Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Resistance Measurement of Semiconductors PDF
Uploaded by
John John0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageOriginal Title
Resistance Measurement of Semiconductors.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageResistance Measurement of Semiconductors PDF
Uploaded by
John JohnCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
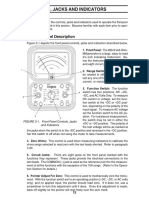
4.21 Measuring Resistance
a. Before measuring resistance in a circuit, make sure the power is off to the
circuit being tested and all capacitors are discharged. Disconnect shunting
‘components from the circuit before measuring its resistance.
b. Set the range switch to one of the resistance range positions as follows (Fig-
ure 4-12)
1 Use R X 1 for resistance readings from 0 to 200 ohms.
2 Use R X 100 for resistance readings from 200 to 20,000 ohms.
3. Use R X 10,000 for resistance readings above 20,000 ohms.
c. Set the function switch at either -DC or +DC position:
Operation is the same in either position except if there are semicon-
ductors in the circuit. (See paragraph 4.22.) Adjust ZERO OHMS
control for each resistance range.
d. Observe the reading on the OHMS scale at the top of the dial.
NOTE: The OHMS scale reads from right to left for increasing values of resis-
tance.
e. To determine the actual resistance value, multiply the reading by the factor at
the switch position. (K on the OHMS scale equals one thousand.)
4.22 Resistance Measurement of Semiconductors
Make sure that the OHMS range being used will not damage any of
the semiconductors (refer to Table 1-1, item 8, Section 1).
If there is a “forward” and “backward” resistance such as in diodes, the resistance
should be relatively low in one direction (for forward polarity) and higher in the
‘opposite direction.
Rotate the function switch between the two DC positions to reverse polarity. This
will determine if there is a difference between the resistance in the two directions.
To check a semiconductor in or out of a circuit (forward and reverse bias resis-
tance measurements) consider the following before making the measurement:
a. The polarity of the battery voltage will be as marked at the jacks when the
switch is in the +DC position and reversed in the -DC position.
b. Ensure that the range selected will not damage the semiconductor. (Refer to
Table 1-1, item 8, and review the specification limits of the semiconductor
according to the manufacturer's ratings.)
¢. If the semiconductor is a silicon diode or conventional silicon transistor, no
precautions are normally required.
d. If the semiconductor material is germanium, check the ratings of the device
and refer to Table 1-1, item 8
NOTE: The resistance of diodes will measure differently from one resistance
range to another on the VOM with the function switch in a given position. For
‘example, a diode which measures 80 ohms on the R X 1 range may measure 300
‘ohms on the R X 100 range. The difference in values is a result of the diode
characteristics and is not indicative of any fault in the VOM.
26
You might also like
- Snow Part 2 PDFDocument1 pageSnow Part 2 PDFJohn JohnNo ratings yet
- Fuse ReplacementDocument1 pageFuse ReplacementJohn JohnNo ratings yet
- Snow Part 2Document1 pageSnow Part 2John JohnNo ratings yet
- Knowledge RequirementsDocument1 pageKnowledge RequirementsJohn JohnNo ratings yet
- Instructions PDFDocument1 pageInstructions PDFJohn JohnNo ratings yet
- Category B1 B2 LicenceDocument1 pageCategory B1 B2 LicenceJohn JohnNo ratings yet
- Category C LicenceDocument1 pageCategory C LicenceJohn JohnNo ratings yet
- OHMS ScaleDocument1 pageOHMS ScaleJohn JohnNo ratings yet
- Power Source Requirements PDFDocument1 pagePower Source Requirements PDFJohn JohnNo ratings yet
- 0-1ma Through 0-500ma RangeDocument1 page0-1ma Through 0-500ma RangeJohn JohnNo ratings yet
- OHMS ScaleDocument1 pageOHMS ScaleJohn JohnNo ratings yet
- Fuse ReplacementDocument1 pageFuse ReplacementJohn JohnNo ratings yet
- AC Voltage MeasurementDocument1 pageAC Voltage MeasurementJohn JohnNo ratings yet
- Resistance MeasurementsDocument1 pageResistance MeasurementsJohn JohnNo ratings yet
- Unpacking and InspectionDocument1 pageUnpacking and InspectionJohn JohnNo ratings yet
- Overload ProtectionDocument1 pageOverload ProtectionJohn JohnNo ratings yet
- Front Panel DescriptionDocument1 pageFront Panel DescriptionJohn JohnNo ratings yet
- DC Voltage MeasurementDocument1 pageDC Voltage MeasurementJohn JohnNo ratings yet
- Safety PrecautionsDocument1 pageSafety PrecautionsJohn JohnNo ratings yet
- Technical DataDocument1 pageTechnical DataJohn JohnNo ratings yet
- Proposed Packing List Part3Document1 pageProposed Packing List Part3John JohnNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual ContentDocument1 pageInstruction Manual ContentJohn JohnNo ratings yet
- 260 8man PDFDocument32 pages260 8man PDFJohn JohnNo ratings yet
- Writing Your ReportDocument1 pageWriting Your ReportJohn JohnNo ratings yet
- SG MBSDocument2 pagesSG MBSJohn JohnNo ratings yet
- Proposed Packing List Part2Document1 pageProposed Packing List Part2John JohnNo ratings yet
- SG MBSDocument2 pagesSG MBSJohn JohnNo ratings yet
- Writing Your ReportDocument1 pageWriting Your ReportJohn JohnNo ratings yet
- 奇門遁甲Document1 page奇門遁甲John JohnNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)