100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote) 3K views4 pagesPedigree and Punnett Square Practice Answer Key
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content,
claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online on Scribd
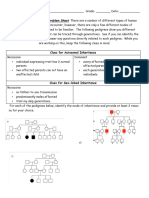
- Pedigree 1: Colorblindness
- Pedigree 2: Autosomal Dominant Disorder
- Punnett Square Practice
- Genetic Carrier and Disease Probability
S, vane LLY
_ Date:
, Anatomy & Physiology II
. Unit 4: Genetics
Pedigree and Punnett Square Practice
Pedigree 1
‘The pedigree below is for colorblindness (colorblind individuals are shaded). First, determine the
genotypes for persons 1-15, then answer the questions below.
Ok Oye
¥Ax8 | KAY were | x6
10 © &
© f] Oz
AKT KAY KEKE KY et x KAY
xey X°X" xy xex*
a. Explain how you determined the genotype of individual 3.
She does Not Naw Color blinavess, so she MUT Nave
Ot (ast ory dominant alleles Sinu she nad & Colovblind
SOM, ne oer Gilele mutt be Meuse, anu sins gtt thar
b. Yoni MMs Sau 3 Re aN eee individual 6, who is colorblind?
BHecaum He morrer (1) Va camer of the Culurblidnes
allele.
cc. Draw a punnett square showing how individuals 7 and 8 must have produced a colorblind daughter.
x’
4. Ifindividual 13 marries a man who is not colorblind, what is the probability that their sons will be
colorblind? Draw a punnett square.
A . .
ra XY ait of trae sons wint be
ex" | XY Calor bind.
Xe POC XY�Pedigree 2
‘The trait represented by the pedigree below is inherited as an autosomal dominant disorder. Shaded
individuals have the disorder. First, determine the genotypes for persons 1-10, then answer the questions
below.
@- 2
Aa | ha
aa
3L a she
aa} Aa Go| aaa
CT
Ont 3] ©
Ga ha OO aa
a. Are there any homozygous dominant individuals in the pedigree above? Explain.
No. Bath parents wold haw Dh naw i, ond ali
offspnoy would have “h haw tt
b. Ifindividuals 7 and 9 have children together, what is the probability of the disorder appearing?
e�‘Punnett Square Practice
For each of the following problems, draw a punnett square determine your answer.
1. A man with type O blood marries a woman with type AB blood. What are the odds they will have a
child with type A blood?
2, Aman with type A blood (whose parents had type A and type O blood) marries a woman with type O
blood. What are the odds they will have a child with type O blood?
A 0
I=] gy
0 {Ae
a�3. A woman who is a catrier for cystic fibrosis marries a man who does not have cystic fibrosis and is
homozygous dominant. What are they odds they will have a child with cystic fibrosis? What are the
‘odds they will have a child that is a cartier for the cystic fibrosis allele?
Ot W\ CF
By camer
4, A.45 year old woman leams she has Huntington’s disease. Her husband is $5 and does not show any
symptoms, and likely will not develop the disease. What are the odds that each of their 2 children will
develop the disease?
\