Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bearing Capacity of Soil by Plate LOad Bearing Test
Bearing Capacity of Soil by Plate LOad Bearing Test
Uploaded by
Nimra Khan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesBearing Capacity of Soil by Plate LOad Bearing Test
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBearing Capacity of Soil by Plate LOad Bearing Test
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesBearing Capacity of Soil by Plate LOad Bearing Test
Bearing Capacity of Soil by Plate LOad Bearing Test
Uploaded by
Nimra KhanBearing Capacity of Soil by Plate LOad Bearing Test
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
12, BEARING CAPACITY OF SOIL BY PLATE LOAD BEARL
(CIS : 1888 - 1982 )
2 TEST.
INTRODUCTIO’
This is the method of conducting the load test on soils and the evaluation of bearing
capacities and settlement fiom this test. This method assumes that down to the depth of
influence of stresses the soil strata is reasonably uniform. This should be vetified by
boring or sounding,
Apparatus:
The apparatus consists of bearing plates, loading equipment and instruments to measure
the applied toads and resulting settlement
a) Bearing plates: Consist of a mild steel 75 cm in diameter and 1.5 to 2.5 cm thickness,
and few other plates of same thickness, but smaller diameters (usually 60, 45, 30 and 22.
em dia.) used as stiffeners,
b) Loading equipment: Consist of a reaction or dead load and a hydraulic jack. The
reaction frame may suitable be loaded to give the needed reaction load on the plate. The
load applied may be measured either by a proving ring and dial gauge assembly or a
pressure gauge connected to the output end of the hydraulic jack.
©) Settlement measurements: May be made by means of three or four dial gauges fixed
on the periphery of the bearing plate from an independent datum frame. The datum frame
should be supported far from the loaded area.
Procedure:
The test site is prepared and loose material is removed so that the 75 cm diameter plate
rests horizontally in fill contact with the soil sub-grade. If the modulns of sub-grade
reaction of natural ground is needed, the topsoil may be removed up to a depth of about
20 cm before testing.
The plate is seated accurately and then a seating load equivalent to a pressure of 0.07
kg/cm’ (320 kg for 75 cm diameter plate) is applied and released after a few seconds. The
settlement dial readings are now noted corresponding to zero load. A load is applied by
means of the jack, sufficient to cause an average settlement of about 0.25 mm. When
there is no perceptible increase in settlement or when the rate of settlement is less than
0.025 mm per minute (in the case of soils with high moisture content or in clayey soils)
the load dial reading and the settlement dial readings are noted. The average of the three
(or four) settlement dial readings is taken as the average settlement of the plate
corresponding to the applied load
‘The load is then increased till the average settlement increase to a further amount of
about 0.25 mm, and the load and average settlement readings are noted as before. The
procedure is repeated till the settlement is about 1.75 mm or more.
(Kom
og
‘Mean Bearing Press
° a7 2
Mean Settlement (cm)
A graph is plotted with the mean settlement versus bearing pressure (load per unit area)
as shown in above. The pressure ‘p’ (kg/cm) corresponding to a settlement + = 0.125 em
is obtained from the graph. The modulus of sub grade reaction ‘K’ is calculated fiom the
relation,
You might also like
- 101 Problems in AlgebraDocument160 pages101 Problems in AlgebraTrishaii Cuaresma96% (28)
- Flow Design Formulas For Calculation - Exported From (HTM - 02 - 01 - Part - A)Document8 pagesFlow Design Formulas For Calculation - Exported From (HTM - 02 - 01 - Part - A)wesam allabadi50% (2)
- Business Startup Guides-Preparing Yourself Ver 2Document4 pagesBusiness Startup Guides-Preparing Yourself Ver 2Minh Huỳnh100% (1)
- Calculus Cheat Sheet DerivativesDocument4 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet DerivativesRajatNo ratings yet
- Excercise in FDocument2 pagesExcercise in FPaz Villahoz100% (2)
- ElvisDocument1 pageElvismaui3No ratings yet
- All The Things You AreDocument1 pageAll The Things You ArePeppe LiottaNo ratings yet
- Music To Watch Girls by MJDocument3 pagesMusic To Watch Girls by MJMarvin JongNo ratings yet
- Como Quien Pierde Una Estrella VozDocument2 pagesComo Quien Pierde Una Estrella VozGerardo100% (2)
- Mix Serpiente - BandaDocument53 pagesMix Serpiente - BandaJohn Carlos Vilca VelizNo ratings yet
- GM Relés y Fusibles Corsa PDFDocument1 pageGM Relés y Fusibles Corsa PDFcorylinNo ratings yet
- Mind MappingDocument33 pagesMind MappingManoj Janardan Jayashree TerekarNo ratings yet
- 388 1006 1 PBDocument20 pages388 1006 1 PBGabriel Evangelista dos SantosNo ratings yet
- 5Document2 pages5Abel Salazar PianoNo ratings yet
- Extreme Rhyming Poetry: Over 400 Inspirational Poems of Wit, Wisdom, and Humor (Five Books in One)From EverandExtreme Rhyming Poetry: Over 400 Inspirational Poems of Wit, Wisdom, and Humor (Five Books in One)No ratings yet
- Renault Inyección Electrónica Kangoo RL-RN 1.6 1999 Siemens Sirius 32b PDFDocument2 pagesRenault Inyección Electrónica Kangoo RL-RN 1.6 1999 Siemens Sirius 32b PDFOsvaldo LópezNo ratings yet
- Aural RitmoDocument1 pageAural RitmofabioNo ratings yet
- Renault Inyección Electrónica Clio 1.4 Ac Delco Monopoint P PDFDocument2 pagesRenault Inyección Electrónica Clio 1.4 Ac Delco Monopoint P PDFGood CarNo ratings yet
- Rain Water Harvesting ProjectDocument19 pagesRain Water Harvesting ProjectManoj Janardan Jayashree Terekar100% (1)
- All Art Is Propaganda PDFDocument2,708 pagesAll Art Is Propaganda PDFPau_Brand_255033% (3)
- A Seminar On Rotating BuildingDocument20 pagesA Seminar On Rotating BuildingManoj Janardan Jayashree Terekar81% (16)
- Taita Salasaca - Conga Drums 2Document2 pagesTaita Salasaca - Conga Drums 2Carlos XavierNo ratings yet
- A Case Study of Town PlanningDocument49 pagesA Case Study of Town PlanningManoj Janardan Jayashree Terekar50% (4)
- Xsara 18 - Berlingo 18 - 18 Xu7jb PDFDocument2 pagesXsara 18 - Berlingo 18 - 18 Xu7jb PDFJorge Daniel DiazNo ratings yet
- Tema 6. CULTURADocument7 pagesTema 6. CULTURAMarinaNo ratings yet
- Indian Express 19 AugustDocument20 pagesIndian Express 19 AugustTension Dene kaNo ratings yet
- Escort 18 16 ZetecDocument2 pagesEscort 18 16 ZetecOsvaldo LópezNo ratings yet
- Extracto Destinos-Elementos-para-la-gestión-de-destinos-turisticosDocument76 pagesExtracto Destinos-Elementos-para-la-gestión-de-destinos-turisticosEnzo Navarrete UlloaNo ratings yet
- Tu Me Gustas Trompeta 1Document2 pagesTu Me Gustas Trompeta 1JonathanNo ratings yet
- Hecho Del PíncipeDocument11 pagesHecho Del PíncipeEdisson MoralesNo ratings yet
- 01 - Lista de Parametros SimplificadaDocument8 pages01 - Lista de Parametros SimplificadaLuis Felipe VidigalNo ratings yet
- Enfermeiro Ebsrh 2015Document10 pagesEnfermeiro Ebsrh 2015Neila Reis da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Ampacidad AlimentacionDocument1 pageAmpacidad Alimentacionluis miguel sanchez estrellaNo ratings yet
- Trompeta 2Document2 pagesTrompeta 2Mauricio TorresNo ratings yet
- PDF Parts Catalog Tvs Rockz - CompressDocument104 pagesPDF Parts Catalog Tvs Rockz - CompressaspareteNo ratings yet
- 2020Document14 pages2020mintrikpalougoudjoNo ratings yet
- Building ActDocument136 pagesBuilding ActVeronika RaušováNo ratings yet
- 5756867Document1,027 pages5756867Sách Việt Nam50% (2)
- 09 - Chapter 1Document20 pages09 - Chapter 1Dr. POONAM KAUSHALNo ratings yet
- 6periostitisDocument10 pages6periostitisAntonioNo ratings yet
- Lagenda Violin PDFDocument2 pagesLagenda Violin PDFMarvin Jong0% (1)
- Cicuta Tibia - TubaDocument2 pagesCicuta Tibia - TubaYohan Octavio Vera DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Planes APIDocument10 pagesPlanes APIManuel FigueroaNo ratings yet
- GM Inyección Electrónica S10 Blazer 2.2 Efi Delphi Multec emDocument2 pagesGM Inyección Electrónica S10 Blazer 2.2 Efi Delphi Multec emyayixdfuego131No ratings yet
- Elec 4 BlackDocument1 pageElec 4 Blackyudo08No ratings yet
- Mix Trompeta ChilombianoDocument1 pageMix Trompeta ChilombianoDenise AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Strong Enough - DrumsDocument2 pagesStrong Enough - DrumsКолянсур ИвановNo ratings yet
- Paradise Violín IIDocument2 pagesParadise Violín IIJavier Rubio PérezNo ratings yet
- UTS ELT MDE S1 Coursebook Evaluation ChecklistDocument3 pagesUTS ELT MDE S1 Coursebook Evaluation ChecklistHanin Khalishah WaqqasNo ratings yet
- El Pastor - VihuelaDocument1 pageEl Pastor - VihuelaDamian Guardia SalazarNo ratings yet
- Fiat CoupeDocument1 pageFiat CoupeJulio FaninNo ratings yet
- Trompeta 1Document2 pagesTrompeta 1Mauricio TorresNo ratings yet
- Ibfc 142 Engenheiro MecanicoDocument16 pagesIbfc 142 Engenheiro MecanicoJosé Maria junior100% (2)
- What A Wonderful World Eb - Bass Trombone PDFDocument1 pageWhat A Wonderful World Eb - Bass Trombone PDFJose HerreroNo ratings yet
- Greenwashing Nas EmpresasDocument37 pagesGreenwashing Nas EmpresasLara GagoNo ratings yet
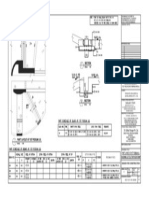
- Detail (1-1) To R.C. Strip Footing (Sf1) : A B E F H J KDocument1 pageDetail (1-1) To R.C. Strip Footing (Sf1) : A B E F H J KThomas Garcia0% (1)
- Los Mareados Arreglo Hernan PossettiDocument2 pagesLos Mareados Arreglo Hernan PossettiteomondejarmusicaNo ratings yet
- Charles D Ghilani - Paul R Wolf - Elementary Surveying - An Introduction To Geomatics-Pearson Prentice Hall (2012) - ExtractoDocument19 pagesCharles D Ghilani - Paul R Wolf - Elementary Surveying - An Introduction To Geomatics-Pearson Prentice Hall (2012) - ExtractoRodrigo DelBarrioNo ratings yet
- What Squirt Teaches Me about Jesus: Kids Learning about Jesus while Playing with FidoFrom EverandWhat Squirt Teaches Me about Jesus: Kids Learning about Jesus while Playing with FidoNo ratings yet
- AskelandPhuleNotes CH07PrintableDocument56 pagesAskelandPhuleNotes CH07PrintableManoj Janardan Jayashree TerekarNo ratings yet
- Soil Reinforcement and FoundationsDocument56 pagesSoil Reinforcement and FoundationsManoj Janardan Jayashree TerekarNo ratings yet
- Source Code For RWHSDocument1 pageSource Code For RWHSManoj Janardan Jayashree TerekarNo ratings yet
- Key Plan: Issued For ConstructionDocument1 pageKey Plan: Issued For ConstructionManoj Janardan Jayashree TerekarNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument3 pagesCase StudyManoj Janardan Jayashree TerekarNo ratings yet
- U.D Fabricator PDFDocument4 pagesU.D Fabricator PDFManoj Janardan Jayashree TerekarNo ratings yet
- Sanjay Puri: Pragatej Builders & Developers Pvt. LTDDocument1 pageSanjay Puri: Pragatej Builders & Developers Pvt. LTDManoj Janardan Jayashree TerekarNo ratings yet
- Iodiversity AND Onservation: Genetic DiversityDocument6 pagesIodiversity AND Onservation: Genetic DiversityManoj Janardan Jayashree TerekarNo ratings yet
- Indias Iniatied PDFDocument2 pagesIndias Iniatied PDFManoj Janardan Jayashree TerekarNo ratings yet
- Class11 Geography1 PhysicalGeography Unit02 NCERT TextBook EnglishEdition PDFDocument8 pagesClass11 Geography1 PhysicalGeography Unit02 NCERT TextBook EnglishEdition PDFManoj Janardan Jayashree TerekarNo ratings yet