Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9300 Quick Start Guide
9300 Quick Start Guide
Uploaded by
Juan PerezCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
9300 Quick Start Guide
9300 Quick Start Guide
Uploaded by
Juan PerezCopyright:
Available Formats
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
V100R006C00
Quick Start - SPU
Issue
01
Date
2011-09-30
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2011. All rights reserved.
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written
consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks and Permissions
and other Huawei trademarks are trademarks of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks and trade names mentioned in this document are the property of their respective holders.
Notice
The purchased products, services and features are stipulated by the contract made between Huawei and the
customer. All or part of the products, services and features described in this document may not be within the
purchase scope or the usage scope. Unless otherwise specified in the contract, all statements, information,
and recommendations in this document are provided "AS IS" without warranties, guarantees or representations
of any kind, either express or implied.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every effort has been made in the
preparation of this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but all statements, information, and
recommendations in this document do not constitute the warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Address:
Huawei Industrial Base
Bantian, Longgang
Shenzhen 518129
People's Republic of China
Website:
http://www.huawei.com
Email:
support@huawei.com
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
About This Document
About This Document
Versions
The following table provides the mapping between versions.
Table 1 Mapping between VASP version and S9300 version
VASP
S9300
Remarks
VASP
V100R003C01
S9300 V100R006C00
Intended Audience
This document is intended for:
l
Hardware installation engineers
Commissioning engineers
On-site maintenance engineers
System maintenance engineers
Symbol Conventions
The symbols that may be found in this document are defined as follows.
Symbol
Description
DANGER
WARNING
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Indicates a hazard with a high level of risk, which if not
avoided, will result in death or serious injury.
Indicates a hazard with a medium or low level of risk, which
if not avoided, could result in minor or moderate injury.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
ii
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
Symbol
About This Document
Description
CAUTION
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation, which if not
avoided, could result in equipment damage, data loss,
performance degradation, or unexpected results.
TIP
Indicates a tip that may help you solve a problem or save
time.
NOTE
Provides additional information to emphasize or supplement
important points of the main text.
Change History
Updates between document issues are cumulative. Therefore, the latest document issue contains
all updates made in previous issues.
Changes in Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Initial commercial release.
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
iii
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
Contents
Contents
About This Document.....................................................................................................................ii
1 Overview of the SPU.....................................................................................................................1
1.1 Introduction to the SPU......................................................................................................................................2
1.2 Functions and Typical Applications of the SPU................................................................................................2
2 Hardware Structure of the SPU................................................................................................12
2.1 Panel.................................................................................................................................................................13
2.2 Description of Interfaces on the SPU...............................................................................................................14
2.3 Attributes of Interfaces on the SPU..................................................................................................................14
2.4 Technical Specifications...................................................................................................................................15
3 Logging In to the SPU.................................................................................................................16
3.1 Logging In to the SPU Through the Console Interface....................................................................................17
3.2 Logging In to the SPU Through the Console Interface of the SPU That Is Redirected from MPU.................20
3.3 Logging In to the SPU Through Telnet............................................................................................................21
4 Service Features of the SPU.......................................................................................................25
5 Replacing an SPU........................................................................................................................29
6 Technical Specifications of the SPU........................................................................................32
6.1 System Configurations of the SPU...................................................................................................................33
6.2 Technical Specifications of the SPU................................................................................................................33
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
iv
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
1 Overview of the SPU
Overview of the SPU
About This Chapter
Functioning as the value-added service (VAS) board of the S9300, the Service Process Unit
(SPU) provides service functions such as load balancing, firewalls, Network Address Translation
(NAT), IP Security (IPSec), NetStream,and Wireless Local Area Network(WLAN) thus meeting
requirements of different application scenarios for diverse industry networks.
1.1 Introduction to the SPU
The SPU provides service functions such as load balancing, firewalls, NAT, IPSec,
NetStream,WLAN in diverse network application scenarios. These functions are mainly used
on industry networks.
1.2 Functions and Typical Applications of the SPU
The SPU can be installed in any LPU slot of the S9300 to process the packets that are transmitted
from the MPU of the S9300. The SPU is applicable to load balancing, NAT, firewall, IPSec,
NetSream and WLAN solutions.
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
1 Overview of the SPU
1.1 Introduction to the SPU
The SPU provides service functions such as load balancing, firewalls, NAT, IPSec,
NetStream,WLAN in diverse network application scenarios. These functions are mainly used
on industry networks.
In modern enterprises, video conferences and video monitoring devices are widely used; shared
files such as pictures and high-definition video files are transmitted on intranets; servers and
storage devices need to back up data periodically. With the preceding requirements of
enterprises, people have higher requirements for the reliability, security, and simplified operation
and management of industry networks.
As the VAS unit of the S9300, the SPU provides diverse VAS functions for industry networks,
such as load balancing, IPSec VPN, NAT, firewalls, NetStream,WLAN and two-node cluster
backup. In addition, the SPU provides solutions to network security of communities,
interconnection between communities, and wireless local area networks (WLANs). The SPU
provides the high-efficient load balancing solution, which accelerates the response speed of the
IT system, shortens the application delay, and balances the traffic on network devices. Service
reliability is improved and services can be expanded flexibly. Multiple firewalls and the IPSec
VPN facilitate integration of the VLAN switching technology of switches with security network
technologies, providing security services and implementing the secure and encrypted interaction
among departments of customers. NetStream provides data support for charging and settlement,
network planning, and network operation and management for most carriers. WLAN increases
network construction flexibility and terminal mobility.
1.2 Functions and Typical Applications of the SPU
The SPU can be installed in any LPU slot of the S9300 to process the packets that are transmitted
from the MPU of the S9300. The SPU is applicable to load balancing, NAT, firewall, IPSec,
NetSream and WLAN solutions.
Currently, the SPU supports only one board, namely, VAMPA, which is installed in the LPU
slot of the S9300. The system transmits the packets to be processed to the SPU. Then the SPU
processes the packets related to the VASs. Figure 1-1 shows the processing procedure.
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
1 Overview of the SPU
Figure 1-1 Processing packets by the SPU
Receiving Transmitting
Packets
Packets
LPU
Switching Packets
MPU
Processing Packets
SPU
The VAMPA provides the following functions:
l
Service functions
IPSec VPN, firewall/NAT, load balancing, NetStream and WLAN
Data processing capability of 10 Gbit/s
Routing and addressing for packets
Traffic management, congestion control, and forwarding scheduling for packets
Line-speed forwarding of packets
Debugging functions
Configuration and alarm
Board environment monitoring
Watchdog
Hierarchical reset
Commissioning
The SPU is applicable to the following solutions.
Load Balancing
l
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Server load balancing
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
1 Overview of the SPU
Figure 1-2 Networking of server load balancing
Intranet
Intranet
User
ServerA
Switch
External
Network
ServerB
ServerC
As shown in Figure 1-2, an Intranet user accesses the internal server that is deployed in
the group of load balancing servers through the external network. The group is composed
of three servers. As the load balancing (LB) device, the Switch implements load balancing
at layers from L4 to L7. The service load varies according to servers. When one or more
servers are faulty, the system automatically switches services to normal servers so that
services are not interrupted. In this manner, network faults are reduced and the reliability
of service processing is improved.
l
Egress link load balancing
Figure 1-3 Networking of egress link load balancing
RouterA
ISP1
External
Network
Intranet
user
Switch
RouterB
ISP2
As shown in Figure 1-3, an enterprise rents links of multiple carriers as egresses between
the Intranet and the external network. The bandwidth and delay vary according to carriers.
You can configure the Switch (SPU) to select the optimal link according to requirements
for external network access of different enterprise users. The Switch also supports the
reverse NAT function.
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
1 Overview of the SPU
IPSec
Figure 1-4 Networking of IPSec
SwitchA
SwitchB
Internet
Intranet
User A
Intranet
User B
As shown in Figure 1-4, an IPSec tunnel is set up between Switch A and Switch B. In this way,
data flows of intranet user A and intranet user B can be protected when being transmitted on
insecure networks. IPSec allows network users or administrators to control the granularity of
security services between peers. The Security Association (SA) can be established manually or
in IKE negotiation mode. The SA provides security protection for different data flows.
NAT
Figure 1-5 Networking of NAT
Internet
Intranet
10.1.1.1/24
PC2
PC1
10.1.2.1/24
WWW
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
FTP
SMTP
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
1 Overview of the SPU
As shown in Figure 1-5, IP addresses of PC1 and PC2 on the intranet can be mapped to the
public IP addresses on the external network through NAT. In this way, users on private networks
can access external networks, thus saving public IP addresses. The NAT mapping table is used
to limit hosts on internal networks that access hosts on external networks.
By configuring the internal servers, you can map the corresponding external IP addresses and
port numbers to internal servers. In this manner, users on external networks can access internal
servers. For example, an enterprise provides World Wide Web (WWW), File Transfer Protocol
(FTP), and Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) services externally.
Firewall
l
Virtual firewall
Figure 1-6 Networking of the virtual firewall
Internet
Switch
VLAN2
Interior
Subnetwork
VLAN3
VLAN4
Interior
Subnetwork
FTP
Server
Interior
Subnetwork
WWW
Server
Telnet
Server
As shown in Figure 1-6, an intranet can be divided into multiple subnets through VLANs.
The Switch (SPU) configures a virtual firewall for each subnet. The server on each subnet
can access external networks through the Switch and provide different services externally.
l
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Firewall in transparent mode
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
1 Overview of the SPU
Figure 1-7 Networking of the firewall in transparent mode
PC A
Zone A
VLAN 10
PC B
Switch
VLAN 20
Zone B
VLAN 30
PC C
Zone C
As shown in Figure 1-7, the Switch functions as the firewall in transparent mode. In this
case, all interfaces are L2 interfaces and the network is divided into multiple access zones
through different VLANs. All PCs in a zone share the same network segment. The packet
filtering, attack defense, and traffic monitoring policies are defined for different VLANs
on the Switch. For example, PC A can access Zone B and Zone C. PC B can send packets,
whereas the packets cannot pass the firewall.
l
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Firewalls in backup mode
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
1 Overview of the SPU
Figure 1-8 Networking of firewalls in backup mode
SPU1
SPU2
Internet
Switch
PC 1
PC 2
As shown in Figure 1-8, SPU 1 and SPU 2 are installed on the Switch. VRRP is enabled
on these two SPUs to provide a virtual IP address for the switch and thus to back up services.
When SPU 1 functions as the master, data flows are transmitted to the Internet through
SPU 1. At the same time, data is synchronized from SPU 1 to SPU 2. After SPU 1 becomes
faulty, data flows are transmitted to the Internet through SPU 2.
NetStream
l
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Monitoring MPLS network traffic
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
1 Overview of the SPU
Figure 1-9 Monitoring MPLS network traffic
PE
AS 200
P
Web Server
Mail Server
PE
PE
PE
FTP Server
AS 100
NSC&NDA
PE
PE
PC
PC
PC
As shown in Figure 1-9, users can collect statistics on IP traffic from MPLS to IP (IPv4
or IPv6) and from IP (IPv4 or IPv6) to MPLS by deploying NetStream on user-side
interfaces of PEs. Users can also collect statistics on MPLS packets by deploying NetStream
on network-side interfaces of PEs and P devices. According to the analysis result of the
statistics, users can understand the composition and mode of the MPLS service accurately.
l
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Monitoring traffic carried by a tunnel
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
1 Overview of the SPU
Figure 1-10 Monitoring traffic carried by a tunnel
Web Server
Mail Server
AS 100
FTP Server
Tunnel
AS 100
NSC&NDA
PC
PC
PC
As shown in Figure 1-10, if a user collects statistics on the traffic transmitted through a
tunnel on physical interfaces of the switch, the user cannot differentiate the traffic carried
by the tunnel. In this case, the user needs to collect traffic statistics by using NetStream
twice, that is, before the traffic enters the tunnel and after the traffic exits the tunnel. In this
way, the user can accurately analyze the traffic composition in the tunnel.
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
10
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
1 Overview of the SPU
WLAN
Figure 1-11 WLAN network
IP backbone
NMS
RADIUS server
BAS
MAN aggregate
network
Aggregate switch
AC
AC
Access switch
AP
AP
AP
Figure 1-11 shows the networking mode of (AC+fit AP). Data traffic sent from wireless stations
to the Internet is transmitted over two types of media: wireless links between the wireless stations
and APs and wired links between APs and ACs. WLAN uses the wireless technology to
implement fast Ethernet access. It allows terminals, such as computers, to access a network
through a wireless medium but not a physical cable. This facilitates network construction and
allows users to move around without interrupting communication.
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
11
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
2 Hardware Structure of the SPU
Hardware Structure of the SPU
About This Chapter
This topic describes hardware information about the VAMPA. Currently, the SPU supports only
the VAMPA.
2.1 Panel
This topic describes the appearance of the SPU, including interfaces, indicators and the colors
and blinking states of interface and board indicators.
2.2 Description of Interfaces on the SPU
This topic describes types, quantity, and functions of interfaces on the SPU.
2.3 Attributes of Interfaces on the SPU
This topic describes connector types, attributes, operation modes, and compliance standards of
the interfaces on the panel.
2.4 Technical Specifications
This topic describes technical specifications of the SPU, such as board dimensions, panel
dimensions, maximum power consumption, and weight.
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
12
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
2 Hardware Structure of the SPU
2.1 Panel
This topic describes the appearance of the SPU, including interfaces, indicators and the colors
and blinking states of interface and board indicators.
Currently, the SPU supports only the VAMPA.
The VAMPA is installed horizontally. A serial interface (identified as CON) and an FE electrical
interface (identified as ETH) are located on the panel. Figure 2-1 shows the panel.
Figure 2-1 VAMPA panel
1. ACT indicator
2. LINK indicator
The board indicator RUN/ALM and interface indicators ACT and LINK are located on the
VAMPA panel. Table 2-1 describes the colors and blinking states of the indicators.
Table 2-1 Buttons and indicators on the VAMPA panel
Indicator/Button
Color
Description
RUN/ALM
Green
If the indicator is on, it indicates that the board is
powered on but the software is not running.
If the indicator blinks slowly (0.5 Hz), it indicates
that the system runs normally.
If the indicator blinks quickly (4 Hz), it indicates that
the system is being started.
ACT
Red
If the indicator is on, it indicates that the board is
faulty.
Orange
If the indicator is on, it indicates that the board is
installed in the slot and is powered on.
Amber
If the indicator blinks, it indicates that data is being
transmitted or received.
If the indicator is off, it indicates that no data is being
transmitted or received.
LINK
Green-yellow
If the indicator is on, it indicates that the link is
connected.
If the indicator is off, it indicates that the link is
blocked.
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
13
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
2 Hardware Structure of the SPU
NOTE
There are two labels on the SPU board:
l 03020RRN: indicates the BBOM or SBOM of the board.
l 781DBAA383F0-F2(3): indicates that there are three MAC addresses on the front panel of the board.
Each board has two XGE interfaces, and each XGE interface has a MAC address. In addition, the
management interface has a MAC address.
2.2 Description of Interfaces on the SPU
This topic describes types, quantity, and functions of interfaces on the SPU.
Table 2-2 describes types and functions of interfaces on the VAMPA.
Table 2-2 Interfaces on the VAMPA and their functions
Interface
Quantity
Description
Console interface
Provides a serial interface. A user can log in to the local
SPU by connecting the serial interface on the host and
the console interface on the SPU through a cable to
configure the SPU locally.
Ethernet interface
Provides an FE electrical interface. A user can log in to
the SPU through Telnet to configure the SPU.
2.3 Attributes of Interfaces on the SPU
This topic describes connector types, attributes, operation modes, and compliance standards of
the interfaces on the panel.
Table 2-3 and Table 2-4 describe attributes of the interfaces on the panel.
Table 2-3 Serial interface attributes
Attribute
Description
Connector type
RJ45
Interface attribute
RS232
Compliance standard
EIA/TIA-232
Table 2-4 Ethernet interface attributes
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Attribute
Description
Connector type
RJ45
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
14
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
2 Hardware Structure of the SPU
Attribute
Description
Interface attribute
10BASE-T/100BASE-TX
Operation mode
Full duplex
Compliance standard
IEEE 802.3
2.4 Technical Specifications
This topic describes technical specifications of the SPU, such as board dimensions, panel
dimensions, maximum power consumption, and weight.
Table 2-5 describes technical specifications of the VAMPA.
Table 2-5 Technical specifications of the VAMPA
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Parameter
Description
Board dimensions
426.80 mm x 394.70 mm x 35.10 mm (width
x depth x height)
Maximum power consumption
153.27 w
Board weight
2.6 kg
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
15
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
3 Logging In to the SPU
Logging In to the SPU
About This Chapter
A user can log in to the SPU in either of the following ways: logging in to the SPU through the
console interface; logging in to the SPU through Telnet; logging in to the MPU of the S9300 for
redirection, and then logging in to the SPU through the console interface of the SPU.
3.1 Logging In to the SPU Through the Console Interface
If a user cannot log in to the MPU of the S9300, the user needs to log in to the SPU through the
console interface for the first time. This topic describes how to log in to the SPU on a PC through
the console interface.
3.2 Logging In to the SPU Through the Console Interface of the SPU That Is Redirected from
MPU
If a user has logged in to the MPU of the S9300, the user can log in to the SPU after redirection
to the console interface of the SPU.
3.3 Logging In to the SPU Through Telnet
This topic describes how to log in to the SPU through Telnet.
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
16
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
3 Logging In to the SPU
3.1 Logging In to the SPU Through the Console Interface
If a user cannot log in to the MPU of the S9300, the user needs to log in to the SPU through the
console interface for the first time. This topic describes how to log in to the SPU on a PC through
the console interface.
Networking Requirements
When logging in to the SPU through the console interface, a user needs to connect the console
interface on the SPU to the RS232 interface on the host through a serial cable, as shown in
Figure 3-1.
Figure 3-1 Logging in to the SPU through the console interface
RS232
interface
Console Cable
Console
interface
Procedure
Step 1 Connect the PC with the SPU through a serial cable according to Figure 3-1.
Step 2 Enable the HyperTerminal on the PC.
Choose Start > All Programs > Accessories > Communications > HyperTerminal to start
the HyperTerminal.
Step 3 Set up a new connection.
As shown in Figure 3-2, enter the name of the new connection in the Name text box and choose
an icon. Click OK.
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
17
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
3 Logging In to the SPU
Figure 3-2 Setting up a new connection
Step 4 Configure the connected interface.
In the Connect window shown in Figure 3-3, select an interface from the Connect drop-down
list box according to the interface on the PC or terminal. Then click OK.
Figure 3-3 Configuring the connected interface
Step 5 Set communication parameters.
In the COM1 Properties window shown in Figure 3-4, set communication parameters
according to Table 3-1.
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
18
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
3 Logging In to the SPU
NOTE
In the Windows operating systems of some versions, Bit per second may be called Baud rate and Flow
control may be called Traffic control.
Figure 3-4 Setting communication parameters
Table 3-1 Communication parameters
Parameter
Value
Bit per second (baud)
9600
Data bit
Parity check
None
Stop bit
Flow control (traffic control)
None
Step 6 After starting the HyperTerminal, choose File > Attributes to display the COMM1
Properties dialog box, as shown in Figure 3-5. Click the Settings tab, and select Auto detect
or VT100 from the Emulation drop-down list box. Click OK to complete the settings.
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
19
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
3 Logging In to the SPU
Figure 3-5 Selecting a terminal type
After the preceding settings, press Enter. If the <Quidway> prompt is displayed, it indicates
that you have logged in to the SPU. In this case, you can enter commands to configure or manage
the SPU.
----End
3.2 Logging In to the SPU Through the Console Interface of
the SPU That Is Redirected from MPU
If a user has logged in to the MPU of the S9300, the user can log in to the SPU after redirection
to the console interface of the SPU.
Networking Requirements
A user can log in to the MPU of the S9300 through a serial interface or through Telnet, and then
run the corresponding command for redirection. Then the user redirects the login process to the
console interface of the SPU as prompted and logs in to the SPU through the console interface,
as shown in Figure 3-6.
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
20
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
3 Logging In to the SPU
Figure 3-6 Networking of redirecting to the console interface of the SPU through the MPU of
the S9300
Login
PC
Redirection
Console
interface of
the SPU
S9300
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to the MPU of the S9300.
Step 2 Run the following command in the user view: spu connect slot slot-num.
slot-num indicates the number of the slot where the SPU is installed on the S9300.
The following message is displayed:
******************************************************
*
Slot 2 output to mainboard
*
******************************************************
Press Ctrl+D to quit
Step 3 Press Enter. The system displays the following information:
The console can not be used now, pleae press Ctrl+Y.
Press Ctrl+Y. The system redirects you to the serial interface of the SPU so that you can log in
to the SPU.
NOTE
To return to the MPU of the S9300, press Ctrl+D.
The serial interface of the SPU can be used as:
l Ingress for redirecting to the SPU from the MPU of the S9300
l Ingress for logging in to the SPU
You can press Ctrl+Y to switch the roles of the serial interface on the SPU. The serial interface can be
function as either the ingress for redirecting to the SPU from the MPU of the S9300 or the ingress for
logging in to the SPU .
To log in to the SPU on the backup switch in a cluster, run the local-telnet command on the master switch's
MPU to log in to the backup switch, and then run the spu connect command to log in to the SPU.
----End
3.3 Logging In to the SPU Through Telnet
This topic describes how to log in to the SPU through Telnet.
Networking Requirements
Telnet supports local and remote login, facilitating maintenance. After setting the Telnet user
of the SPU, a user can log in to the SPU through Telnet from the Ethernet interface or service
interfaces such as XGE sub-interface or the Eth-Trunk sub-interface whose member interfaces
are XGE interfaces, as shown in Figure 3-7.
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
21
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
3 Logging In to the SPU
Figure 3-7 Logging in to the SPU through Telnet on the PC
PC
STC
SPU
PC
Crossover
cable
STC
HUB
PC
STC
Crossover
cable or
optical fiber
SPU
SPU
L2 Switch
NOTE
The SPU is a board installed on the S9300. Generally, the ETH port of the SPU is not used to connect to
the network; therefore, the service interface of the SPU is usually used for logging in to the SPU through
Telnet.
In this way, you can configure the user name and password of the Telnet user on the SPU. The
method for configuring a Telnet user on the SPU is the same as that for configuring a Telnet
user on the S9300. For details, see the Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch Configuration
Guide - Basic Configuration.
If you do not configure the Telnet user on the SPU, the user name and password are absent for
the first login through Telnet.
Procedure
Step 1 Set the IP address of the Ethernet interface of the SPU.
You can log in to the SPU by using the following methods:
l Using the console port of the SPU
l Redirecting to the SPU from the S9300
After logging in to the SPU, do as follows:
l Assign an IP address to the ETH port.
1.
Run the system-view command to enter the system view.
2.
Run the interface interface-type interface-number command to enter the interface view.
Here, Ethernet 0/0/0 is used.
3.
Run the ip address ip-address { mask | mask-length } command to set the IP address
of the interface.
l Assign an IP address to the service interface.
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
22
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
3 Logging In to the SPU
The service interface of the SPU is the Eth-Trunk sub-interface whose member interfaces
are XGE interfaces or the XGE sub-interface. The configuration methods of the Eth-Trunk
interface and the XGE sub-interface are different. The details are as follows:
Assign an IP address to the XGE sub-interface.
1.
Run the system-view command to enter the system view.
2.
Run the interface xgigabitethernet interface-number.subinterface-number
command to enter the XGE sub-interface view.
3.
Run the ip address ip-address { mask | mask-length } [ sub ] command to assign an
IP address to the XGE sub-interface.
Assign an IP address to the Eth-Trunk sub-interface whose member interfaces are XGE
interfaces.
1.
Run the system-view command to enter the system view.
2.
Run the interface eth-trunk trunk-id command to enter the Eth-Trunk interface
view.
3.
Run the trunkport xgigabitethernet { interface-number1 [ to interfacenumber2 ] } &<1-8> command to add two virtual interfaces of the SPU to the EthTrunk interface to complete link aggregation.
4.
Run the quit command to exit the Eth-Trunk interface view.
5.
Run the interface eth-trunk trunk-id.subtrunk-id command to enter the Eth-Trunk
sub-interface view.
6.
Run the ip address ip-address { mask | mask-length } [ sub ] command to assign an
IP address to the Eth-Trunk sub-interface.
Step 2 Log in to the SPU through Telnet.
A user can log in to the SPU on the local PC or terminal through Telnet.
1.
Open the Command Prompt window on the PC.
Choose Start > Programs > Accessories > Command Prompt. The Command
Prompt window is displayed.
The Command Prompt window displays the following messages:
Microsoft Windows XP [version 5.1.2600]
(c) Versions 1985-2001 Microsoft Corp.
C:\>
2.
Access the Telnet client.
At the prompt C:\>, enter Telnet. The Command Prompt window displays the following
messages:
Microsoft Windows XP [Versions 5.1.2600]
(c) Version 1985-2001 Microsoft Corp.
C:\> telnet
Press Enter to access the Telnet client. The Command Prompt window displays the
following messages:
Welcome to use Microsoft Telnet Client
Escape character is CTRL+]
Microsoft Telnet>
3.
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Connect the Telnet server.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
23
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
3 Logging In to the SPU
At the prompt Microsoft Telnet>, enter the following command to connect to the Telnet
server. The format is as follows:
open { ip-address | host-name } [ port ]
ip-address: specifies the IP address of a Telnet server.
host-name: specifies the host name of a Telnet server.
port: specifies the number of the interface for the Telnet service on a Telnet server. The
default value is 23.
Exampe:
# Connect to the SPU whose IP address is 1.1.1.1. The default port number is 23.
Welcome to use Microsoft Telnet Client
Escape character is '[CTRL+]'
Microsoft Telnet> open 1.1.1.1
Trying 1.1.1.1 ...
Press CTRL+K to abort
Connected to 1.1.1.1 ...
Info: The max number of VTY users is 20, and the number
of current VTY users on line is 1.
<Quidway>
----End
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
24
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
4 Service Features of the SPU
Service Features of the SPU
This topic describes all the features supported by the SPU according to the feature description
in each volume (basic configuration, Ethernet, IP service, IP routing, QoS, security, reliability,
device management, network management, and VPN).
Basic Configuration
Feature
Remarks
File system
The feature of the SPU is the same as that of the S9300. For details, see
Management of Configuration Files in the Quidway S9300 Terabit
Routing Switch Configuration Guide - Basic Configuration.
NOTE
The configuration file needs to be backed up on both S9300 and SPU.
Login through
the Console
interface
The feature of the SPU is the same as that of the S9300. To log in to the
SPU through the console interface, see 3.1 Logging In to the SPU
Through the Console Interface.
Login through
Telnet
The feature of the SPU is the same as that of the S9300 in some aspects.
The difference is as follows: A user can configure the IP address of the
Ethernet interface on the SPU by logging in to the MPU of the S9300. To
log in to the SPU through Telnet, see 3.3 Logging In to the SPU Through
Telnet.
SSH login
The feature of the SPU is the same as that of the S9300. For details, see
Configuration of the SSH Server and Client in the Quidway S9300 Terabit
Routing Switch Configuration Guide - Basic Configuration.
Feature
Remarks
MAC
The feature of the SPU is the same as that of the S9300. For details, see
MAC Address Table Configuration in the Quidway S9300 Terabit
Routing Switch Configuration Guide - Ethernet.
Ethernet
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
25
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
4 Service Features of the SPU
Feature
Remarks
ARP
The feature of the SPU is the same as that of the S9300. For details, see
ARP Configuration in the Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Configuration Guide - Ethernet.
Link
aggregation
The feature of the SPU is the same as that of the S9300. The difference is
that each Eth-Trunk on the SPU contains a maximum of 2 member
interfaces and the upper limit of link aggregation bandwidth is 2. For
details, see Link Aggregation Configuration in the Quidway S9300
Terabit Routing Switch Configuration Guide - Ethernet.
Feature
Remarks
IP address
setting
The SPU supports setting IP addresses on sub-interfaces and tunnel
interfaces only. For the configuration method, see the Quidway S9300
Terabit Routing Switch Configuration Guide - IP Services.
Feature
Remarks
IPv4 unicast
static routes,
RIP, OSPF, ISIS, and BGP
The feature of the SPU is similar to that of the S9300. For details, see the
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch Configuration Guide - IP
Routing.
Routing policies
and policybased routing
The feature of the SPU is the same as that of the S9300. For details, see
the Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch Configuration Guide - IP
Routing.
Route iteration
The feature of the SPU is the same as that of the S9300. For details, see
the Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch Configuration Guide - IP
Routing.
Feature
Remarks
Names of the
traffic
classification,
traffic behavior,
and traffic
policy
The feature of the SPU is similar to that of the S9300. The difference is
that the SPU does not support URPF. For details, see the Quidway
S9300 Terabit Routing Switch Configuration Guide - QoS.
IP Services
IP Routing
QoS
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
26
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
4 Service Features of the SPU
Feature
Remarks
Priority
mapping
The feature of the SPU is the same as that of the S9300. For details, see
the Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch Configuration Guide QoS.
Feature
Remarks
ACL
The feature of the SPU is similar to that of the S9300. The difference is
that the SPU does not support named ACL or user-defined ACL. For
details, see the Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch Configuration
Guide - Security.
URPF
The feature of the SPU is the same as that of the S9300. For details, see
the Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch Configuration Guide Security.
Feature
Remarks
BFD
The feature of the SPU is similar to that of the S9300. The difference is
that the SPU does not support static BFD6 session with automatically
negotiated discriminators or multi-hop packet TTL. For details, see the
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch Configuration Guide Reliability.
VRRP
The feature of the SPU is the same as that of the S9300. For details, see
the Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch Configuration Guide Reliability.
Security
Reliability
Device Management
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Feature
Remarks
Interface
mirroring
The feature of the SPU is the same as that of the S9300. For details, see
the Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch Configuration Guide - Device
Management.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
27
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
4 Service Features of the SPU
Network Management
Feature
Remarks
Ping and Tracert
The feature of the SPU is the same as that of the S9300. For details, see
the Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch Configuration Guide Network Management.
SNMP
No
The feature of the SPU is the same as that of the S9300. For details, see
the Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch Configuration Guide Network Management.
VPN
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Feature
Remarks
GRE
The feature of the SPU is similar to that of the S9300. The difference is
that the tunnel destination address on the SPU cannot be a VPN instance
address. For details, see the Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Configuration Guide - VPN.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
28
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
5 Replacing an SPU
Replacing an SPU
This topic describes precautions and procedure for replacing an SPU.
Precautions
Before replacing an SPU, pay attention to the following points:
Before replacing an SPU, prepare an SPU with the same specifications of the SPU to be replaced.
Tools
l
ESD-preventive wrist straps or gloves
ESD-preventive bag
Procedure
Step 1 Check the position of the SPU to be replaced.
Before removing the SPU that you need to replace, check the position of the cabinet, chassis,
and slot where the SPU is installed.
l An S9312 has 12 LPU slots, which are numbered from 1 to 12.
l An S9306 has 6 LPU slots, which are numbered from 1 to 6.
l An S9303 has 3 LPU slots, which are numbered from 1 to 3.
Find out the SPU to be replaced in the chassis and attach a label to identify the SPU.
Step 2 Check whether there is any bent pin in the connector of the new SPU.
Step 3 Remove the cable from the SPU.
Step 4 Remove the SPU to be replaced from the chassis.
1.
Wear ESD-preventive wrist straps and connect the grounding terminal to the ESD jack on
the chassis.
2.
Hold the left and right ejector levers of the board with your hands. Press the springs of the
ejector levers to loosen the ejector levers. Turn the ejector levers of the SPU outwards.
When the ejector levers and the panel form a 45-degree angle, the SPU is removed from
the backplane, as shown in (2) of Figure 5-1.
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
29
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
5 Replacing an SPU
CAUTION
l During the operation, remove the SPU slowly and smoothly to prevent it from colliding
with other boards and causing failures of the running boards.
l When swapping an SPU, do not touch the parts on the SPU to prevent it from being
damaged.
3.
Hold the two ejector levers and pull out the SPU smoothly from the chassis along the guide
rail of the slot, as shown in (2) of Figure 5-1.
4.
Place the removed board in the ESD-preventative bag.
Figure 5-1 Schematic diagram of removing an SPU
Step 5 Install the new SPU into the chassis.
1.
Take out the new SPU from the ESD-preventive bag.
CAUTION
l During the operation, install the SPU slowly and smoothly to prevent it from colliding
with other boards and causing failures of the running boards.
l When swapping an SPU, do not touch the parts on the SPU to prevent it from being
damaged.
2.
Hold the two ejector levers and insert the SPU smoothly into the chassis along the guide
rail of the slot, as shown in (1) of Figure 5-2. Push the SPU until the bayonets of the ejector
levers touch the edges of the chassis.
3.
Secure the bayonets of the ejector levers on the edges of the chassis, and then push the
ejector levers inwards until you hear a click, as shown in (2) of Figure 5-2.
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
30
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
5 Replacing an SPU
Figure 5-2 Schematic diagram of installing an SPU
Step 6 Connect the cables to the corresponding interfaces in the original sequence.
Step 7 Check the running status of the new SPU.
In normal situations, after the new SPU is installed into the chassis, the SPU automatically
communicates with the MPU. In this case, check the running status of the new SPU as follows:
l If the RUN/ALM indicator on the panel of the SPU is green and blinks at the frequency of
0.5 Hz, it indicates that the SPU is running normally.
l You can check the alarms. In normal situations, the system does not generate any alarm
related to the new SPU.
l Run the display device command on the client after logging in to the SPU to view the running
status of the new SPU. If the output is displayed as follows, it indicates that the SPUs in the
corresponding slots are running normally.
<Quidway> display device
S9300 SPU's Device status:
Slot Sub Type
Online
Power
Register
Alarm
Primary
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 13
VAMPA
Present
PowerOn
Registered
Normal
Master
Step 8 Check service operations.
----End
Follow-up Procedure
After finishing the replacement, put all the tools away. If an SPU that is replaced is confirmed
to be faulty, maintainers should fill in the Faulty Card for Repair, and mail the card and the
faulty SPU together to Huawei local office for timely maintenance.
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
31
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
6 Technical Specifications of the SPU
Technical Specifications of the SPU
About This Chapter
This topic describes system parameters and technical specifications of the SPU.
6.1 System Configurations of the SPU
This topic describes the processor, DRAM, flash, CF card, and forwarding capability of the
SPU.
6.2 Technical Specifications of the SPU
This topic describes the software service features (Ethernet services, QoS, ACL, L3VPN, IP
unicast, and reliability services) and hardware (integrated system reliability) technical
specifications of the SPU.
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
32
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
6 Technical Specifications of the SPU
6.1 System Configurations of the SPU
This topic describes the processor, DRAM, flash, CF card, and forwarding capability of the
SPU.
Table 6-1 describes system configurations of the SPU.
Table 6-1 System configurations of the SPU
Description
Example
Remarks
Processor
Two multi-kernal CPUs.
Each CPU is configured with
16 kernals. The dominant
frequency is 600 MHz.
Two CPUs
DDR2 DRAM
16 GB (8 bit, 2 x 4 GB). Each
CPU is connected to a
memory of 8 GB.
Flash
64 MB
CF card
512 MB
A CF card serves as a mass
storage device to save data
files and logs.
Forwarding capability
10 Gbit/s
6.2 Technical Specifications of the SPU
This topic describes the software service features (Ethernet services, QoS, ACL, L3VPN, IP
unicast, and reliability services) and hardware (integrated system reliability) technical
specifications of the SPU.
Table 6-2 describes the software service features and hardware technical specifications of the
SPU.
Table 6-2 Software service features and hardware technical specifications of the SPU
Attribute
Service Feature
Technical Specification
Ethernet service
performance
Number of MAC addresses
128,000
Number of trunk groups and
maximum number of interfaces
supported by each trunk group
Two trunk groups, each of which
supports a maximum of two
interfaces
Rate of learning MAC addresses
3000 addresses/second
Number of ARPs
16,000
CAR
8 kbit/s
QoS performance
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
33
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Quick Start - SPU
6 Technical Specifications of the SPU
Attribute
Service Feature
Technical Specification
ACL
ACLv4
Global: 32 thousand
VPN
VRF
1000
VPN route
230,000
Routing entries
230 thousand
IPv4 FIB
144 thousand
BFD
Number of static sessions of the
BFD: 32
IP unicast
Reliability
service
Minimum fault discovery interval:
less than 100 ms
VRRP
l VRRP groups: 255
l VRRP management groups: 16
l Virtual IP addresses in each
VRRP group: 16
l Minimum switchover interval:
3s if the BFD is not used; 100
ms if BFD for VRRP is used.
Issue 01 (2011-09-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
34
You might also like
- Adjacent Channel Interference Impact On The Capacity of Wcdma FDDDocument5 pagesAdjacent Channel Interference Impact On The Capacity of Wcdma FDDTAOUACHINo ratings yet
- Post-Stroke Lower Limb Spasticity Alters The Interlimb Temporal Synchronisation of Centre of Pressure Displacements Across Multiple TimescalesDocument10 pagesPost-Stroke Lower Limb Spasticity Alters The Interlimb Temporal Synchronisation of Centre of Pressure Displacements Across Multiple TimescalesTAOUACHINo ratings yet
- Sample HF ArchitectureDocument1 pageSample HF ArchitectureTAOUACHINo ratings yet
- Improved Biomedical Device For Spasticity QuantificationDocument4 pagesImproved Biomedical Device For Spasticity QuantificationTAOUACHINo ratings yet
- Haptic Simulation of Elbow Joint SpasticityDocument2 pagesHaptic Simulation of Elbow Joint SpasticityTAOUACHINo ratings yet
- RANAP Location Reporting Control MessageDocument1 pageRANAP Location Reporting Control MessageTAOUACHINo ratings yet
- RANAP RAB Assignment Request For A CS Video CallDocument1 pageRANAP RAB Assignment Request For A CS Video CallTAOUACHINo ratings yet
- Compressed Mode Using SFdiv2 - HLSDocument1 pageCompressed Mode Using SFdiv2 - HLSTAOUACHINo ratings yet
- RANAP RAB Assignment Request For A CS Speech CallDocument1 pageRANAP RAB Assignment Request For A CS Speech CallTAOUACHINo ratings yet
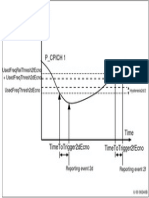
- Measurement Quantity P - Cpich 1: Usedfreqthresh2Decno + Utranrelthresh3AecnoDocument1 pageMeasurement Quantity P - Cpich 1: Usedfreqthresh2Decno + Utranrelthresh3AecnoTAOUACHINo ratings yet
- Measurement Quantity: Usedfreqrelthresh2Fecno + Usedfreqthresh2Decno Usedfreqthresh2DecnoDocument1 pageMeasurement Quantity: Usedfreqrelthresh2Fecno + Usedfreqthresh2Decno Usedfreqthresh2DecnoTAOUACHINo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- Evaluator Guide: Docucolor 242 / 252 / 260Document14 pagesEvaluator Guide: Docucolor 242 / 252 / 260Patricia SolisNo ratings yet
- Udyogaadhaar - Gov.in UA PrintAcknowledgement PDFDocument1 pageUdyogaadhaar - Gov.in UA PrintAcknowledgement PDFthrigunNo ratings yet
- RYX-59HD User ManualDocument10 pagesRYX-59HD User ManualGirish SinghNo ratings yet
- Virtual Lans: Vlan Concepts Vlan Configuration Troubleshooting VlansDocument7 pagesVirtual Lans: Vlan Concepts Vlan Configuration Troubleshooting Vlansnaya hazelNo ratings yet
- InternetDocument34 pagesInternetapi-19998385No ratings yet
- NF18ACV User GuideDocument123 pagesNF18ACV User GuideAqeel HasanNo ratings yet
- OptiX PTN 900 Products BrochureDocument5 pagesOptiX PTN 900 Products BrochuregomezjcrNo ratings yet
- CD Rom DriveDocument35 pagesCD Rom Driveapi-258581198No ratings yet
- CAN Protocol Principles of Data ExchangeDocument4 pagesCAN Protocol Principles of Data Exchangerenju88100% (1)
- Site-To-Site VPN Technologies ComparisonDocument1 pageSite-To-Site VPN Technologies ComparisonSyed Ali Raza GardeziNo ratings yet
- ITS323Y12S1L01 Data Communications and NetworksDocument25 pagesITS323Y12S1L01 Data Communications and NetworksK. V. RopNo ratings yet
- Usermanual Synaps CSD-300 en WebDocument29 pagesUsermanual Synaps CSD-300 en WebMaria MoiseNo ratings yet
- Line CodingDocument37 pagesLine CodingAliImran0% (1)
- Sony Hdr-hc5, Hc5e, Hc7, Hc7e Service Manual Level 2 Ver 1.1 2007.03 (9-852-176-32)Document112 pagesSony Hdr-hc5, Hc5e, Hc7, Hc7e Service Manual Level 2 Ver 1.1 2007.03 (9-852-176-32)Сергей ДымковNo ratings yet
- How To Read SIP TracesDocument4 pagesHow To Read SIP TracesZeeshan DawoodaniNo ratings yet
- Access Evolution 211014 1510 Ahmed Ossama Telecom EgyptDocument12 pagesAccess Evolution 211014 1510 Ahmed Ossama Telecom EgyptAmila NagasingheNo ratings yet
- ITE v6 Final Exam 2016Document18 pagesITE v6 Final Exam 2016anon_788551900No ratings yet
- Moving To The Media CloudDocument12 pagesMoving To The Media CloudlucidNo ratings yet
- UPT PresentationDocument5 pagesUPT PresentationRoland VladutescuNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing Using Smart Biometric SolutionsDocument11 pagesDigital Signal Processing Using Smart Biometric SolutionsMuhammed JaleelNo ratings yet
- SAP FICO Training Videos - Materials Folder Screenshots PDFDocument8 pagesSAP FICO Training Videos - Materials Folder Screenshots PDFSajanAndyNo ratings yet
- MessagesDocument34 pagesMessagesJosephJosephNo ratings yet
- Philips 32pw6542 Manual Do UtilizadorDocument2 pagesPhilips 32pw6542 Manual Do UtilizadorBruno FoscaNo ratings yet
- KL42GT618 Service ManualDocument23 pagesKL42GT618 Service ManualQasim Syed0% (1)
- SpeakingDocument420 pagesSpeakinganon_254355400No ratings yet
- Your Guide To Troubleshooting Voip: Network Instruments White PaperDocument9 pagesYour Guide To Troubleshooting Voip: Network Instruments White PaperKrishnaRoyNo ratings yet
- Samsung LEB550 ManualDocument74 pagesSamsung LEB550 ManualCraciun CosminNo ratings yet
- EUG Projector Price List 2018.Document10 pagesEUG Projector Price List 2018.Anel Alejo BellidoNo ratings yet
- Basics of Telecommunications and NetworkingDocument25 pagesBasics of Telecommunications and NetworkingSujeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Syrus3GQuickProgrammingGuide-v1 3Document7 pagesSyrus3GQuickProgrammingGuide-v1 3LOGIRASTREO SASNo ratings yet