. As the effective value increases, the valve opening decreases.
Conversely, as the effective value decreases, the valve opening increases.
Operation Section
1 5
(2) When the SCV energization duration (duty ON time) is short
When the SCV energization time is short, the average current flowing through the solenoid is small. As a
result, the needle valve is returned by spring force, creating a large valve opening. Subsequently, the fuel
suction quantity increases.
(3) When the SCV energization duration (duty ON time) is long
When the energization time is long, the average current flowing to the solenoid is large. As a result, the
needle valve is pressed out (in the compact SCV, the needle valve is pulled), creating a small valve
opening. Subsequently, the fuel suction quantity decreases.
1 6
Operation Section
2.3 Fuel Temperature Sensor
The fuel temperature sensor detects the fuel temperature, and sends a corresponding signal to the engine
ECU. Based on this information, the engine ECU calculates the injection volume correction that is
appropriate for the fuel temperature.
Operation Section
1 7
3. RAIL
3.1 Outline
The rail used in the CRS equipped with the 4N13 and 4N14 engines has a system pressure of 200 MPa.
As such, a rail pressure sensor and pressure limiter are used that comply with the system pressure.
3.2 Rail Pressure Sensor (Pc Sensor)
The rail pressure sensor (Pc sensor) detects the fuel pressure of the rail, and sends a signal to the engine
ECU. The sensor is made from a semiconductor that uses the Piezo resistive effect to detect changes in
electrical resistance based on the pressure applied to the elemental silicon. In comparison to the old model,
this sensor is compatible with high pressure.
1 8
Operation Section
3.3 Pressure Limiter
The pressure limiter releases pressure when the internal rail pressure becomes abnormally high. The
pressure limiter opens when internal pressure reaches 241 MPa (2458 kg/cm2), and closes when rail
pressure reaches a given set value. Fuel released from the pressure limiter is returned to the fuel tank.
Operation Section
1 9
4. INJECTOR
4.1 Outline
G3 injectors are used in the CRS equipped with the 4N13 and 4N14 engines. G3 injectors comply with a
system pressure of 200 MPa, and were designed to show improved responsiveness, as well as to increase
resistance against foreign material adherence to the nozzle.
1 10
Operation Section
(1) Correction points using QR codes
295050-012#
295050-034#
Operation Section
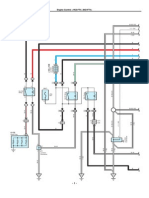
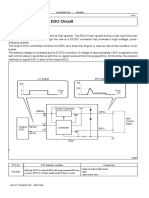
5. OPERATION OF CONTROL SYSTEM COMPONENTS
5.1 Engine Control System Diagram
1 11
1 12
Operation Section
5.2 Engine Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
The engine ECU is the command center that controls the fuel injection system and overall engine operation.
Operation Section
1 13
5.3 Sensor Operation
(1) Mass Air Flow (MAF) meter
The MAF meter used in the CRS equipped with the 4N13 and 4N14 engines is a plug-in type, and is
constructed so that a portion of the intake air flows through detector of the meter. Directly measuring the
quantity and flow volume of the intake air improves detection accuracy, and decreases intake air
resistance.
The MAF meter is built into the intake air temperature sensor.
(2) Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor
The MAP sensor is a semiconductor pressure sensor that utilizes changes in electrical resistance that
occur when the pressure applied to a silicon crystal changes. The MAP sensor uses a VSV to alternate
between atmospheric pressure and manifold absolute pressure so that a single sensor can perform both
pressure measurements.
1 14
Operation Section
(3) Diesel throttle
Outline
The diesel throttle is interlocked with the key switch to reduce vibration when the engine is stopped by
blocking the intake of air.
Operation
Operation Section
1 15
6. FUEL INJECTION CONTROL
6.1 Outline
The following explains the types of fuel injection control used in MITSUBISHI vehicle systems. For details
on each type of control, refer to "General Edition Manual: Common Rail System (Doc ID: 00400076E)."
Fuel injection rate control function
The fuel injection rate control function regulates the amount of fuel discharged from the injector orifice per
unit of time.
Fuel injection quantity control function
The fuel injection quantity control function replaces the conventional governor function. Fuel injection
quantity control adjusts the fuel injection to the optimal injection quantity based on the engine speed and
accelerator position signals.
Fuel injection timing control function
The fuel injection timing control function replaces the conventional timer function, and controls the
injection to an optimal timing based on the engine rotational speed and the injection quantity.
Fuel injection pressure control function (rail pressure control function)
The fuel injection pressure control function (rail pressure control function) controls the discharge volume
of the pump by measuring the fuel pressure at the rail pressure sensor and feeding a signal back to the
ECU. Pressure feedback control is performed so that the discharge volume matches the optimal
(command) value set in accordance with the engine rotational speed and the injection quantity.
6.2 Fuel Injection Quantity Control
The following explains controls unique to MITSUBISHI vehicles. For other types of basic fuel injection
quantity control, refer to "General Edition Manual: Common Rail System (Doc ID: 00400076E)."
(1) Maximum injection quantity
The basic maximum injection quantity is determined by the engine rotational speed, the added
corrections for intake air pressure, and gear position.
1 16
Operation Section
(2) Idle speed control (ISC) system
The ISC system controls the idle speed by regulating the injection quantity so that the actual speed
matches the target speed calculated by the engine ECU.
The target speed varies depending on whether the A/C is on or off, and the coolant temperature.
Operation Section
1 17
6.3 Other Controls
The following explains microinjection quantity learning control.
(1) Microinjection quantity learning control
Outline
Microinjection quantity learning control is used in every vehicle engine (injector) to preserve the accuracy
of the quantity (specifically, the pilot injection quantity.)
This type of control is first performed when shipped from the factory (L/O), and later is automatically
performed every time the vehicle runs a set distance (for details, see item "(A) below). Microinjection
quantity learning control not only preserves the accuracy of each injector initially, but also as deterioration
in injection occurs over time. Microinjection quantity learning also records the correction values to the
ECU. During normal driving operations, these correction values are used to make modifications to
injection commands, resulting in accurate microinjection.
Learning operations
Microinjection quantity learning control takes place for every two no-load, idle instability conditions
established (see chart "(A)" below). This control can also be performed manually as a diagnostic tool.
1 18
Operation Section
Operational outline
Learning control sends ISC (target speed correction quantity) and FCCB (cylinder-to-cylinder correction
quantity) feedback based on engine speed to apply injection control. Corrections are applied to each
cylinder based on ISC and FCCB correction information, and the corrected injection quantities are
calculated. Under microinjection quantity learning control, injection is divided into five injections.
Therefore, the "learning value" is calculated as the corrected injection quantities for ISC and FCCB,
divided by five injections.
Operation Section
1 19
7. OTHER SYSTEMS
7.1 Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) System
Outline
For details on basic DPF construction and operation, refer to "General Edition Manual: Common Rail
System (Doc ID: 00400076E)". The differential pressure sensors and exhaust gas temperature sensors in
the systems for the applicable vehicles are DENSO products.
Differential pressure sensor
The construction and operation of the current differential pressure sensor is identical to that of the
conventional differential pressure sensor. The differential pressure sensor detects the difference in exhaust
gas pressure across the DPF.
Exhaust gas temperature sensors
The construction and operation of the current exhaust gas temperature sensors is identical to that of the
conventional differential pressure sensor. The exhaust gas temperature sensors detect the temperature of
the exhaust gas both before and after the DPF.
1 20
Operation Section
7.2 Fuel Filter with Filter Clog Switch, In-Tank Pump
Fuel filter with filter clog switch
The filter clog switch detects filter clogs using the pressure difference between the fuel filter inlet and outlet.
When a filter clog is detected, a diagnostic signal is outputted. (The fuel filter with filter clog switch is made
by DENSO.)
In-tank pump
The CRS equipped with the 4N13 and 4N14 engines uses an in-tank pump. The in-tank pump sends fuel
from inside the fuel tank to the supply pump, thereby assisting the pump in suctioning fuel to stabilize the
feed pressure. (The in-tank pump is made by another company.)
Operation Section
1 21
8. DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTC)
8.1 Codes Shown in the Table
The "SAE" DTC column below indicates codes that are output through the use of the STT (MUT-III).
(SAE: Society of Automotive Engineers)
8.2 DTC Details
Applicable Engine
DTC
P0003
P0004
P0016
Detection Item
Suction Control Valve (SCV) actuation line
abnormality
SCV +B short circuit
Crankshaft position sensor, cylinder recognition
sensor phase gap malfunction
4N13
4N14
Detection
MIL
Detection
MIL
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0047
Turbo PWM output (low side)
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0048
Turbo PWM output (high side)
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0072
P0073
Intake air temperature sensor abnormality (low
side)
Intake air temperature sensor abnormality (high
side)
P0088
Abnormally high rail pressure
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0089
SCV stuck
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0093
Fuel leak
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0102
P0103
P0106
Mass Air Flow (MAF) meter abnormality (low
side)
MAF meter abnormality (high side)
Abnormal Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
sensor characteristics
P0107
MAP sensor abnormality (low side)
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0108
MAP sensor abnormality (high side)
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0112
P0113
P0117
P0118
Intake manifold intake air temperature sensor
abnormality (low side)
Intake manifold intake air temperature sensor
abnormality (high side)
Coolant temperature sensor abnormality (low
side)
Coolant temperature sensor abnormality (high
side)
Operation Section
1 22
Applicable Engine
DTC
Detection Item
4N13
4N14
Detection
MIL
Detection
MIL
P0122
Intake valve sensor low
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0123
Intake valve sensor high
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0130
A/F sensor element abnormality
YES
YES
P0134
A/F sensor activation abnormality
YES
YES
P0135
A/F sensor heater abnormality
YES
YES
P0182
Fuel temperature sensor abnormality (low side)
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0183
Fuel temperature sensor abnormality (high side)
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0191
Abnormal rail pressure sensor characteristics
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0192
Rail pressure sensor (time) abnormality (low side)
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0193
Rail pressure sensor (time) abnormality (high
side)
P0201
TWV 1 (cylinder 1) actuation line open circuit
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0202
TWV 4 (cylinder 4) actuation line open circuit
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0203
TWV 2 (cylinder 2) actuation line open circuit
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0204
TWV 3 (cylinder 3) actuation line open circuit
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0219
Engine overrun abnormality
YES
P0234
High boost abnormality
P0299
Low boost abnormality
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0301
Injector function (non-injection) 1
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0302
Injector function (non-injection) 2
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0303
Injector function (non-injection) 3
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0304
Injector function (non-injection) 4
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0335
P0336
P0340
P0341
YES
YES
No crankshaft position sensor (NE sensor) pulse
input
Abnormal number of crankshaft position sensor
pulses
No cylinder recognition sensor pulse input
Abnormal number of cylinder recognition sensor
pulses
YES
P0381
Glow plug open/short circuit abnormality
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0401
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) insufficient flow
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0403
EGR DC motor status abnormality
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0420
No
temperature
increase
during
regeneration
DOC
P0427
Exhaust gas temperature sensor 2 low
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0428
Exhaust gas temperature sensor 2 high
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0489
EGR lift sensor low
YES
YES
YES
YES
Operation Section
1 23
Applicable Engine
DTC
Detection Item
4N13
4N14
Detection
MIL
Detection
MIL
P0490
EGR lift sensor high
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0500
Vehicle speed abnormality (low)
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0545
P0546
Exhaust gas temperature sensor 1 abnormality
(low side)
Exhaust gas temperature sensor 1 abnormality
(high side)
P0602
EOL not programmed
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0604
RAM abnormality
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0605
ECU flash-ROM abnormality
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0606
ECU CPU abnormality (main IC abnormality)
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0607
ECU
CPU
abnormality
(monitoring
IC
abnormality)
P062F
EEPROM diagnosis
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0630
VIN not programmed
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0638
Intake valve stuck
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0642
Sensor voltage 1 (low side)
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0643
Sensor voltage 1 (high side)
YES
YES
YES
YES
P064C
Glow control unit malfunction
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0652
Sensor voltage 2 (low side)
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0653
Sensor voltage 2 (high side)
YES
YES
YES
YES
P0683
Glow control unit communication abnormality
YES
YES
YES
YES
P1203
Low charging
YES
YES
YES
YES
P1204
Overcharging
YES
YES
YES
YES
P1210
Throttle valve opening malfunction
P1272
Pressure limiter valve opening abnormality
YES
YES
YES
YES
P1273
Supply pump single side pumping abnormality
YES
YES
YES
YES
P1274
Supply pump protective fail flag
YES
YES
YES
YES
P1275
Supply pump replace fail flag
YES
YES
YES
YES
P1276
Fuel filter clog abnormality
YES
YES
YES
YES
P1298
Turbo system (positive deviation)
YES
YES
YES
YES
P1299
Turbo system (negative deviation)
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
P1427
P1428
P1474
Exhaust gas temperature sensor 3 abnormality
(low side)
Exhaust gas temperature sensor 3 abnormality
(high side)
Temperature sensor for the Diesel Particulate
Filter (DPF) differential pressure sensor (low side)
YES
YES
YES
Operation Section
1 24
Applicable Engine
DTC
P1475
Detection Item
Temperature sensor for the DPF differential
pressure sensor (high side)
4N13
4N14
Detection
MIL
Detection
MIL
YES
YES
YES
YES
P1496
DOC temperature abnormality
YES
YES
P1497
DOC regeneration time exceeded
YES
YES
YES
YES
P1498
No opportunity for regeneration
YES
YES
YES
YES
P1499
DPF heat loss temperature abnormality
YES
YES
YES
YES
P1546
Exhaust gas temperature abnormality during
YES
regeneration
YES
P1625
QR data abnormality
YES
YES
YES
YES
P1626
QR data failure to write abnormality
YES
YES
YES
YES
P1639
Throttle abnormality during regeneration
P2009
EGR cooler bypass open load/short to ground
P2010
EGR cooler bypass short to battery
P20CF
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
Exhaust injector stuck open abnormality
YES
YES
P20D0
Exhaust injector stuck closed abnormality
YES
YES
P2118
DC motor overcurrent abnormality
P2122
P2123
P2124
P2127
Accelerator position sensor 1 abnormality
(low side)
Accelerator position sensor 1 abnormality
(high side) final
Accelerator position sensor 1 abnormality
(high side)
Accelerator position sensor 2 abnormality
(low side)
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
Accelerator position sensor 2 abnormality
P2128
YES
YES
YES
(high side)
Accelerator position sensor 2 abnormality
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
ACCP characteristic abnormality
YES
YES
YES
YES
P2146
Common 1 line open circuit
YES
YES
YES
YES
P2147
COM 1 TWV actuation line ground short
YES
YES
YES
YES
P2148
COM 1 TWV actuation line +B short circuit
YES
YES
YES
YES
P2149
Common 2 line open circuit
YES
YES
YES
YES
P2150
COM 2 TWV actuation line ground short
YES
YES
YES
YES
(high side) final
Accelerator position sensor duplicate malfunction
(high side)
P2138
Accelerator position sensor duplicate malfunction
(low side)
Operation Section
1 25
Applicable Engine
DTC
P2151
P2228
P2229
Detection Item
4N13
COM 2 TWV actuation line +B short circuit
Atmospheric pressure sensor abnormality (low
side)
Atmospheric pressure sensor abnormality (high
side)
4N14
Detection
MIL
Detection
MIL
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
P2238
A/F sensor positive (+) terminal (low side)
YES
YES
P2239
A/F sensor positive (+) terminal (high side)
YES
YES
P2252
A/F sensor negative (-) terminal (low side)
YES
YES
P2253
A/F sensor negative (-) terminal (high side)
YES
YES
YES
YES
P2297
Atmospheric
learning
value
abnormality/
malfunction detection
P2413
EGR feedback abnormality
YES
YES
YES
YES
P2426
VSS output (VSV) open load/short to ground
YES
YES
YES
YES
P2427
VSS output (VSV) open load/short to battery
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
P2454
P2455
DPF differential pressure sensor abnormality (low
side)
DPF differential pressure sensor abnormality
(high side)
P2463
Manual regeneration timing abnormality
U0131
Power steering ON malfunction
1 26
Operation Section
9. CONTROL SYSTEM COMPONENTS
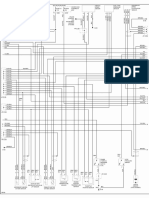
9.1 Engine ECU External Wiring Diagrams
(1) LANCER
Operation Section
1 27
1 28
Operation Section
(2) ASX, OUTLANDER
Operation Section
1 29
1 30
Operation Section
9.2 ECU Connector Terminal Layouts
(1) LANCER
Operation Section
(2) ASX, OUTLANDER
1 31
Service Department DENSO CORPORATION
1-1, Showa-cho, Kariya-shi, Aichi-ken, 448-8661, Japan
You might also like
- Mitsubishi L200 Triton Service ManualDocument51 pagesMitsubishi L200 Triton Service Manualloveluna94% (18)
- 4Ja1-Tc & 4Jh1-Tc Engine: Engine Management System Operation & DiagnosisDocument91 pages4Ja1-Tc & 4Jh1-Tc Engine: Engine Management System Operation & DiagnosisNguyễn ĐángNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi Pajero 4m41 EngineDocument42 pagesMitsubishi Pajero 4m41 Engineesyjam100% (14)
- Mazda 3 6 MZR-CD2.2 EngineDocument46 pagesMazda 3 6 MZR-CD2.2 EnginejorgeNo ratings yet
- 4JH1 Gestión ElectrónicaDocument79 pages4JH1 Gestión ElectrónicaAna Lorca89% (19)
- Fuel Sistem D4EB 2.2 PDFDocument544 pagesFuel Sistem D4EB 2.2 PDFcarnori100% (1)
- Hino j05d Turbo VNTDocument58 pagesHino j05d Turbo VNTEric Porter91% (32)
- Nissan XtrailThrottle and Idle RelearnDocument4 pagesNissan XtrailThrottle and Idle RelearnRa Aranzaso100% (1)
- Crdi System 1 Hyundai H1Document2 pagesCrdi System 1 Hyundai H1Ra Aranzaso100% (6)
- Dokumen - Tips Isuzu 07tf Immobilizer Training Ver1Document50 pagesDokumen - Tips Isuzu 07tf Immobilizer Training Ver1Chamila tharanga madushanNo ratings yet
- Toyota Hilux Kijyang Innova 1kd 2kd PDFDocument68 pagesToyota Hilux Kijyang Innova 1kd 2kd PDFpalaboy88892% (13)
- Denso Mitsubishi L200 Common Rail PDFDocument53 pagesDenso Mitsubishi L200 Common Rail PDFAlex Renne Chambi100% (10)
- DENSO Common Rail Mitsubishi L200 Triton 4D56 4M41 Service Manual PagesDocument11 pagesDENSO Common Rail Mitsubishi L200 Triton 4D56 4M41 Service Manual PagesJB0109198275% (16)
- Transfer D22Document38 pagesTransfer D22Jose FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Preparation 2zr-Fe Engine Mechanical SST PDFDocument3 pagesPreparation 2zr-Fe Engine Mechanical SST PDFAlbert BriceñoNo ratings yet
- Nissan Patrol Y61 Series 1 Brake SystemDocument10 pagesNissan Patrol Y61 Series 1 Brake SystemKofetoNo ratings yet
- Removing Mitsubishi Pajero ECUDocument2 pagesRemoving Mitsubishi Pajero ECUJose GilmerNo ratings yet
- Common Rail Hino - ToyotaDocument41 pagesCommon Rail Hino - Toyota0808833892% (24)
- Honda Civic EK Wiring Diagram Engine Controls 2 of 3Document1 pageHonda Civic EK Wiring Diagram Engine Controls 2 of 3Ra Aranzaso100% (1)
- Nissan Xtrail DTC P0335Document6 pagesNissan Xtrail DTC P0335Ra Aranzaso67% (3)
- Engine Controls Except HX 1 of 3Document1 pageEngine Controls Except HX 1 of 3Ra AranzasoNo ratings yet
- Motorul D4DDocument185 pagesMotorul D4Ddoruk1964100% (5)
- Enviando Denso Mitsubishi l200 Common RailDocument55 pagesEnviando Denso Mitsubishi l200 Common Railisrael machicado calle100% (4)
- Service Manual: Common Rail System For NISSAN YD1-K2 Type EngineDocument40 pagesService Manual: Common Rail System For NISSAN YD1-K2 Type EngineBryan Edu Curay ZavalaNo ratings yet
- Dmax Mux PDFDocument102 pagesDmax Mux PDFibnu malkanNo ratings yet
- DTC P0200-97 Injector Circuit - Open PDFDocument9 pagesDTC P0200-97 Injector Circuit - Open PDFMortada AlsonniNo ratings yet
- Denso - Ecd IIDocument26 pagesDenso - Ecd IIVASEK100% (4)
- Common Rail System (CRS) SERVICE MANUAL: Operation: YD2K3 EngineDocument44 pagesCommon Rail System (CRS) SERVICE MANUAL: Operation: YD2K3 EngineAntony ColonnaNo ratings yet
- Transfer: Workshop ManualDocument92 pagesTransfer: Workshop ManualmailforspamNo ratings yet
- Auto-Tech EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesAuto-Tech Encyclopediajhonathan hernandezNo ratings yet
- Toyota 14Document76 pagesToyota 14Dadang Lukmanul HakimNo ratings yet
- Taller New Actyon Sport Motor D20DTRDocument260 pagesTaller New Actyon Sport Motor D20DTRFernando MorenoNo ratings yet
- TFBRK We 0871 BrakesDocument216 pagesTFBRK We 0871 Brakessoenge100% (5)
- Fuel Inspection (4JJ1 Without DPD)Document157 pagesFuel Inspection (4JJ1 Without DPD)Patricio ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Nissan Tb45e Engine Controlpdf PRDocument7 pagesToaz - Info Nissan Tb45e Engine Controlpdf PRAfshin GhafooriNo ratings yet
- Transfer Control Unit Isuzu D-Max UbicacionDocument1 pageTransfer Control Unit Isuzu D-Max UbicacionEltiezo EcheverriaNo ratings yet
- 2018 D 2.5 TCI-A2 Schematic Diagrams Engine Electrical System Engine Control System (With Euro6) Schematic DiagramsDocument1 page2018 D 2.5 TCI-A2 Schematic Diagrams Engine Electrical System Engine Control System (With Euro6) Schematic DiagramsANH LÊNo ratings yet
- Diagrama ABS Toyota HiluxDocument2 pagesDiagrama ABS Toyota HiluxMário Oliveira100% (1)
- Engine 4JG2 PDFDocument233 pagesEngine 4JG2 PDFАлексNo ratings yet
- Group 37 SteeringDocument71 pagesGroup 37 SteeringNeoGaraNo ratings yet
- Actyon FuelSystem D20DTRDocument24 pagesActyon FuelSystem D20DTRAnonymous 7t2BOJbNo ratings yet
- 2018 D 2.5 TCI-A2 Schematic Diagrams Engine Electrical System Engine Control System (With Euro6) Schematic DiagramsDocument1 page2018 D 2.5 TCI-A2 Schematic Diagrams Engine Electrical System Engine Control System (With Euro6) Schematic DiagramsANH LÊNo ratings yet
- Engine ControlDocument15 pagesEngine ControlMichael Porter100% (4)
- 1GD-FTV Engine Control Ecm ComponentsDocument3 pages1GD-FTV Engine Control Ecm ComponentsDaniel rodriguez alayo100% (5)
- Motor 4M41 MitsubishiDocument105 pagesMotor 4M41 MitsubishiMario Rogers100% (13)
- 6hkeed We 0325arDocument274 pages6hkeed We 0325arhumberto100% (5)
- w58 RebuildDocument49 pagesw58 RebuildtfphoenixNo ratings yet
- 1KD EduDocument5 pages1KD EduMakokha Mumelo100% (1)
- ECD-V4 OutlineDocument4 pagesECD-V4 OutlineВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- Connection of The STAG-300Document1 pageConnection of The STAG-300Anonymous IkfTLYBNo ratings yet
- Cylinder Head Bolt Tightening SequenceDocument2 pagesCylinder Head Bolt Tightening Sequenceອູ່ ໄຊ ອິນເຕີNo ratings yet
- Denso Fuel Injection Pump HP3 5 - L200 - 2.5DI-D MitsubishiDocument51 pagesDenso Fuel Injection Pump HP3 5 - L200 - 2.5DI-D MitsubishiJohnny Chia91% (11)
- DENSO Common Rail Hino E13C Service Manual PagesDocument11 pagesDENSO Common Rail Hino E13C Service Manual PagesYohanor Saputera88% (26)
- Avensis2 0cr-ServmanualDocument46 pagesAvensis2 0cr-ServmanualAmadeus De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: Common Rail System (HP3) For Mitsubishi L200/Triton 4D56/4M41Engine (All The Destinations)Document53 pagesService Manual: Common Rail System (HP3) For Mitsubishi L200/Triton 4D56/4M41Engine (All The Destinations)Pizarro Andres100% (3)
- Toyot Common Rail System-2AD Denso For Avensis Service Manual PDFDocument32 pagesToyot Common Rail System-2AD Denso For Avensis Service Manual PDFNery CastellanosNo ratings yet
- Service Manual NissanDocument39 pagesService Manual NissanSky TripNo ratings yet
- Fuso 6m60Document20 pagesFuso 6m60Dowane Charles94% (31)
- Common Rail System For NISSANDocument40 pagesCommon Rail System For NISSANAntonio Ramos Vazquez90% (10)
- VECTOR 8500: Operation & Service ManualDocument74 pagesVECTOR 8500: Operation & Service ManualDM Truck100% (1)
- Variable Speed Pumping: A Guide to Successful ApplicationsFrom EverandVariable Speed Pumping: A Guide to Successful ApplicationsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Microprocessor Programming and Applications for Scientists and EngineersFrom EverandMicroprocessor Programming and Applications for Scientists and EngineersNo ratings yet
- Toyota Hilux ECM TerminalsDocument2 pagesToyota Hilux ECM TerminalsRa Aranzaso100% (2)
- 1kz-Te Pedal TroubleshootDocument6 pages1kz-Te Pedal TroubleshootLance Ramai100% (9)
- 99 Civic EK Engine Controls Wiring 3 of 3Document1 page99 Civic EK Engine Controls Wiring 3 of 3Ra AranzasoNo ratings yet
- MAX1 Conventional 19nov2010Document2 pagesMAX1 Conventional 19nov2010Ra AranzasoNo ratings yet