Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MCF 83 EME Fact Sheet Network - Update
Uploaded by
husanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MCF 83 EME Fact Sheet Network - Update
Uploaded by
husanCopyright:
Available Formats
MCF Fact Sheets
How the mobile phone network operates
Mobile phones work by sending and receiving low power radio The location of the base station within the cell is determined by a
signals, much like a 2 way radio system. The signals are sent to number of factors, including topography and other physical
and received from antennas that are attached to radio transmitters constraints such as trees and buildings, the cell capacity or
and receivers, commonly referred to as mobile phone base number of calls expected to be made in the cell, and the radio
stations. The base stations are linked to the rest of the mobile and frequency at which the base station will operate.
fixed phone network and pass the signal/call on into those
Topography and physical constraints
networks.
In essence, a mobile phone needs to have sight of a mobile
What happens when I make a call from phone base station. In other words, the radio signal from the phone
to the base station needs to be uninterrupted. Hills, trees and tall
my mobile phone? buildings can obscure this line of sight and so base stations need
The first step in the process is for the phone to check that there is to be very carefully located to maximise the coverage available.
coverage in the area that the call is made. Once the phone has Cell capacity
verified that there is sufficient signal strength to make the call, the Each base station can only carry a finite number of calls. In areas of
phone establishes a connection with a nearby mobile phone base high mobile phone use, such as central business districts and high
station. This base station then establishes the call and holds the density areas, more base stations are required to handle the level of
call as long as the phone user remains on the call and in the range call traffic. In high use areas, there are often a range of base
of that base station. stations, from very specific in-building solutions (designed to give
quality coverage within a specific building), to very small base
What is a mobile phone base station? stations known as microcells. Microcells cover a small geographic
A mobile phone base station provides coverage to a geographic area and are often found at intersections and in heavy pedestrian
area known as a cell. Cells are aligned next to each other in a traffic areas. In rural areas, or areas where mobile phone use is not
similar pattern to a honeycomb, and it is for this reason that mobile as high, base stations will often be located on hills or tall structures
phone networks are sometimes referred to as cellular networks. to maximise the coverage area.
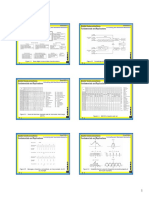
NETWORK STRUCTURE NETWORK COVERAGE EXAMPLE
suburban industrial city base station
heavy usage = more antennas
Indicative illustration only
MCF Fact Sheets
What do people mean when they talk
about second generation (2G) and third
generation (3G) networks?
Radio Frequency 3G, or third generation networks, operate in a different way to 2G
Each base station has a number of radio channels, or frequencies, networks. When a call is made on 2G, a line is held open for the
to communicate with mobile phones. Because this number of users conversation throughout the duration of the call. With 3G
frequencies is limited, frequencies are often reused in adjoining networks, the data sent across them is parcelled up in to little
cells. This is achieved by reducing the power level of the base packets which are reassembled in the correct order at the
station to ensure that there is minimal or no overlap of the coverage receiving end. This smart encoding means more data can be sent
between cells. and it is sent more efficiently. In addition, 3G handsets can be in
contact with more than one base station at a time and this
How does it work if I am moving around? provides improved performances in voice quality and data rates.
Some people call 3G mobile broadband because the evolution is
Calls can be transferred from one base station to another. As you
similar to the difference between dial up internet and the always
move out of the cell, the phone will automatically look for signal
available broadband internet services.
from an adjoining base station. There is usually a smooth transition
or handover from cell to cell. During the duration of a call, the Where can I get more information?
phone may have handed over to and from a number of base
stations. If there is no adjoining base station, such as on the fringes Mobile Carriers Forum
of the mobile phone network, the call will drop out. Email us at contact@mcf.amta.org.au
MCF Contact Details: www.mcf.amta.org.au/pages/Contact.Us
What does a base station do? www.mcf.amta.org.au
GSM Association
A base station connects the call in to the fixed line network.
www.gsmworld.com/health/networks/how.shtml
Depending on the type of call, it will be directed to either another
mobile phone or to a fixed line phone. Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agency
Ph: 03 9433 2211
A base station is made up of antennas connected by cable to
www.arpansa.gov.au/pubs/eme/fact6.pdf
electronic (radio) equipment usually housed in a room or shelter.
Some base stations have radio communications dishes (shaped Australian Communications and Media Authority (ACMA)
like a drum) that connect the base station to the rest of the base Ph: 03 9963 6800
station network. www.acma.gov.au/WEB/STANDARD//pc=PC_310377
CALL TRANSFER PATH
transfer to
anywhere in
the world
antenna
mobile phone
exchange
mobile phone
base station
fixed landline
Indicative illustration only
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- General KnowlwdgeDocument115 pagesGeneral KnowlwdgeMUDASSAR IDRIS98% (44)
- Request For SponsorshipDocument5 pagesRequest For SponsorshipBlessed Arguiñoso MangloNo ratings yet
- APFC Panel DesigningDocument16 pagesAPFC Panel Designingyrmn200% (1)
- Clutches & BrakesDocument17 pagesClutches & BrakesIlias ChahbanNo ratings yet
- Tyco HV Cable and Arresters Ans InsulatorDocument104 pagesTyco HV Cable and Arresters Ans InsulatorRazvan MaresNo ratings yet
- SM PDFDocument607 pagesSM PDFGladwin SimendyNo ratings yet
- Mobile Evolution v1.5.1Document7 pagesMobile Evolution v1.5.1Nae GoguNo ratings yet
- Extracting Text Part Using MATLAB: Poonam Rani, Payal Taneja Daulat SihagDocument3 pagesExtracting Text Part Using MATLAB: Poonam Rani, Payal Taneja Daulat SihaghusanNo ratings yet
- A Matlab Project in Optical Character RecognitionDocument7 pagesA Matlab Project in Optical Character Recognitionsubramanyam62No ratings yet
- Mcna Architecture d794-10184-1 Rev ADocument125 pagesMcna Architecture d794-10184-1 Rev AhusanNo ratings yet
- WeedPestControlConventionalITO13 PDFDocument214 pagesWeedPestControlConventionalITO13 PDFhusanNo ratings yet
- Ltu PB Ex 0613 SeDocument91 pagesLtu PB Ex 0613 SehusanNo ratings yet
- ch02 PDFDocument5 pagesch02 PDFhusanNo ratings yet
- 3g ReportDocument29 pages3g ReportLuc NguyenNo ratings yet
- Examples of Programming in MatlabDocument12 pagesExamples of Programming in Matlabmilad100% (1)
- Mathematics Sample Test Questions BookletDocument15 pagesMathematics Sample Test Questions BookletJohn TingNo ratings yet
- Motorola's STARLINE Cable Simulator Are Used in Place of Fixed Forward Equalizer in Systems Where The Amplifiers Are Located Close TogetherDocument2 pagesMotorola's STARLINE Cable Simulator Are Used in Place of Fixed Forward Equalizer in Systems Where The Amplifiers Are Located Close TogetherRodrigo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Pelco Dome CCTV Camera ics090-CA8Document6 pagesPelco Dome CCTV Camera ics090-CA8Jamie DeltonNo ratings yet
- Pdtech Deltamaxx: Digital Loss Factor/Capacitance Analyzer and Partial Discharge Detector For Test Voltages Up To 50 KVDocument4 pagesPdtech Deltamaxx: Digital Loss Factor/Capacitance Analyzer and Partial Discharge Detector For Test Voltages Up To 50 KVJagadish Babu DegalaNo ratings yet
- Masibus MFT20 R0F 0620 Multi-Function TransducerDocument3 pagesMasibus MFT20 R0F 0620 Multi-Function Transducerparth sapariaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Emerging Nonvolatile Memory Technologies: Nanoreview Open AccessDocument33 pagesOverview of Emerging Nonvolatile Memory Technologies: Nanoreview Open Accessdonald141No ratings yet
- Final CN Lab ManualDocument49 pagesFinal CN Lab Manualharishpillai1994No ratings yet
- Modulos 37 en 1 Arduino GeekcreitDocument14 pagesModulos 37 en 1 Arduino GeekcreitSebastián Retes CalixNo ratings yet
- Drossel EnglishDocument48 pagesDrossel EnglishJuliet SinghNo ratings yet
- ECE 421 Lab4Document39 pagesECE 421 Lab4LuelsonCordovaDeclaradorNo ratings yet
- Ink Viscosity Tester KVST-12 Operation Manual: Serial No.Document10 pagesInk Viscosity Tester KVST-12 Operation Manual: Serial No.liebofreakNo ratings yet
- Military HandbookDocument80 pagesMilitary HandbookLuthfyatma HardyNo ratings yet
- I Dump ProDocument67 pagesI Dump ProYuri Mendonça MarchioriNo ratings yet
- Antminer APW3 Power Supply Repair GuideDocument17 pagesAntminer APW3 Power Supply Repair GuidesalmodantasNo ratings yet
- Ricoh MP2852 PDFDocument93 pagesRicoh MP2852 PDFJohn JuquenNo ratings yet
- ZX95 2536C S+ DashboardDocument6 pagesZX95 2536C S+ DashboardAugusto RadaelliNo ratings yet
- Fujitsu 9RLFW, 12RLFW, 18RLXFW and 24RLXFW HFI Mini Split Systems BrochureDocument2 pagesFujitsu 9RLFW, 12RLFW, 18RLXFW and 24RLXFW HFI Mini Split Systems Brochuree-ComfortUSANo ratings yet
- Skripsi Tanpa Bab Pembahasan PDFDocument65 pagesSkripsi Tanpa Bab Pembahasan PDFYusuf FauziNo ratings yet
- Presentasi MultimeterDocument41 pagesPresentasi MultimetermdNo ratings yet
- String Box LT - 1500V - SB-24-LT04-1500VDocument3 pagesString Box LT - 1500V - SB-24-LT04-1500VAgostino MilaneseNo ratings yet
- Mesa Boogie Mark II-BDocument10 pagesMesa Boogie Mark II-BscheisshandyNo ratings yet
- Stock Statement AUG-18.Document38 pagesStock Statement AUG-18.Atul TiwariNo ratings yet
- GB de CZ EuDocument60 pagesGB de CZ EuConstantin AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Tensile Test ResultsDocument7 pagesTensile Test ResultsImran QayyumNo ratings yet
- Canon Pixma Mp610Document45 pagesCanon Pixma Mp610promatis5746100% (2)
- M100700D - MME For Fanuc 6 - 11 - 12 ManualDocument38 pagesM100700D - MME For Fanuc 6 - 11 - 12 ManualTony AntonyNo ratings yet