Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Formula Sheet
Uploaded by
Steven Hoernicke0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesformula sheet
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentformula sheet
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesFormula Sheet
Uploaded by
Steven Hoernickeformula sheet
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
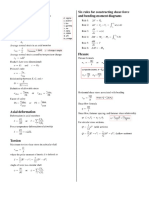
Basic definitions
Average normal stress in an axial member
LF
ome =
Average direct shear stress
ap
wey
Average bearing stress
ot
oO Ay
Average normal strain in an axial member
6 —__
Sng = Fremens = Sd) = change in angie
Average normal strain caused by temperature change
+ = oT
Hooke’s Law (one-dimensional)
Be and
Poisson's ratio
Relationship between B, G, and
E
+n
Definition of allowable stress
= Zits opr. Toate
iS lem
Factor of safety
FS = Zt ge BS
Fas Tut
Axial deformation
Deformation in axial members
i. hb
eg poh
a Uae,
Force temperature deformation relationship
6
Fe oan
aE
Torsion
Maximum torsion sear tess ina eur shat
_k
md
where the polar moment of neti Js defined as
6, sigma
2, apsion
‘tau
‘r.gamma,
5 ata
, sipna
phi
©, ome93
Six rules for constructing shear-force
and bending-moment diagrams
Rules av
Ral 2
Rule 3:
Rule 4:
Rule 5:
Rule 6:
Flexure
Flexure formula
it
Shear low formula,
=
oT
Shear flow, fastener spacing, and fastener shear relationship
gSnYy amd, Og
For circular cross sections,
2= da (ois
2
= FR} 5
@= 51k
1
LD — a) (hollow sections
5D =) tions)
Plane stress transformations
Normal and shear stresses on an arbitrary plane
0, = 0, 6080 +0,,Sin? 0 + 2r,, sinBcosd
~(o, ~ 0,)sindcos0 + +, (cos* 8 ~ sin? 0)
”" a, +9,
20820 +7, in20
in20 + 7,, c0s26
(o, —o,)/2
‘Maximum in-plane shear stress magnitude
an29,
uty
Pweg =
Absolute maximum shear stress magnitude
Toma
Normal, stress invariance
Oy + Oy = Oy +0, = Oy FO
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Final Paper PromptDocument2 pagesFinal Paper PromptSteven HoernickeNo ratings yet
- Probability ProjectDocument2 pagesProbability ProjectSteven HoernickeNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesFormula Sheet PDFSteven HoernickeNo ratings yet
- AL: Mike Trout NL: Clayton KershawDocument1 pageAL: Mike Trout NL: Clayton KershawSteven HoernickeNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)