Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Frame Rate (Also Known As Frame Frequency)
Uploaded by
Marathi CalligraphyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Frame Rate (Also Known As Frame Frequency)
Uploaded by
Marathi CalligraphyCopyright:
Available Formats
Frame Rate (also known as frame frequency)
a) The rate at which frames of video data are scanned on the screen. In an NTSC system, the
frame rate is 29.97 frames per second. For PAL, the frame rate is 25 frames per second. b)
The number of frames per second at which a video clip is displayed. c) The rate at which
frames are output from a video decoding device or stored in memory.[1]
Frame Transfer
A CCD imager where an entire matrix of pixels is read into storage before being output from
the camera. This differs from interline transfer where lines of pixels are output.
Frequency Interlace
The method by which color and black-and-white sideband signals are interwoven within the
same channel bandwidth.
Frequency Response
The range of frequencies that a piece of equipment can process and is directly related to the
systems ability to uniformly transfer signal components of different frequencies over the
entire video spectrum without affecting their amplitudes. This parameter is also known as
gain/frequency distortion or amplitude versus frequency response. The amplitude variation
maybe expressed in dB, percent or IRE.
Front Porch
The portion of a composite picture signal that lies between the leading edge of the horizontal
blanking pulse and the leading edge of the corresponding sync pulse.
F-Stop (also known as f-number or f-system)
The speed or ability of a lens to pass light. It is calculated by dividing the focal length of the
lens by its diameter. The f-stop also is a factor in more areas of focus in the image known as
Depth of Field.
You might also like
- Television Transmission: Program Studi S1 Teknik Telekomunikasi Jurusan Teknik Elektro STT TelkomDocument55 pagesTelevision Transmission: Program Studi S1 Teknik Telekomunikasi Jurusan Teknik Elektro STT Telkomalbar_hafizhNo ratings yet
- Unit - 6 Fundamentals of Digital VideoDocument29 pagesUnit - 6 Fundamentals of Digital Videoxx69dd69xxNo ratings yet
- Pulse Code PCMDocument13 pagesPulse Code PCMumerisahfaqNo ratings yet
- Picture Carrier Sound Carrier ChrominanceDocument4 pagesPicture Carrier Sound Carrier ChrominanceMyla GarciaNo ratings yet
- Audio and Video Engineering: Lecture-7 Principles of VideoDocument24 pagesAudio and Video Engineering: Lecture-7 Principles of VideoGhshshehNo ratings yet
- The Lecture Contains:: Lecture 4: Introducing Digital Video and Digital Video StandardsDocument6 pagesThe Lecture Contains:: Lecture 4: Introducing Digital Video and Digital Video StandardsKarajá PtahNo ratings yet
- Video Glossary: Definition of TermsDocument5 pagesVideo Glossary: Definition of TermsEditha SaloNo ratings yet
- Representation of Digital Images and Video: Pertemuan 4Document55 pagesRepresentation of Digital Images and Video: Pertemuan 4Michael TownleyNo ratings yet
- Components of TV SystemDocument16 pagesComponents of TV SystemRaja RNo ratings yet
- The Lecture Contains:: Lecture 3: Characterisation of Video Raster, Parameters of Analog TV Systems, Signal BandwidthDocument5 pagesThe Lecture Contains:: Lecture 3: Characterisation of Video Raster, Parameters of Analog TV Systems, Signal BandwidthAdeoti OladapoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document42 pagesChapter 5arunkorathNo ratings yet
- T Rec H.100 198811 I!!pdf eDocument9 pagesT Rec H.100 198811 I!!pdf eAriel Encinas LiraNo ratings yet
- Multimedia Technology CH 7 VideoDocument5 pagesMultimedia Technology CH 7 VideoSyed Fateh Ali ShahNo ratings yet
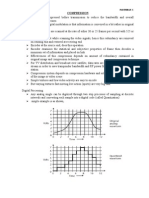
- CompressionDocument3 pagesCompressionJesse VincentNo ratings yet
- Video: Frame Rate (Frames/second)Document8 pagesVideo: Frame Rate (Frames/second)Collins JimNo ratings yet
- Hearn and Baker - Chapter 2Document56 pagesHearn and Baker - Chapter 2Rashika Jain100% (5)
- Composite Video Signal: Communications NetworkDocument1 pageComposite Video Signal: Communications NetworkMarathi CalligraphyNo ratings yet
- Video ProcessingDocument3 pagesVideo ProcessingBanafsheh RezaeianNo ratings yet
- 6 Fundamental Concepts in VideoDocument27 pages6 Fundamental Concepts in Videosolo IvorNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Digital TV: A, y A, XDocument47 pagesUnit 3: Digital TV: A, y A, XSameer ShirhattimathNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Video and AnimationDocument16 pagesChapter 4 Video and AnimationrpNo ratings yet
- BT0046 Communication Technology: (1 Mark Each)Document7 pagesBT0046 Communication Technology: (1 Mark Each)Natasha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Amit Kumar Singh Anand Kumar Anita Bhavana KeshwaniDocument40 pagesAmit Kumar Singh Anand Kumar Anita Bhavana KeshwaniAjit BabaNo ratings yet
- Multimedia CommunicationDocument60 pagesMultimedia CommunicationkavigrNo ratings yet
- Digital VideoDocument26 pagesDigital VideoRichurajanNo ratings yet
- Video Fundamentals: Signal Processing For Digital TVDocument86 pagesVideo Fundamentals: Signal Processing For Digital TVAndrewWerdnaNo ratings yet
- Pulse-Code Modulation (PCM) Is A Method Used ToDocument53 pagesPulse-Code Modulation (PCM) Is A Method Used Tosugu2k88983No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Digital TelevisionDocument40 pagesLecture 2 - Digital TelevisionGerald Emmanuel100% (1)
- 18EC62 Module 2 FINALDocument8 pages18EC62 Module 2 FINALDr. Madhumathy PNo ratings yet
- Video TechnologyDocument57 pagesVideo TechnologyArun0daya100% (2)
- CCTV BasicsDocument23 pagesCCTV BasicsKasiviswanathan Ramanathan50% (4)
- Video A Multimedia ComponentDocument41 pagesVideo A Multimedia ComponentR. JhansiraniNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Fundamental Concepts in Video Types of Video SignalsDocument13 pagesUnit 2 Fundamental Concepts in Video Types of Video SignalsEzo'nun BabasıNo ratings yet
- Digital CommunicationDocument2 pagesDigital CommunicationHarshal SonarNo ratings yet
- Gyan TVEDocument7 pagesGyan TVEGyan AnandNo ratings yet
- PCR Measur Tektronix PDFDocument24 pagesPCR Measur Tektronix PDFGrzegorz ZissNo ratings yet
- IC DGM Video DefinitionsDocument3 pagesIC DGM Video Definitionsrachel_tracyNo ratings yet
- Matrix SwitcherDocument2 pagesMatrix SwitcherMarathi CalligraphyNo ratings yet
- Digital CommunicationsDocument39 pagesDigital Communicationsmakomdd100% (1)
- Discuss The Composite Video Signal.: Explain Why 3.58 MHZ Was Selected As The Color Subcarrier FrequencyDocument4 pagesDiscuss The Composite Video Signal.: Explain Why 3.58 MHZ Was Selected As The Color Subcarrier FrequencyJoshua CruzNo ratings yet
- DC Quiz Bits 1 MidDocument12 pagesDC Quiz Bits 1 MidAllanki Sanyasi Rao100% (1)
- Glossary of Colorist TermsDocument34 pagesGlossary of Colorist Termsdiegoale8_rNo ratings yet
- CNS-ST3.1Document17 pagesCNS-ST3.1Achilles AldaveNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document35 pagesCH 2Laxmi GkNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Priya Raina 13-516Document68 pagesPresented By: Priya Raina 13-516Priya RainaNo ratings yet
- Technical Introduction To TimecodeDocument4 pagesTechnical Introduction To TimecodeFirdaus SikumbangNo ratings yet
- Video and AnimationDocument14 pagesVideo and AnimationPawan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- MCQ Comm-2Document18 pagesMCQ Comm-2shwet_vNo ratings yet
- CG Into ch1Document83 pagesCG Into ch1Nilesh RanaNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Digital Television TermsDocument342 pagesGlossary of Digital Television TermsTar AsraniNo ratings yet
- 01ec 302 DC - 1Document37 pages01ec 302 DC - 1ShelNo ratings yet
- Multimedia Systems Chapter 5Document6 pagesMultimedia Systems Chapter 5Sanyogita ShindeNo ratings yet
- T.V Engineering. Learning Outcome:: 1. Basic of Television Scanning and SynchronizingDocument7 pagesT.V Engineering. Learning Outcome:: 1. Basic of Television Scanning and SynchronizingRuhulamin SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Pondicherry UniversityDocument17 pagesPondicherry Universityjohn billy balidioNo ratings yet
- DMC 1934Document160 pagesDMC 1934Kajendran KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Doordarshan Seminar ReportDocument48 pagesDoordarshan Seminar ReportHimanshu Mahajan100% (1)
- Advanced Multicarrier Technologies for Future Radio Communication: 5G and BeyondFrom EverandAdvanced Multicarrier Technologies for Future Radio Communication: 5G and BeyondNo ratings yet
- Arly Life and EducationDocument2 pagesArly Life and EducationMarathi CalligraphyNo ratings yet
- JDisability OutreachDocument1 pageJDisability OutreachMarathi CalligraphyNo ratings yet
- ViewsDocument1 pageViewsMarathi CalligraphyNo ratings yet
- Publications: Popular BooksDocument2 pagesPublications: Popular BooksMarathi CalligraphyNo ratings yet
- Marriages: Jane WildeDocument1 pageMarriages: Jane WildeMarathi CalligraphyNo ratings yet
- See Also: Bibcode DoiDocument1 pageSee Also: Bibcode DoiMarathi CalligraphyNo ratings yet
- In 2007 Hawking and His DaughterDocument1 pageIn 2007 Hawking and His DaughterMarathi CalligraphyNo ratings yet
- Principles and Terminology PDFDocument2 pagesPrinciples and Terminology PDFMarathi CalligraphyNo ratings yet
- HIn His WorkDocument2 pagesHIn His WorkMarathi CalligraphyNo ratings yet
- Hawking Did Not Rule Out The Existence of A CreatorDocument1 pageHawking Did Not Rule Out The Existence of A CreatorMarathi CalligraphyNo ratings yet
- EthodsDocument2 pagesEthodsMarathi CalligraphyNo ratings yet
- World Health OrganizationDocument2 pagesWorld Health OrganizationMarathi CalligraphyNo ratings yet
- Principles and Terminology PDFDocument2 pagesPrinciples and Terminology PDFMarathi CalligraphyNo ratings yet
- Illnesses Portrayed: Gentleman's MagazineDocument1 pageIllnesses Portrayed: Gentleman's MagazineMarathi CalligraphyNo ratings yet