Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ECON212 MTII With Answer Key PDF
ECON212 MTII With Answer Key PDF
Uploaded by
cristal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views12 pagesOriginal Title
ECON212 MTII with answer key.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views12 pagesECON212 MTII With Answer Key PDF
ECON212 MTII With Answer Key PDF
Uploaded by
cristalCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
VANCOUVER ISLAND UNIVERSITY
ECON212: PRINCIPLES OF MACROECONOMICS, Spring 2013
MIDTERM TEST It
Name (Last, First):
ID a:
Signature:
This Exam has total 12 pages including the cover page
INSTRUCTIONS:
* TOTAL MARKS: 75. DURATION: 75 MINUTES.
© PLEASE ANSWER YOUR MCQS IN THE TABLE PROVIDED ON THE ADDITIONAL SHEET
PROVIDED AND OTHER ANSWERS IN THE SPACE PROVIDED.
© FOR SHORT ANSWER AND EASY TYPE QUESTIONS
> YOU MUST SHOW YOUR ALL WORK TO GET FULL MARKS. IF YOU DO NOT SHOW
WORK, YOU MAY NOT GET FULL MARKS EVEN FOR A CORRECT ANSWER.
> USE THE MARKS ASSIGNED TO EACH QUESTION AS A GUIDE TO ALLOCATING YOUR
TIME ACROSS QUESTIONS.
Luck on Your Exam
ECON212: Midterm Exam I! | 2
‘March 18, 2013,
PART A: MCQ
(There are 30 MCQs in this section which is worth 30 marks)
01. In macroeconomics, the “output gap" is the difference between
‘a) real and nominal national income
b) output and employment
) potential real national income and actual real national income
4d) real GNP and real GDP
) output in the current year and output in the base year
(02. When the unemployment rate is higher than the natural unemployment rate, real GDP is than
potential GOP and the output gap is
a) unchanged; unchanged
b) smaller; positive
) smaller; negative
d)_ greater; positive
e) greater; negative
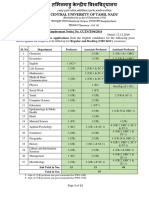
03, The table below provides macroeconomic data for a hypothetical economy, Dollar amounts are all in constant-
dolar terms
teal
Pate Unem
Year | output titionsat | Potential Outpt oloyment
3)
2002 402 404 | 71
2008 “408 ant | 72
[aooe ass 63
200s _|___420 418 [ss
2006 220 0
2007 20 223 70
[_ 2008 a5 25 ___63
Refer tothe table. In which years was this economy experiencing an inflationary gap?
a) 2002, 2003
b) 2006, 2007
©) 2005, 2006
4) 2004, 2008,
04, in the simple macroeconomic model, “autonomous expenditures" are
a) induced expenditures
'b) non-domestic expenditures
)__ not dependent on national income
d) dependent on national income
e) those which are constant
0s.
07.
09,
10,
1.
ECON212:
‘erm Exam Il
March 18, 2013
‘The CPI in 2007 was 120 and in 2008 was 125. The inflation rate is
a) 5%
b) 2.6%
4.2%
@) 1128
) Insufficient information
. The inflation rate is the annual percentage change in
a) real GDP
b)_ the quantity of money
©) the price level
4d) labour productivity
Between 1910 and 2010, the real GPD grew at a faster rate than the population growth rate. So, the average
growth rate of real GDP per person in Canada was
a) Negative
b) positive
zero
d) unknown
- Other things being equal, a reduction in the money supply will ead to a
{2) rise in the rate of interest and no change in investment expenditure
b)_ fallin the rate of interest and an increase in investment expenditure
©) rise in the rate of interest and a decrease in investment expenditure
4) ise in the rate of interest and in increase in investment expenditure
€e) fallin the rate of interest and a decrease in investment expenditure
According to the quantity theory of money, if the money supply doubles
a) real income will double
b) money prices will be halved
©) there will be no effect on money prices
4d) money prices will double
€) relative prices will double
The largest component of the liabilities of the Bank of Canada is,
a) Government of Canada securities
'b) deposits of commercial banks and other financial institutions
©) loans to private individuals
4) Government of Canada deposits
e) Canadian dollars in circulation
Refer to the table. Assume that Bank North is operating with no excess reserves. What is their actual reserve
ratio?
Bank North's Balance Sheet
a) 13.6% |
by 20% Assets Liabilities
©) 12% Reserves | $500 _| Deposits $2200 |
5 ee [Loans [$2000 [Capital_[$300__
$2500 $2500
He hed |e ee
v
3.
14.
15,
16.
17.
18,
19,
ECON212: Midterm Exam II
March 18, 2013
The main objective of the Bank of Canada is to
a) Maintain a low and stable inflation rate
b) Keep the unemployment rate low
¢)__ Increase economic growth rate high
4d) Keep the prime interest rate at 3 percent
Fullemployment level of unemployment or the natural unemployment is
a) a goal that can never be achieved by the economy
b) then unemployment when the economy's resources were fully employed at a normal intensity of use
©) achieved during periods when all of the labour force is employed
d) the GOP that could be produced if the economy's resources were fully employed at their maximum
intensity of use
‘The currency that isin circulation in Canada today is
a) fractionally backed by gold
bb) backed by the U.S. dollar
©) not officially backed by anything.
d)_ fully backed by gold held at the central bank
e) backed by the euro
Commercial banks hold a fraction of their deposits in cash in their vaults (or as deposits with the central bank).
‘his fraction is known as
a) the excess reserve ratio
bb) the fractional reserve
©) the required reserve
4d) the reserve ratio
€) the target res erve
‘The theory of economic growth concentrates on the. over the long run, not on
a) growth of real GDP; growth of potential GOP
factor utilization rates; growth of real GDP
€) factor utilization rates; growth of the supplies of factors
4d) growth of investment in capital goods; short-run fluctuations of investment
‘e) growth of potential output; fluctuations of output around potential
Adesire by has no effect on the ability of the banking system to expand bank deposits.
1a) households to stash money in safety-deposit boxes
'b) households to maintain a certain fraction of thelr money holdings in the form of currency
)__ potential borrowers to be more cautious in their borrowing
4d) banks to maximize profits
The concept of “near money" refers to
‘) financial assets whose capital values are too unstable for them to be classified as money
'b) assets that fulfil the medium-of-exchange function but not the store of value function
)_ assets that fulfil the temporary store-of-value function but not the medium-of-exchange function
d) cheques on demand deposits
‘The AD curve relates the price level to
a) equilibrium nominal GOP if output is demand determine
'b) equilibrium real GDP if output is demand determined
©) equilibrium savings and wealth
4) desired aggregate expenditure
ECON212: Midterm Exam I! | 5
March 18, 2013,
20. Consider the basic AD/AS macro model. Arise in an input price lke the price of oll would be expected to cause
‘a new macroeconomic equilibrium in which the price level
a) Is higher and real GDP lower than in the initial equilibrium
b) and real GDP are lower than in the initial equilibrium.
) is higher and real GDP remained the same as in the initial equilibrium
4)_ is lower and real GDP higher than in the intial equilibrium
211. What is sometimes called the “long-run aggregate supply curve” shows the relationship between the price
level and the amount of output have adjusted to output gaps.
a) supplied by firms after all output prices
b) supplied by firms after all factor prices
c)_ demanded by households before all factor prices
d) supplied by firms before all factor prices
22. A characteristic of the short run in macroeconomics is that
a) actual GD? is always less than potential GOP
) the output gap opens or closes as the economy moves through the phases of the business cycle
) actual GD? is always greater than potential GDP
4) actual GOP is always growing at the same rate as potential GOP
23. The diagram shows an AD/AS model for a hypothetical economy. The economy begins in long-run equilibrium
at point A,
After the positive aggregate supply shock shown in the diagram, which of the following would shift the AS
curve leftward during the economy's adjustment process?
a. a decrease in wages and other factor prices,
bb. an increase in wages and other factor prices
©. an increase in factor supplies
d. an increase in the unemployment rate
24, GDP can be represented by the equation: GDP = F x
£2) x (22) tisequation
2). factor supply and employment rat are long run components but productivity isa short run component
8). factor supply and unemployment rate ae short run companents But product is aong run
component
€)_factor supply and produ
component
4) employment rate and productivity are shor run components but factor suppl i longun component
a short run
ity rate are long run components but employment rate i
ECON212: Midterm Exam Il
March 18, 2013
25, Refer to the figure. Suppose the economy isin equilibrium at ¥, .A contractionary fiscal policy would restore
the economy to potential output (¥") by shifting the
Rat cor
a) AS curve to the left to intersect AD at C
b) Ab to the left to intersect AS at point A
©) AS curve to the right
4d} potential GOP and the AS curve to the left
26. For a given level of national income, a decrease in private consumption or government purchases will ause
the equilibrium interest rate to
a) decrease and the flow of national saving to increase
b) increase and the flow of national saving to decrease
‘o)_increase and the flow of investment to decrease
d)_ increase and the flow of investment to increase
27. The functions of the Bank of Canada include
‘) setting the exchange rate for the Canadian dollar on world markets,
'b) acting as banker for the commercial banks
acting as the lender of last resort for the largest private corporations
4) providing deposit insurance at Canadian commercial banks
28. A decrease in the money supply is most likely to
a) raise interest rates and investment, and lower aggregate expenditures
b) lower interest rates, investment, and aggregate expenditures
¢) raise interest rates, lower investment, and lower aggregate expenditures
4) raise interest rates, investment, and aggregate expenditures
29. The overnight interest rate is crucial to the Bank of Canada when it implements its monetary policy because
a) the Bank of Canada has no ability to influence other interest rates
b) the Bank of Canada's first priority is to ensure the solvency of commercial banks
overnight loans constitute a major source for open-market operations
4d) the overnight interest rate is linked to both short-term and long-term interest rates
ECON212: Midterm Exam It | 7
March 18, 2013,
30. Refer to the figure. This figure illustrates
b)
o
a)
e)
Quant of Sney
(Maney demand an py
the loanable funds market
‘only the first step of the monetary transmission mechanism
the entire monetary transmission mechanism
the ultimate effect of a change in the money supply on real GDP
the first two steps of the monetary transmission mechanism
ECON212: Midterm Exam it | 8
March 18, 2013,
PART B: SAQ
This section is worth 5X7=35 marks. Please use a diagram/figure whenever required/necessary
a) Why are checks and credit cards not money? Explain,
Chaths and cit crds ont not wereg beau May
ane vot aq rrreame of paymint. A cham 4 dn order by
framefer a depose fro ore persre fo anolltr. The hpasis
fre merty. but checks au ri.
A crt und cp an DD earch tok |e & persrre
tape v4 a loan at Gt imrtant he ov she begs commas
The lean patil reek te be paid ik mene Ao te
ert und 2 PSP a wear of paryenind — Utes ni}
monty.
b) What are the defining features of classical macroeconomics and what policies do classical
macroeconomists recommend?
Canrsierl werrvermomint fodive below Jol +
Ge cermemy dan Left aleme, i erred operate at
Gott evcplryrret — in eumvng 4 olf nynlatay:
Claseiel weertiammmns!s arrert Mint tr Maple
Prper povernment pobiig A fo wmiinindze C4 olsen wmbve
feds 4 faxes on ecptogensnt , wnvesthnet anol
feeamilegrical change .
ECON212: Midterm Exam I! | 9
March 18, 2013,
©) Using the Quantity Theory of Money, show how does the quantity of money trigger the inflation
in the economy
Tre huanctity Theery oy mereg | MU = PY
Dr shart run, uwcler prtewel Urumsbenus, cb
anu t tal veloity my mong, VG covotant.
Hever fy rent B® owt Y
MY = PY (7 te wceoke (ae
te noe es fone?
So, d Brady of poomny aA rrsents, pric leek P
tuv =1PY
Ue Lt lhe
d) What is stagflation and why does cost-push inflation cause stagflation?
Seg flatern means, a niseng prieelerel (unflahe )
We ne eurronie grew lx nearive Grok rak)
A cast push unfintere vray rewll thes
Yo Trane a Softly rheck, e
As oth PO lft —
ane foe creas prs
ae ovlpent foe ty, ae
A, AD super ping o
token, cnflabsh ocr.
Bet orvtget pater Gelrd
(ost of he pe) & SIM
Gt |
ECON212: Midterm Exam 1! | 10
March 18, 2013,
) Why does the Aggregate demand function slope downward?
Beane 4 weal, and P
Sirbs habe pis
Utne prin falls, for ertiner,
real yalas of Den mninnir,
pemple gud more, lat
Ceres.
or prin foto people ab
prifey fo renee 08 Z : o
i ips tp wea. from foo pemraton
Mer temp orok rtsh hehe qhE:
) Why is the Long-run Aggregate supply function vertical?
if
4 Las
n De LR, o>
connrg pradners
fe eanploryreit
level af ovdpat, wick
o Undep bet C ys Y
pnce lel .
ECON212: Midterm Exam I! | 14
March 18, 2013,
8) How does a government budget surplus or deficit influence the loanable funds market?
Tn the loarnobte ks uarkel, supply
4 loamtle fre 3 dehemed by natenl
pany SH 6 hob 4 g Pe
phe
rt
iar
m
i: loannfle
Y Ton 0 apt
fr bert — affect ;
Tie demand are a -
ree
L, *
Ook r pF u tp’
fe Chane
ay
p* PY fons
ECON212: Midterm Exam I! | 12
March 18, 2013
PART C: Essay Question
(This section is worth 10 marks)
Debate on Causes of Jobl:
‘What is the cause of the high unemployment rate? One side says unemployment is a cyclical problem. The
other side says itis structural.
Which business cycle theory would say that the rise in US unemployment in last few years is cyclical? Which
would say itis an increase in the natural rate? Why
How Faery Bal worst of Ga wemurcthene
busene S$ gee rern'es pry dal Ma vise Ba
wnanpleymet rade a egehial ua neater: Brepori febg
Bu heyre aw tyke Mery and ney Kuypevian uyele Dery
ayree Bol ba vise 4 vy.
The rerl burcress aye (Abe), Misay pen»
ie megend pale aul ummplegrenl an woken
and we ik aol) aunt Ant Mr vise m Gy
npn pete vifledt a Nie ce ke nab
“END OF EXAMINATION*
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5814)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Mlie 102Document291 pagesMlie 102ecobalas7No ratings yet
- ReferencesDocument3 pagesReferencesecobalas7No ratings yet
- BBB KamalDocument9 pagesBBB Kamalecobalas7No ratings yet
- AppointmentsDocument5 pagesAppointmentsecobalas7No ratings yet
- The Socio-Economic Determinants of HIV/AIDS Infection Rates in Lesotho, Malawi, Swaziland and ZimbabweDocument22 pagesThe Socio-Economic Determinants of HIV/AIDS Infection Rates in Lesotho, Malawi, Swaziland and Zimbabweecobalas7No ratings yet
- Hemavathi Nandhan PDFDocument1 pageHemavathi Nandhan PDFecobalas7No ratings yet
- T 04 Fac 2016Document11 pagesT 04 Fac 2016ecobalas7No ratings yet
- SET15 Eeconomics P III BDocument12 pagesSET15 Eeconomics P III Becobalas7No ratings yet
- How To Apply Panel ARDL Using EVIEWSDocument4 pagesHow To Apply Panel ARDL Using EVIEWSecobalas7100% (3)
- The Relationship Between Debt Level and Fiscal Sustainability in Organization For Economic Cooperation and Development CountriesDocument21 pagesThe Relationship Between Debt Level and Fiscal Sustainability in Organization For Economic Cooperation and Development Countriesecobalas7No ratings yet
- Growing Bank Deposits PostDocument5 pagesGrowing Bank Deposits Postecobalas7No ratings yet
- Correlation PDFDocument7 pagesCorrelation PDFecobalas7No ratings yet