Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Neufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 34
Uploaded by
Lulus Prasetiyo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
55 views1 pageNeufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 34
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentNeufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 34
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
55 views1 pageNeufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 34
Uploaded by
Lulus PrasetiyoNeufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 34
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
20
areca: | O)oaan aes
© Cominued rasan: golden sseton
— ae
© spanation othe vate
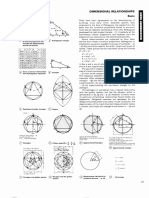
DIMENSIONAL RELATIONSHIPS
Application of Le Modulor
The architect Le Corbusier developed a theory of
Proportion, which Is based on the golden section and the
‘dimensions of the human body. The golden section of a
segment of line can be determined either geometrically or
by formulae. t means that a line segment can be divided so
that the whole of the line segment can be related toa bigger
dividing seqment, just as the larger isto the smaller +
Thats: 1 major
‘and shows the connection of proportional relationships
between the square, the cicie and the triangle (2)
The golden section of a line segment can also be
determined by a continued fraction
Gatel
6
This i the simplest unending regular continued fraction. Le
Corbusier marked out three intervals in the human body,
Which form a known golden section series according to
Fibonacci. These are between the foot, the solar plexus, the
hhead, the finger ofthe raised hand. First ofall Le Corbusier
started out from the knewn average height for Europeans
(1.75m pp. 16-17), which he divided up in accordance
with the golden section into 108.2 - 66.8 - 41.45 ~25.4em
4s this last dimension was almost exactly equal to 10
inches, he found in this way a connection withthe English
inch, although not for the larger dimensions. For this
reason, Le Corbusier changed over in 1947 to 6 English feet
(7.828m) as the height of the body. By golden. section
division he built the red row up and down =). As the stops
in this row are much too big for practical use, ho also but
Up a blue row, starting from 2.26m lie, the fingertips of the
raised hand, which gave double the values expressed in
the red row -- . The values ofthe red and blue rows were
converted by Le Corbusier into dimensions which were
Practically applicable.
You might also like
- Neufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 32Document1 pageNeufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 32Lulus PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Neufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 31Document1 pageNeufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 31Lulus PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Neufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 29Document1 pageNeufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 29Lulus PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Neufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 33Document1 pageNeufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 33Lulus PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Neufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 30Document1 pageNeufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 30Lulus PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Neufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 27Document1 pageNeufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 27Lulus PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Neufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 20Document1 pageNeufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 20Lulus Prasetiyo0% (1)
- Neufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 22Document1 pageNeufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 22Lulus PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Neufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 28Document1 pageNeufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 28Lulus PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Neufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 14 PDFDocument1 pageNeufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 14 PDFLulus PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Neufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 25Document1 pageNeufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 25Lulus PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Neufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 26Document1 pageNeufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 26Lulus PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Neufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 4Document1 pageNeufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 4Lulus Prasetiyo0% (1)
- Neufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 21Document1 pageNeufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 21Lulus PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Neufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 16Document1 pageNeufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 16Lulus PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Neufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 14 PDFDocument1 pageNeufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 14 PDFLulus PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Neufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 17Document1 pageNeufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 17Lulus PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Neufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 2Document1 pageNeufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 2Lulus PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Neufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 6Document1 pageNeufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 6Lulus PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Neufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 3Document1 pageNeufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 3Lulus PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Neufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 13Document1 pageNeufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 13Lulus PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Hasil PerhitunganDocument1 pageHasil PerhitunganLulus PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Neufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 7Document1 pageNeufert - Data Arsitek Jilid 3 7Lulus PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Denah PotDocument1 pageDenah PotLulus PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Typikal Jembatan PipaDocument10 pagesTypikal Jembatan PipaLulus PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- 8Document1 page8Lulus PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- ADENDUM DED Pemenuhan Air Baku Kab GroboganDocument19 pagesADENDUM DED Pemenuhan Air Baku Kab GroboganLulus PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- BA Format 12Document1 pageBA Format 12Lulus PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Permen PER 88-PB-2011 PDFDocument13 pagesPermen PER 88-PB-2011 PDFLulus PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)