0% found this document useful (0 votes)
281 views32 pagesHPLC Principles and Instrumentation
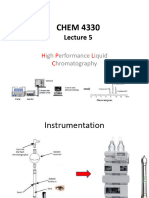
The document discusses high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), including its principles, classifications based on stationary and mobile phases, instrumentation components like pumps, columns, and detectors, and an example procedure for creating standard curves to quantify caffeine concentration in energy drinks. HPLC is an improved form of column chromatography that uses high pressure to force mobile phases through columns for faster separation of sample components.
Uploaded by
Ma. Ellah Patricia M. GutierrezCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
281 views32 pagesHPLC Principles and Instrumentation
The document discusses high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), including its principles, classifications based on stationary and mobile phases, instrumentation components like pumps, columns, and detectors, and an example procedure for creating standard curves to quantify caffeine concentration in energy drinks. HPLC is an improved form of column chromatography that uses high pressure to force mobile phases through columns for faster separation of sample components.
Uploaded by
Ma. Ellah Patricia M. GutierrezCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd