Professional Documents
Culture Documents
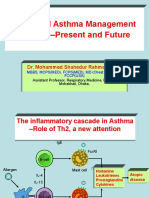
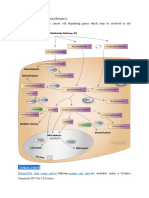
IL-5-directed Approaches in The Treatment of Eosinophil-Driven Disease
IL-5-directed Approaches in The Treatment of Eosinophil-Driven Disease
Uploaded by
Marcelo AlvesOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IL-5-directed Approaches in The Treatment of Eosinophil-Driven Disease
IL-5-directed Approaches in The Treatment of Eosinophil-Driven Disease
Uploaded by
Marcelo AlvesCopyright:
Available Formats
https://www.karger.
com/ProdukteDB/Katalogteile/isbn3_8055/_95/_66/prrer0
39_03.pdf
IL-5-directed approaches in the treatment of eosinophil-driven
disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14523040
Anti-IL-5 treatment reduces deposition of ECM proteins in the
bronchial subepithelial basement membrane of mild atopic
asthmatics
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21958585
Mepolizumab, a humanized antiIL-5 mAb, as a treatment option for
severe nasal polyposis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17088140
Nasal IL-5 levels determine the response to antiIL-5 treatment in
patients with nasal polyps
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20371394
A review of treatment with mepolizumab, an antiIL-5 mAb, in
hypereosinophilic syndromes and asthma
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12765424
Monoclonal anti-interleukin5 treatment suppresses eosinophil but not
Tcell functions
http://eds.a.ebscohost.com/eds/detail/detail?vid=1&sid=11312f10-169049c1-952d-563aa5d59e4d
%40sessionmgr4007&hid=4203&bdata=JkF1dGhUeXBlPWlwLGNvb2tpZSxza
GliLHVpZCZsYW5nPXB0LWJyJnNpdGU9ZWRzLWxpdmUmc2NvcGU9c2l0ZQ
%3d%3d#AN=S0091674913004193&db=edselp
Food, drug, insect sting allergy, and anaphylaxis: AntiIL-5 therapy
reduces mast cell and IL-9 cell numbers in pediatric patients with
eosinophilic esophagitis
http://eds.a.ebscohost.com/eds/detail/detail?vid=2&sid=11312f10-169049c1-952d-563aa5d59e4d
%40sessionmgr4007&hid=4203&bdata=JkF1dGhUeXBlPWlwLGNvb2tpZSxza
GliLHVpZCZsYW5nPXB0LWJyJnNpdGU9ZWRzLWxpdmUmc2NvcGU9c2l0ZQ
%3d%3d#AN=S0091674911013248&db=edselp
Rhinitis, sinusitis, and upper airway disease: Mepolizumab, a
humanized antiIL-5 mAb, as a treatment option for severe nasal
polyposis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21809010
Omalizumab in the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis and food
allergy.
You might also like
- Printer Friendly View PackDocument76 pagesPrinter Friendly View PackfrabziNo ratings yet
- Serology Answer Sheet 100 Point ExamDocument5 pagesSerology Answer Sheet 100 Point ExamKate Camat Faminialagao100% (1)
- Monoclonal Antibodies and Engineered AntibodiesDocument24 pagesMonoclonal Antibodies and Engineered AntibodiesMunawar AliNo ratings yet
- PulmCrit - Mastering The Dark Arts of BiPAP & HFNCDocument13 pagesPulmCrit - Mastering The Dark Arts of BiPAP & HFNCTusar KoleNo ratings yet
- Plasma FractionationDocument40 pagesPlasma FractionationJoseph ChandyNo ratings yet
- Matera 2017Document8 pagesMatera 2017Yuni RochyaningsihNo ratings yet
- Clinical Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of Fingolimod For The Treatment of Relapsing-Remitting Multiple SclerosisDocument11 pagesClinical Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of Fingolimod For The Treatment of Relapsing-Remitting Multiple SclerosisAnonymous nOY0Q1No ratings yet
- Tailored Therapy For Severe Asthma: Review Open AccessDocument8 pagesTailored Therapy For Severe Asthma: Review Open AccessSardar IjlalNo ratings yet
- Anti IL 4 13 Based Therapy in AsthmaDocument5 pagesAnti IL 4 13 Based Therapy in AsthmaMoch Ridwan Pujiar PamungkasNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2095881118301379 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S2095881118301379 MainAnita DewiNo ratings yet
- Dr. Mohammed Shahedur Rahman Khan Bronchial Asthma Management Aspects - Current and FutureDocument32 pagesDr. Mohammed Shahedur Rahman Khan Bronchial Asthma Management Aspects - Current and FutureShahadat Hossain BabuNo ratings yet
- Use of Human Intravenous Immunoglobulin in VeterinDocument13 pagesUse of Human Intravenous Immunoglobulin in VeterinTactvisNo ratings yet
- Immuno2008, Vol.28, Issues 4, Intravenous Immunoglobulin Treatment of ImmunodeficiencyDocument187 pagesImmuno2008, Vol.28, Issues 4, Intravenous Immunoglobulin Treatment of ImmunodeficiencydudapaskasNo ratings yet
- Anti-Asthmatic Agents: Visit: For More Ppt'sDocument38 pagesAnti-Asthmatic Agents: Visit: For More Ppt'sGANESH KUMAR JELLANo ratings yet
- Table S1 English Translation of The MIR ExaminationDocument43 pagesTable S1 English Translation of The MIR Examinationهادي تركي شنبارةNo ratings yet
- Ballow 1997Document7 pagesBallow 1997Norsarida AryaniNo ratings yet
- Omalizumab: Clinical Use For The Management of AsthmaDocument14 pagesOmalizumab: Clinical Use For The Management of Asthmaall_dedicateNo ratings yet
- MRCP 1 Pastpaper Jan 2020Document2 pagesMRCP 1 Pastpaper Jan 2020muneebaNo ratings yet
- 2014 Mechanisms of Immune Regulation by IVIGDocument7 pages2014 Mechanisms of Immune Regulation by IVIGamallullaNo ratings yet
- Aapsj 070487Document8 pagesAapsj 070487jokifarmasiyukNo ratings yet
- Drug Discovery 2017 AbstractDocument1 pageDrug Discovery 2017 AbstractAhmed aboraiaNo ratings yet
- Flucytosi Review of PharmacologyDocument10 pagesFlucytosi Review of PharmacologyHanung PujanggaNo ratings yet
- Biochem Revision 1 by Dr. PossibilityDocument5 pagesBiochem Revision 1 by Dr. PossibilityVisionous LionNo ratings yet
- Molecular Characterization and Resistance of H. Influenzae Isolated From Nasopharynx of Students in North LebanonDocument6 pagesMolecular Characterization and Resistance of H. Influenzae Isolated From Nasopharynx of Students in North LebanonInternational Medical PublisherNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Potential Drug Candidates To Treat COVID-19: PHR 213: Pharmacology-IDocument7 pagesAssignment On Potential Drug Candidates To Treat COVID-19: PHR 213: Pharmacology-Isamarah arjumandNo ratings yet
- Immunoglobulin Treatment of Immunodeficient Patients: Yıldız CamcıoğluDocument24 pagesImmunoglobulin Treatment of Immunodeficient Patients: Yıldız Camcıoğlukj185No ratings yet
- Rifampicin Induced Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic PurpuraDocument2 pagesRifampicin Induced Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic PurpuraInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Assessment of in Vitro Antifungal Efficacy and in Vivo Toxicity of Amphotericin B-Loaded Plga and Plga-Peg Blend NanoparticlesDocument11 pagesAssessment of in Vitro Antifungal Efficacy and in Vivo Toxicity of Amphotericin B-Loaded Plga and Plga-Peg Blend NanoparticlesNurul syam annisaNo ratings yet
- Management From MRCP 1 Past PapersDocument7 pagesManagement From MRCP 1 Past PapersmuneebaNo ratings yet
- Antimycobacterial DrugsDocument7 pagesAntimycobacterial Drugsنشط عقلكNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological Therapy of Bronchial Asthma: The Role of BiologicalsDocument12 pagesPharmacological Therapy of Bronchial Asthma: The Role of BiologicalsNia Satila ZariNo ratings yet
- FibrinogenDocument14 pagesFibrinogennthangbvcr10No ratings yet
- AbzymesDocument11 pagesAbzymesdeepali_m100% (1)
- The Correct Answer Is Highlighted Below: FeedbackDocument197 pagesThe Correct Answer Is Highlighted Below: Feedbackkibitokstephen1No ratings yet
- Treatment Options For MycobacterialDocument2 pagesTreatment Options For MycobacterialFalaq2No ratings yet
- BMC Medicine: Recent Developments in Alzheimer's Disease TherapeuticsDocument4 pagesBMC Medicine: Recent Developments in Alzheimer's Disease TherapeuticsneuronitasNo ratings yet
- Acute Phase ProteinsDocument4 pagesAcute Phase ProteinsAbhel CalderonNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Resistance and Clinical Use in Respiratory InfectionsDocument23 pagesAntimicrobial Resistance and Clinical Use in Respiratory InfectionsWamique IzharNo ratings yet
- In Silico Optimization of A Guava Antimicrobial Peptide Enables Combinatorial Exploration For Peptide DesignDocument12 pagesIn Silico Optimization of A Guava Antimicrobial Peptide Enables Combinatorial Exploration For Peptide DesignJPIAMR GrantNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Alergi - Rendra PS - Phosphodiesterase 4 Inhibitors in Allergic Rhinitis - 125114Document16 pagesJurnal Alergi - Rendra PS - Phosphodiesterase 4 Inhibitors in Allergic Rhinitis - 125114Anggoro SatrioNo ratings yet
- Mekanisme IVIGDocument4 pagesMekanisme IVIGRama JosuaNo ratings yet
- ANTIFUNGALS (Autosaved)Document72 pagesANTIFUNGALS (Autosaved)Franci Kay SichuNo ratings yet
- Ek PosterDocument1 pageEk Posterapi-295583705No ratings yet
- Ifosfamide PathwayDocument6 pagesIfosfamide PathwayDiana AhmadNo ratings yet
- John Curling BioPharm Sept 2002Document6 pagesJohn Curling BioPharm Sept 2002Haerus HaerussiaNo ratings yet
- Circrna - 09505 Worsens Swelling and Also Mutual Destruction Throughout Collagen-Induced Arthritis Mice Via Mir-6089/Akt1/Nf-B AxisDocument2 pagesCircrna - 09505 Worsens Swelling and Also Mutual Destruction Throughout Collagen-Induced Arthritis Mice Via Mir-6089/Akt1/Nf-B Axisbirthwave8No ratings yet
- Antimalarial Use in Managing COVID-19 in The Context of Glucose-6-Phosphate-Dehydrogenase G6PD Deficiency: A Mini ReviewDocument6 pagesAntimalarial Use in Managing COVID-19 in The Context of Glucose-6-Phosphate-Dehydrogenase G6PD Deficiency: A Mini Reviewnoordin othmanNo ratings yet
- Zoe Mclemore'S Research ProposalDocument10 pagesZoe Mclemore'S Research Proposalapi-746894400No ratings yet
- New Treatments For SLEDocument6 pagesNew Treatments For SLEzhulwaniezNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2214750018305328 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S2214750018305328 MainBladimir CentenoNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance: DR T. Aswani Ndonga MSC Tid I April 2010Document25 pagesMechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance: DR T. Aswani Ndonga MSC Tid I April 2010GAMING MONKEYNo ratings yet
- IFN yDocument1 pageIFN ytuuuiiitNo ratings yet
- Cep Halo Sporin SDocument51 pagesCep Halo Sporin Smonir61No ratings yet
- Laterality Affects Central Intergrated Regarding Baroreceptor Afferent Input Throughout Men and Women Sprague Dawley RatsighrxDocument2 pagesLaterality Affects Central Intergrated Regarding Baroreceptor Afferent Input Throughout Men and Women Sprague Dawley Ratsighrxheavencarbon7No ratings yet
- Sample First Aid 2016 RevisionsDocument20 pagesSample First Aid 2016 RevisionsFirst Aid/USMLE-Rx100% (2)
- Monoclonal AntibodyDocument3 pagesMonoclonal Antibodyhamzaasghar233No ratings yet
- Project ThesisDocument37 pagesProject ThesisAishu SampathNo ratings yet
- MTB DRUGS and RESISTANCE MECHANISMDocument24 pagesMTB DRUGS and RESISTANCE MECHANISMMINANI TheobaldNo ratings yet
- Immunology MendrosDocument51 pagesImmunology MendrosFrancisco NiegasNo ratings yet
- Anderson 2009Document13 pagesAnderson 2009Marcelo AlvesNo ratings yet
- The Continuous 7-Hour Intravenous Dexamethasone Suppression Test in The Differential Diagnosis of ACTH-dependent Cushing's SyndromeDocument6 pagesThe Continuous 7-Hour Intravenous Dexamethasone Suppression Test in The Differential Diagnosis of ACTH-dependent Cushing's SyndromeMarcelo AlvesNo ratings yet
- Flack 1992Document7 pagesFlack 1992Marcelo AlvesNo ratings yet
- Jama 269 17 035Document8 pagesJama 269 17 035Marcelo AlvesNo ratings yet