Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MScDCOM-Lec03v3 With Annotations
Uploaded by
Jai Gaizin0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesData Comms
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentData Comms
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesMScDCOM-Lec03v3 With Annotations
Uploaded by
Jai GaizinData Comms
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
OCSN/RMCS Data Communication &
Network Principles Section A 3
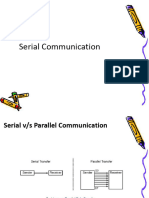
Parallel data transfer
Serial data transmission - asynchronous
Requires one
line per bit
(plus ground)
Requires
additional
timing signals,
e.g. clock or
strobe
Bit-serial transmission
Bit synchronisation
Character and frame synchronisation
Sections to read in Stallings's book
Chapter 6
Relevant sections in Halsalls book:
3.1, 3.2
Data Comm. & Net. Principles, Ed 3, D. Lauder
Section A 3, Page 1
Bit-serial data transmission
What timing information does the receiving
device require in order to decode and
interpret the data?
(Halsall Fig 3.2b)
Data Comm. & Net. Principles, Ed 3, D. Lauder
(Halsall Fig 3.2a)
Data Comm. & Net. Principles, Ed 3, D. Lauder
Section A 3, Page 2
Asynchronous transmission (stop/start bits)
What does asynchronous mean in this context?
(Halsall Fig 3.3)
Section A 3, Page 3
Data Comm. & Net. Principles, Ed 3, D. Lauder
Section A 3, Page 4
Asynchronous transmission principle of operation
Asynchronous transmission bit synchronisation timing principles
What values of N are normally used?
Does RxC need to be exactly equal to N*TxC?
How does the
receiver get
the RxC/N
signal into the
correct phase?
What is a
UART?
(Halsall Fig 3.5b)
(Halsall Fig 3.5a)
Data Comm. & Net. Principles, Ed 3, D. Lauder
Section A 3, Page 5
Asynchronous transmission bit synchronisation using 16 X receiver clock
Data Comm. & Net. Principles, Ed 3, D. Lauder
Section A 3, Page 6
Asynchronous transmission character and frame synchronisation
How is character synchronisation achieved?
(Halsall Fig 3.5c(iii))
Data Comm. & Net. Principles, Ed 3, D. Lauder
Section A 3, Page 7
(Halsall Fig 3.6a)
Data Comm. & Net. Principles, Ed 3, D. Lauder
Section A 3, Page 8
Asynchronous transmission frame synchronisation with 8 bit binary data
What happens if data is not printable ASCII?
(Halsall Fig 3.6b)
Data Comm. & Net. Principles, Ed 3, D. Lauder
Section A 3, Page 9
You might also like
- MScDCOM-Lec02v3 With AnnotationsDocument2 pagesMScDCOM-Lec02v3 With AnnotationsJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- William Stallings Data and Computer Communications 7th Edition Asynchronous and Synchronous TransmissionDocument6 pagesWilliam Stallings Data and Computer Communications 7th Edition Asynchronous and Synchronous TransmissionKrishna KanthNo ratings yet
- M2L5Document12 pagesM2L5YT PremoneNo ratings yet
- Serial Communication Buses: CLK Data OutDocument2 pagesSerial Communication Buses: CLK Data OutAkshay BaswantNo ratings yet
- MScDCOM-Lec05v2 With AnnotationsDocument3 pagesMScDCOM-Lec05v2 With AnnotationsJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- Serial CommunicationsDocument23 pagesSerial CommunicationsPhuoc Trung Tran100% (1)
- Case Study 4Document2 pagesCase Study 4Chirry OoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Serial Interfacing With Microprocessor Based SystemDocument28 pagesChapter 3 - Serial Interfacing With Microprocessor Based SystemAarav PoudelNo ratings yet
- Data and Computer CommunicationsDocument17 pagesData and Computer CommunicationsED GuzNo ratings yet
- SyncE and IEEE 1588Document16 pagesSyncE and IEEE 1588Vijay Agrahari100% (1)
- Serial One 20Document18 pagesSerial One 20dominique fortierNo ratings yet
- Synce and Ieee 1588Document16 pagesSynce and Ieee 1588simog1972No ratings yet
- Serial I-O For 8051: 1 MotivationDocument10 pagesSerial I-O For 8051: 1 MotivationArjun V PrasanthanNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous Data Transfer: Serial Transmission ModesDocument9 pagesAsynchronous Data Transfer: Serial Transmission ModesAslam PervaizNo ratings yet
- 06 DigitalDataCommDocument17 pages06 DigitalDataCommapi-3706794No ratings yet
- RQ 3 PDFDocument58 pagesRQ 3 PDFHải NamNo ratings yet
- Sci Lecture: Dung Nguyen Joseph Glasofer Alan CarrDocument32 pagesSci Lecture: Dung Nguyen Joseph Glasofer Alan Carrhriday_rocksNo ratings yet
- ROI PAC DocDocument63 pagesROI PAC DocRayner De RuytNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Serial Interfacing With Microprocessor Based SystemDocument28 pagesChapter 3 - Serial Interfacing With Microprocessor Based SystemSuroj BurlakotiNo ratings yet
- Multi Level, Multi Transition & Block CodesDocument31 pagesMulti Level, Multi Transition & Block CodesJomariNo ratings yet
- William Stallings Data and Computer CommunicationsDocument26 pagesWilliam Stallings Data and Computer CommunicationsBagus FatkhurroziNo ratings yet
- # cs425 - SlidesDocument96 pages# cs425 - SlidesAbhishek AnandNo ratings yet
- Data Communication InterfaceDocument6 pagesData Communication InterfacejcastroindigoNo ratings yet
- Basic Network Evaluation ParametersDocument42 pagesBasic Network Evaluation ParametersacajahuaringaNo ratings yet
- White Paper: Technical ContactDocument4 pagesWhite Paper: Technical ContactAlex Yang100% (1)
- Ardu CodeDocument41 pagesArdu CodeFahmida IkramNo ratings yet
- Devasi Sir SerialDocument18 pagesDevasi Sir Serialforloginusethis accountNo ratings yet
- Drdo - QuestionsDocument13 pagesDrdo - Questionssaroj4studyNo ratings yet
- 24.1 A 12.5Gb/S Serdes in 65Nm Cmos Using A Baud-Rate Adc With Digital Receiver Equalization and Clock RecoveryDocument3 pages24.1 A 12.5Gb/S Serdes in 65Nm Cmos Using A Baud-Rate Adc With Digital Receiver Equalization and Clock Recoveryapi-127299018No ratings yet
- WE Project Report Moiz, AliDocument17 pagesWE Project Report Moiz, AliMoiz HussainNo ratings yet
- Clock Distribution: Rajeev MurgaiDocument26 pagesClock Distribution: Rajeev MurgaiDmitry LeyzerovichNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks and Internets, 5E by Douglas E. Comer: Lecture Powerpoints Adapted From The NotesDocument54 pagesComputer Networks and Internets, 5E by Douglas E. Comer: Lecture Powerpoints Adapted From The NotessukoraliNo ratings yet
- MN 12 Routing Protocols For Adhoc Networks 12-38 SlidesDocument50 pagesMN 12 Routing Protocols For Adhoc Networks 12-38 SlidesZargham KhanNo ratings yet
- A Synthesisable Quasi-Delay Insensitive Result Forwarding Unit For An Asynchronous ProcessorDocument8 pagesA Synthesisable Quasi-Delay Insensitive Result Forwarding Unit For An Asynchronous ProcessorHoogahNo ratings yet
- Data Transfer Between Asynchronous Clock DomainsDocument10 pagesData Transfer Between Asynchronous Clock DomainsShiva ShankarNo ratings yet
- Overcoming Signal Integrity Channel Modeling Issues Rev2 With FiguresDocument10 pagesOvercoming Signal Integrity Channel Modeling Issues Rev2 With FiguresJohn BaprawskiNo ratings yet
- Y Yyyy Y Y Yyyy Y Yyyyyy Yy Yyyy Yyyyyyyy Y YDocument5 pagesY Yyyy Y Y Yyyy Y Yyyyyy Yy Yyyy Yyyyyyyy Y YintelmasterNo ratings yet
- GIS Unit 2Document25 pagesGIS Unit 233 ABHISHEK WAGHNo ratings yet
- Sar Image FormationDocument15 pagesSar Image FormationMusyarofah HanafiNo ratings yet
- Global Institute of Technology Exam SolutionsDocument33 pagesGlobal Institute of Technology Exam SolutionsprashantvlsiNo ratings yet
- GIS Data StructuresDocument48 pagesGIS Data Structureskrish_mplNo ratings yet
- Unit-V Communication Interface Basics of Serial CommunicationDocument16 pagesUnit-V Communication Interface Basics of Serial CommunicationTechnoGateKhammamNo ratings yet
- Serial Communication Guide: Serial vs Parallel Transfer ModesDocument16 pagesSerial Communication Guide: Serial vs Parallel Transfer ModesM.k. JhaNo ratings yet
- 2020 CoE2DX4 W8Document38 pages2020 CoE2DX4 W8Shahram ShiraniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document26 pagesChapter 6Jason DelumenNo ratings yet
- Main Techniques and Performance of Each CompressionDocument23 pagesMain Techniques and Performance of Each CompressionRizki AzkaNo ratings yet
- Data Com HW4 MaykieDocument3 pagesData Com HW4 MaykieMaykie W.A.100% (1)
- Multiplexing and Multiple AccessDocument15 pagesMultiplexing and Multiple AccessAaron Ursal AquinoNo ratings yet
- CCN Lec8 9Document40 pagesCCN Lec8 9Aroosa JavedNo ratings yet
- TDC462 Data Communications Homework 3, Due July 15, 2002 Monday 5:59:59 PM Jeff AbsherDocument2 pagesTDC462 Data Communications Homework 3, Due July 15, 2002 Monday 5:59:59 PM Jeff Abshersaraalazazy343No ratings yet
- 3D Geometry Loading in Promax, A Practical Crperl ExampleDocument13 pages3D Geometry Loading in Promax, A Practical Crperl Exampleprouserdesigner77No ratings yet
- hwk3 F 11 3 Sol 2Document8 pageshwk3 F 11 3 Sol 2Min LiNo ratings yet
- MCQ - Optical communication standards and protocolsDocument20 pagesMCQ - Optical communication standards and protocolsFia TerryNo ratings yet
- Spectral Content of NRZ Test PatternsDocument5 pagesSpectral Content of NRZ Test PatternsRohan RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Clustering Data Streams: Chun Wei Dept Computer & Information Technology Advisor: Dr. SpragueDocument19 pagesClustering Data Streams: Chun Wei Dept Computer & Information Technology Advisor: Dr. SpragueYienah JinNo ratings yet
- Serial I-O For 8051: 1 MotivationDocument10 pagesSerial I-O For 8051: 1 MotivationParmanand KhajuriyaNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous Asynchronous Transfer Mode Transfer Mode (ATM) (ATM)Document55 pagesAsynchronous Asynchronous Transfer Mode Transfer Mode (ATM) (ATM)Chandan BangeraNo ratings yet
- Serial Data Transfer FundamentalsDocument16 pagesSerial Data Transfer Fundamentalssreekantha2013No ratings yet
- Clockless Chips: Overcoming Limitations of Synchronous DesignDocument17 pagesClockless Chips: Overcoming Limitations of Synchronous DesignMandeep SainiNo ratings yet
- Evaluate Link Grammar AI FrameworkDocument2 pagesEvaluate Link Grammar AI FrameworkJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- Course WorkDocument2 pagesCourse WorkJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- NLP Week 2 Rationalist and Empiricist Paradigms in Natural Language ProcessingDocument28 pagesNLP Week 2 Rationalist and Empiricist Paradigms in Natural Language ProcessingJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- DAI Week1Document6 pagesDAI Week1Jai GaizinNo ratings yet
- Link IntroDocument12 pagesLink IntroJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document46 pagesLecture 1Jai GaizinNo ratings yet
- DAI Week3Document16 pagesDAI Week3Jai GaizinNo ratings yet
- Link ReferenceDocument12 pagesLink ReferenceJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- DAI Week3Document16 pagesDAI Week3Jai GaizinNo ratings yet
- DAI Week3Document6 pagesDAI Week3Jai GaizinNo ratings yet
- DAI Week1Document12 pagesDAI Week1Jai GaizinNo ratings yet
- DAI Week2Document7 pagesDAI Week2Jai GaizinNo ratings yet
- PSTN-PCM Coding and Data Communication PrinciplesDocument7 pagesPSTN-PCM Coding and Data Communication PrinciplesJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- MScDCOM-Lec09v3 With AnnotationsDocument6 pagesMScDCOM-Lec09v3 With AnnotationsJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- MScDCOM-Lec06v2 With AnnotationsDocument5 pagesMScDCOM-Lec06v2 With AnnotationsJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- MScDCOM-Lec04v3 With AnnotationsDocument4 pagesMScDCOM-Lec04v3 With AnnotationsJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- MScDCOM-Lec07v2 With AnnotationsDocument5 pagesMScDCOM-Lec07v2 With AnnotationsJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- MScDCOM-Lec01V3 With AnnotationsDocument4 pagesMScDCOM-Lec01V3 With AnnotationsJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- 11 Detailed DesignDocument6 pages11 Detailed DesignJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- ISAD Tutorial ERM Week7Document1 pageISAD Tutorial ERM Week7Jai GaizinNo ratings yet
- Linear Motion4Document9 pagesLinear Motion4Jai GaizinNo ratings yet
- Access Commands - Accessible From The Help' Menu: Input MaskDocument6 pagesAccess Commands - Accessible From The Help' Menu: Input MaskJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- Exam 02-03Document3 pagesExam 02-03Jai GaizinNo ratings yet
- 10 System DesignDocument5 pages10 System DesignJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- 12 PrototypingDocument1 page12 PrototypingJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- Linear EqnDocument6 pagesLinear EqnJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- 12 PrototypingDocument1 page12 PrototypingJai GaizinNo ratings yet