Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notes Translation
Uploaded by
api-298247873Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Notes Translation
Uploaded by
api-298247873Copyright:
Available Formats
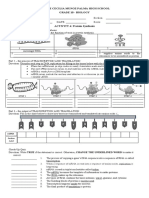
Notes: Translation
Translation
conversion of ______ into ________ _____ sequence that makes a ______________
the mRNA leaves the _____________ and enters the ______________
ribosomes attach to the _________
_______ (carrying ______-________) picks up the correct amino acids and carries them
to the mRNA strand forming
the protein
o ex: tRNA carries
______ (anti-codon) &
looks for _____ on
mRNA
The tRNA also has a special
sequence of ___ _____________
bases known as an
anticodon.
There is at least one type of
tRNA for each of the _____
amino acids.
The Steps of Translation
The _________ molecule
moves through a pore in the
nuclear envelope and into
the ___________. It joins with
a ribosome and is translated
one amino acid at a time.
_______________: the first codon on any mRNA molecule is called the ______________.
This codon is always ______, which codes for the amino acid methionine. This is a
message to START translation.
_______________: the ribosomes job is to position the _______ molecule onto the
matching mRNA molecule.
o This makes it possible for a __________ bond to be formed between the amino
acids attached to the tRNA molecules. These amino acids chains make up
the ____________.
o The enzyme that catalyzes this reaction is called __________ ________________.
________________: The last codon on any mRNA molecule is called the
______________ codon, which is a message to STOP translation.
o This codon will be either _____,_____, or ______. None of these have a
matching _____ anticodon, so when no more tRNAs attach, the ribosome,
protein, and mRNA detach from each other.
You might also like
- Rna and Protein Synthesis Guided NotesDocument6 pagesRna and Protein Synthesis Guided NotesqzweqwNo ratings yet
- From DNA To Protein WorksheetDocument1 pageFrom DNA To Protein WorksheetormattNo ratings yet
- From Gene To Protein - WorksheetDocument4 pagesFrom Gene To Protein - WorksheetpinkNo ratings yet
- Protein-Synthesis WorksheetDocument5 pagesProtein-Synthesis WorksheetAme RealNo ratings yet
- Dna WorksheetDocument8 pagesDna WorksheetLuis100% (6)
- DNA RNA WorksheetDocument5 pagesDNA RNA WorksheetKathleen FrancoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 NOTES 2015Document6 pagesChapter 10 NOTES 2015Cesar DiazNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument4 pagesProtein SynthesisRAQUEL CUNANANNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: TranslationDocument5 pagesStudent Exploration: TranslationAbel QuevedoNo ratings yet
- Bio 1H Genetics Test Addendum 2017Document9 pagesBio 1H Genetics Test Addendum 2017stlcajun55No ratings yet
- RNAProteinSynthesisSE 1 2022-04-29 15 - 38 - 21Document6 pagesRNAProteinSynthesisSE 1 2022-04-29 15 - 38 - 21E ZenaNo ratings yet
- DNA-RNA Worksheet 1Document4 pagesDNA-RNA Worksheet 1inder19125% (4)
- DNA and Proteins Doodle Notes 2Document10 pagesDNA and Proteins Doodle Notes 2Leila BeyyoudhNo ratings yet
- Dna and Protein SynthesisDocument12 pagesDna and Protein SynthesisRichard HampsonNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument3 pagesProtein Synthesis WorksheetG Combalicer Bernice Darielle D.No ratings yet
- 7.3 Translation Nucleic Acid To Polypeptide-Student Sheet PDFDocument3 pages7.3 Translation Nucleic Acid To Polypeptide-Student Sheet PDFMajdalen AzouzNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1670150773883 7005120071502638144Document25 pagesOrca Share Media1670150773883 7005120071502638144RyanNo ratings yet
- GENE TO PROTEIN Notes 2023Document5 pagesGENE TO PROTEIN Notes 2023Kristen LindstromNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma Module For Grade 10 ScienceDocument3 pagesCentral Dogma Module For Grade 10 ScienceJan Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument2 pagesProtein Synthesis WorksheetCamryn BrickerNo ratings yet
- Dna, Rna & Proteins: The Molecules of LifeDocument32 pagesDna, Rna & Proteins: The Molecules of LifeMeri hardinaNo ratings yet
- RNA Protein Synthesis GizmoDocument6 pagesRNA Protein Synthesis Gizmomanuel0% (2)
- Protein Synthesis Simulation ActivityDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesis Simulation ActivitySHARIFAH BINTI HASSAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Rna Protein SynthesisDocument6 pagesRna Protein SynthesisDaniel Hanna86% (7)
- RNAProteinSynthesisSEDocument6 pagesRNAProteinSynthesisSETania Melendez-LainezNo ratings yet
- Science Asynchronous ActivityDocument2 pagesScience Asynchronous Activityjenn.meowwwNo ratings yet
- ds60 Ps Part IIDocument11 pagesds60 Ps Part IIapi-110789702No ratings yet
- Transfer RNA and Protein Building Paper LabDocument7 pagesTransfer RNA and Protein Building Paper LabYESMI GuzmanNo ratings yet
- CC 94 FF 217673Document18 pagesCC 94 FF 217673s2p.idw0ENo ratings yet
- Turn in SheetDocument45 pagesTurn in Sheet25210580No ratings yet
- Gizmo - Rna - Protein SynthesisDocument7 pagesGizmo - Rna - Protein SynthesisMarques AlsoppNo ratings yet
- Bins's PPT Protein SynthesisDocument18 pagesBins's PPT Protein Synthesisvincent malquistoNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: The Protein-Making ProcessDocument20 pagesProtein Synthesis: The Protein-Making ProcessJungkook taekookNo ratings yet
- The Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument5 pagesThe Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyMINt Kookie100% (1)
- Protein SynthesisDocument21 pagesProtein Synthesisnorma thamrinNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: The Protein-Making ProcessDocument21 pagesProtein Synthesis: The Protein-Making ProcessLanie De la Torre100% (1)
- Protein SynthesisDocument21 pagesProtein SynthesisReign Aiken M. LaraNo ratings yet
- Protein PresentationDocument19 pagesProtein PresentationAndre MorganNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Santos Avila Mejia - Crash Course Transcription and Translation WksheetDocument2 pagesKami Export - Santos Avila Mejia - Crash Course Transcription and Translation WksheetKLRSantosNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument2 pagesProtein Synthesis WorksheetErnesto AcostaNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis ActivityDocument2 pagesProtein Synthesis ActivityPrincess Raychel Delos AngelesNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Pogil DNA Vs RNADocument3 pagesKami Export - Pogil DNA Vs RNAEva EllisNo ratings yet
- 6.3 Activity - 3 RNAProteinSynthesisSEDocument6 pages6.3 Activity - 3 RNAProteinSynthesisSEsmol ukeleleNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis GizmoDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesis GizmoCaleb HutchinsonNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument23 pagesProtein SynthesisShyra Nicole AllarseNo ratings yet
- Lecture 05Document36 pagesLecture 05jjmail111No ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesROCHELLE MAGBUONo ratings yet
- GIZMOS RNA Protein Synthesis LabDocument4 pagesGIZMOS RNA Protein Synthesis LabjhonNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis ActivityDocument1 pageProtein Synthesis Activityashoneillauron08No ratings yet
- Human Genetic Inheritance LabDocument5 pagesHuman Genetic Inheritance LabAntonov MikalisNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Model LabDocument7 pagesProtein Synthesis Model Labmarisa corderoNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: RNA and Protein SynthesisDocument7 pagesStudent Exploration: RNA and Protein SynthesisMasonNo ratings yet
- Karas Ghattas - RNA and Protein Synthesis - Pdf.kamiDocument3 pagesKaras Ghattas - RNA and Protein Synthesis - Pdf.kamiKaras GhattasNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Q3 w5 6Document12 pagesScience 10 Q3 w5 6SaviannaNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The Following Passage and Answer The Questions BelowDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The Following Passage and Answer The Questions BelowIris LeuterioNo ratings yet
- Mutations WSDocument3 pagesMutations WSShraddha BNo ratings yet
- Breaking The CodeDocument4 pagesBreaking The CodeRemoh NorenoNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Race WorksheetDocument2 pagesProtein Synthesis Race WorksheetChinee FloresNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology & Genetics: Essential Biology Self-Teaching GuideFrom EverandMolecular Biology & Genetics: Essential Biology Self-Teaching GuideNo ratings yet
- ZikaDocument3 pagesZikaapi-298247873No ratings yet
- Chem BW 47Document1 pageChem BW 47api-298247873No ratings yet
- Bio BW 50Document1 pageBio BW 50api-298247873No ratings yet
- Chem BW 50Document1 pageChem BW 50api-298247873No ratings yet
- Med BW 50Document1 pageMed BW 50api-298247873No ratings yet
- Bio BW 46Document1 pageBio BW 46api-298247873No ratings yet
- Bio BW 47Document1 pageBio BW 47api-298247873No ratings yet
- Med BW 49Document1 pageMed BW 49api-298247873No ratings yet
- Med BW 47Document1 pageMed BW 47api-298247873No ratings yet
- Chem BW 49Document1 pageChem BW 49api-298247873No ratings yet
- Evidence of EvolutionDocument23 pagesEvidence of Evolutionapi-298247873No ratings yet
- Bio BW 44Document1 pageBio BW 44api-298247873No ratings yet
- Med BW 46Document1 pageMed BW 46api-298247873No ratings yet
- Chem BW 46Document1 pageChem BW 46api-298247873No ratings yet
- Chapter16 Section02 EditDocument30 pagesChapter16 Section02 Editapi-298247873No ratings yet
- Chem BW 44Document1 pageChem BW 44api-298247873No ratings yet
- WshhbufferDocument1 pageWshhbufferapi-298247873No ratings yet
- Med BW 44Document1 pageMed BW 44api-298247873No ratings yet
- Bio BW 42Document1 pageBio BW 42api-298247873No ratings yet
- Med BW 42Document1 pageMed BW 42api-298247873No ratings yet
- Chem BW 43Document1 pageChem BW 43api-298247873No ratings yet
- Chem BW 42Document1 pageChem BW 42api-298247873No ratings yet
- VocabatoonsevolutionDocument1 pageVocabatoonsevolutionapi-298247873No ratings yet
- Med BW 41Document1 pageMed BW 41api-298247873No ratings yet
- Bio BW 40Document1 pageBio BW 40api-298247873No ratings yet
- Med BW 40Document1 pageMed BW 40api-298247873No ratings yet
- Med BW 39Document1 pageMed BW 39api-298247873No ratings yet
- Chem BW 41Document1 pageChem BW 41api-298247873No ratings yet
- Chem BW 40Document1 pageChem BW 40api-298247873No ratings yet
- 03 Neutralization Reactions WorksheetDocument2 pages03 Neutralization Reactions Worksheetapi-298247873No ratings yet