Entrepreneurship Management
Business Model: Case Study Analysis
Pranpratim, Priya, Sharang, Shivangi & Shweta
�Social Media and Web 2.0
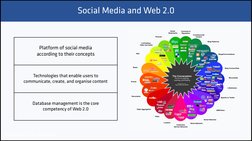
Platform of social media
according to their concepts
Technologies that enable users to
communicate, create, and organise content
Database management is the core
competency of Web 2.0
Facebook Case Analysis
�Classification of Social Media
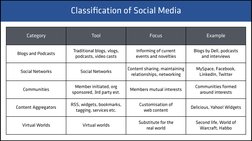
Category
Tool
Focus
Example
Blogs and Podcasts
Traditional blogs, vlogs,
podcasts, video casts
Informing of current
events and novelties
Blogs by Dell, podcasts
and interviews
Social Networks
Social Networks
Content sharing, maintaining
relationships, networking
MySpace, Facebook,
LinkedIn, Twitter
Communities
Member initiated, org
sponsored, 3rd party est.
Members mutual interests
Communities formed
around interests
Content Aggregators
RSS, widgets, bookmarks,
tagging, services etc.
Customisation of
web content
Delicious, Yahoo! Widgets
Virtual worlds
Substitute for the
real world
Second life, World of
Warcraft, Habbo
Virtual Worlds
Facebook Case Analysis
�Comparison of Popular Social Networks
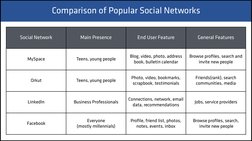
Social Network
Main Presence
End User Feature
General Features
Teens, young people
Blog, video, photo, address
book, bulletin calendar
Browse profiles, search and
invite new people
Teens, young people
Photo, video, bookmarks,
scrapbook, testimonials
Friends(rank), search
communities, media
LinkedIn
Business Professionals
Connections, network, email
data, recommendations
Jobs, service providers
Facebook
Everyone
(mostly millennials)
Profile, friend list, photos,
notes, events, inbox
Browse profiles, search,
invite new people
MySpace
Orkut
Facebook Case Analysis
�Network Effects
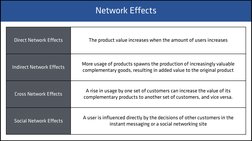
Direct Network Effects
The product value increases when the amount of users increases
Indirect Network Effects
More usage of products spawns the production of increasingly valuable
complementary goods, resulting in added value to the original product
Cross Network Effects
A rise in usage by one set of customers can increase the value of its
complementary products to another set of customers, and vice versa.
Social Network Effects
A user is influenced directly by the decisions of other customers in the
instant messaging or a social networking site
Facebook Case Analysis
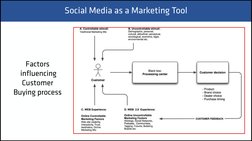
�Social Media as a Marketing Tool
There are growing needs for online service, customer interaction
with both marketers and peer communities.
The value perceptions are based on the feeling of achievement
through personal gratification instead of traditional customer value approach
Consumer behavior is increasingly influenced by peer opinions
Facebook Case Analysis
�Social Media as a Marketing Tool
Factors
influencing
Customer
Buying process
Facebook Case Analysis
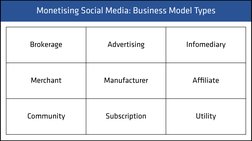
�Monetising Social Media: Business Model Types
Brokerage
Advertising
Infomediary
Merchant
Manufacturer
Affiliate
Community
Subscription
Utility
Facebook Case Analysis
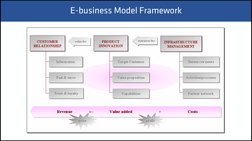
�E-business Model Framework
Facebook Case Analysis
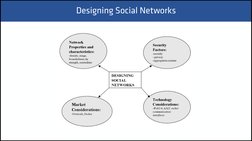
�Designing Social Networks
Facebook Case Analysis
�Modified Business Model Framework
Facebook Case Analysis
�Facebook Business Model
Facebook Case Analysis
�Customer Relationship
Information strategy helps Facebook to provide a safe, efficient, and customised experience
Facebook also shares users information with third parties when permitted by users
Users can access Facebook channels through web portal by facebook.com
Facebook Case Analysis
�Product Innovation
Facebooks value proposition is to offer a social networking platform that
helps people communicate more efficiently with their friends, family and coworkers
It targets global netizens over 13 year-old who have social networking needs.
The major users are college students.
Facebook needs capabilities that can keep the mass data
transmissions under a stable network infrastructure.
Facebook Case Analysis
�Infrastructure Management
A large amount of websites enable the share functionality of
Facebook to share video, photo, news other contents since 2006
Facebook opens its platform and encourages developers to build applications since 2007
Microsoft and Facebook built their advertising strategic alliance,
and Microsoft would be the exclusive third party advertising platform partner for Facebook
Facebook and PayPal built a strategic relationship in February 2010.
It enables to pay for Facebook ads and Credits through PayPal now
Facebook Case Analysis
�Unique Visitors Comparisons
02/2015
03/2015
04/2015
Facebook Case Analysis
05/2015
06/2015
07/2015
08/2015
09/2015
10/2015
11/2015
12/2015
01/2016
02/2016
�Technologies
Facebook uses LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP) as its technology architecture.
Its the largest user in the world of memcached, an open source
caching system, and has one of the largest MySQL database clusters anywhere
Facebook has built a lightweight but powerful multi-language RPC framework that
seamlessly and easily ties together infrastructure services written in any language
Facebook relies heavily on open source software & releases large pieces of its own software infrastructure
Facebook Case Analysis
�Regulations
Facebook states its regulations concerning to the rights and
responsibilities derive from the Facebook Principles
The relevant statements include Privacy Policy, Payment Terms,
Platform Policies, Ads Guidelines, Promotion Guidelines etc.
All Facebook parties must comply with these policies
Facebook Case Analysis
�Financial Aspects
Facebooks revenue was estimated at 2 billion dollars in 2010,
while 1.86 billion dollars from advertising alone
Ads places can be bought directly on Facebooks page. It can be simply created by anyone
Facebook provides social ads pages. Any brands, businesses,
organisations, bands and so on can create their own Facebook page
Facebook and Microsoft Corp. announced in 2007 that the two companies would expand their advertising
partnership, and Microsoft will be the exclusive third party advertising platform partner for Facebook
Facebook Case Analysis
�Facebook Business Model Analysis
Facebook Case Analysis
�Question 1
How is the Facebook Business Model different
from the MySpace Business Model?
Facebook Case Analysis
�Comparison with MySpace Business Model
Facebook Case Analysis
�Comparison with MySpace Business Model
Facebook Case Analysis
�Comparison with MySpace Business Model
Facebook Case Analysis
�Comparison with MySpace Business Model
Facebook Case Analysis
�Comparison with MySpace Business Model
Facebook Case Analysis
�Comparison with MySpace Business Model
Facebook Case Analysis
�Question 2
Suggest Potential Business Models and state
their risks. Compare with a MySpace
Facebook Case Analysis
�Potential Business Models and Risks: Facebook
Customer
Relationship
Recommendations: develop upgrading and membership mechanism similar to MySpace
for keeping users interested and engaged in. Risks: low risk.
Product
Innovation
Recommendations: benchmark other social media services offers; offer more services
like micro-blogging, online music, customisable page. Risk: unable to focus on core
services, too diverse features makes pages loud and noisy
Infrastructure
Management
Recommendations: analyze users needs and design related features; build e-commerce
platform that can make users real life easier, such as Amazon books, ebay, job website
monster, etc. Risks: low risk.
Market
Considerations
Recommendations: integrating services models. Risks: unable to concentrate on its
competitive advantage, too many models sometimes means no an important model;
unable to compete with others who work on the specific service.
Financial
Recommendations: increase virtual items sales; bind with telecommunication services.
Aspects
Risks: people dislike to pay, they might just turn to other free services
Facebook Case Analysis
�Potential Business Models and Risks: MySpace
Customer
Relationship
Recommendations: real name and real information registration enables a safe and
trusted internet environment and offer valuable data to Myspace
Risks: privacy leak and violation, cost increases
Product
Innovation
Recommendations: enhance Myspaces main service Myspace Music.
Risks: need strong resource integration capability.
Infrastructure
Management
Recommendations: adopt real name registration policy for enhancing the strength of
ties of the network properties. Risks: Privacy leak and violation, freedom of speech could
be abridged.
Market
Considerations
Recommendations: integrating business model. Risks: unable to concentrate on its
competitive advantage; the core service in Myspace is not good enough, and integrated
models might bring more difficulties.
Financial
Aspects
Facebook Case Analysis
Recommendations: work on virtuality services and charge in somewhat level; share
revenue with telecommunication provider. Risks: the major problem is keep users
engaged, but charging services would turn away more users
�Learning Outcomes
Business models of Facebook and Myspace have been
studied according to seven components business model ontology
Four components of a successful business model are Core Strategy,
Strategic Resources, Partnership Network and Customer Interface
A Business Model serves as an ongoing extension of feasibility analysis and focuses attention on
how all the elements of a business fit together and constitute a working whole
Facebook Case Analysis
�Thank You
Facebook Case Analysis