Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pierburg 2E3 Functions
Pierburg 2E3 Functions
Uploaded by
Raúl Muñiz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views7 pagescarburador pierburg
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentcarburador pierburg
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views7 pagesPierburg 2E3 Functions
Pierburg 2E3 Functions
Uploaded by
Raúl Muñizcarburador pierburg
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
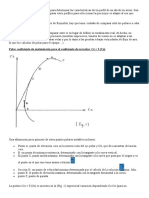
The 263 is a downdraft carburetor without any mixing air recirculation
- Its automatic choke is heated electrically and by coolant
= For a better mixture preparation, the bypass for idle
co mixture is heated.
= The pull-down device regulates the choke flap position
after a cold stare.
= The electromagnetic cut-off valve prevents the engine
from running after it is switched off.
Float chamber ventilation
stage IZ vacuum unit
Pulldown
Electromagnetic
idle cut-off
valve
Heated
bypass
Idle speed screw
Automatic choke
‘Sor Gerbent ieee (electrical and water heated)
The idle speed and co content
can be adjusted by turning in
and out the two adjustment screws
Edie speed co content
Float chanber vent.
‘The float chamber vent is calibrated
by a plastic insert.
Because the vent pipe is tapered,
the pressure in dovn pipe and inside
float chamber is lowered. The vant calibration
allows a limited airflow. This will prevent
fuel spilling from the float chamber.
‘The vapor bubble trap prevents
hot start difficulties.
Bubble-free fuel flows through outlet A
to the carburetor. Vapor bubbles and excess
fuel go through outlet B back to fuel tank
choke flap gap
Second stage
gap adjustment
Diaphragm pull is engaged
In order to avoid an over-rich mixture, the choke flap can be opened by &
specific amount. This is done through the pulldown device
Due to low pressure in the suction pipe, the choke flap is opened using
the pull-diaphragm to an adjustable value to prevent over-enrichment.
Automatic starter
control
Heating coil
Starter
housing
coolant
choke lever
| ceramic noider
Bimetal spring
Due to electrical heating and by the increasing temperature of the coolant,
the bimetal spring is beginning to unwind. The choke flap is gradually opened.
The step cam rotates into its normal position and the throttle plate
is gradually closed by the rapid idle stop screw. At a coolant temperature
of 65° C, a temperature switch cuts the electrical heating of the mixture
in the intake manifold
Tdhing Idling fuel/air et
Electromagnetic
idle cufrott vatve
Heating bypass
Progression slot
uixture screw
(co sere) orittice
Main Jet
Throttle velve is almost closed at idle. The fuel is pre-calibrated by the main
jet for stage I. The idling fuel/air jet reaches to the idling oriffice through
dle cut-off valve. At this time more air is added through a slot to form the
idle mixture, The mixture ratio can be adjusted with the Co-adjusting screw.
The electrical heated bypass prevents carburetor from icing in bad weather.
Idle progression
Idle channel —}
Progression slot d
Idling mixture
oriffice
To achieve a perfect transition from idle to part throttle stage, more holes
are drilled above the idling oriffice in the progression slot area. Tf more gaz
is given, those oriffices are exposed to the vacuum under the throttle valve,
and additional mixture flows from the progression slot into the idle mixing chamber.
Accelerator pump
When throttle valve pivots in the idle position,
‘the diaphragm is pushed outwards by the spring.
The fuel flows into the pump chamber.
Spray nozzle
Pressure relief
valve
Diaphragm
Inlet valve
Pump lever curved cam
During acceleration, the pump lever is actuated by the cam on the throttle
valve shafe and a ted on the diaphragm.
The inlet valve cli ise valve opens the way to the injection tube.
The quantiey of £1 sn be adjusted by rotating the cam.
Air correction jet
Part throttle Pre-atomizer
Main jet
If the throttle valve is opened still further, the drop in pressure is also effective
on the primary system. The fuel metered out by the main jet forms, with the air from
the air correction jet, a pre-mixture, which passes into the mixing chamber via the
pre-atomizer.
The idling mixture oriffice and the progression slot are also still cupplying mixture.
Enrichment,
Part throttle enrichment channel
Enrichment valve,
open
At a predetermined opening of the throttle valve angle, the vacuum in the intake
manifold decreases to such an extent that spring opens the enrichment valve.
Because of this, additional fuel from the float chamber can be fed directly into
the primary system via channels. The supply of pre-mixture from the idling mixture
oriffice and the progression slot becomes less and less until it stops altogether.
Transition to stage II
Transition system
up to a certain position of stage I throttle plate, stage II throttle plate
is locked. If a certain pressure on stage IT diaphragm unit is reached,
stage 11 throttle plate can begin to move. Thereby the transition system
of stage II gets mixture from the main jet of stage II.
Venting Full load enrichment.
Transition air hole
The stage II main system goes to progressive mode, if the lock is removed.
If the pressure drop increases in diffuser area, more and more mixture
is supplied from the main system. At full lead, the full load enrichment
nozzle adds even more mixture to cope with demand.
You might also like
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Keihin CarburetorsDocument33 pagesKeihin CarburetorsRaúl Muñiz100% (1)
- Koil ManualDocument7 pagesKoil ManualRaúl MuñizNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- AnodizadoDocument149 pagesAnodizadoRaúl MuñizNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Gear Cutters 01Document4 pagesGear Cutters 01Raúl MuñizNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Simonit y Sirch Los Pioneros de La Poda para El Bienestar de La Vid - Blog Vila VinitecaDocument8 pagesSimonit y Sirch Los Pioneros de La Poda para El Bienestar de La Vid - Blog Vila VinitecaRaúl MuñizNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- 02 ServiceDocument20 pages02 ServiceRaúl Muñiz100% (1)
- 03 Ford1vDocument8 pages03 Ford1vRaúl MuñizNo ratings yet
- 04 Ford VVDocument15 pages04 Ford VVRaúl MuñizNo ratings yet
- Exploded View of WEBER 34 ICH EURDocument3 pagesExploded View of WEBER 34 ICH EURRaúl MuñizNo ratings yet
- CalendarioTratamientosVID - CalendarioTratamientosVidDocument1 pageCalendarioTratamientosVID - CalendarioTratamientosVidRaúl MuñizNo ratings yet
- PolaresDocument12 pagesPolaresRaúl MuñizNo ratings yet
- How To Make SpringsDocument62 pagesHow To Make Springsrudey18No ratings yet
- Acabado de Pistones - Cilindros PDFDocument7 pagesAcabado de Pistones - Cilindros PDFRaúl MuñizNo ratings yet
- 1816 Temas TecnologicosDocument135 pages1816 Temas TecnologicosJhon CastRoNo ratings yet
- Flash3.0 Nitro enDocument46 pagesFlash3.0 Nitro enRaúl MuñizNo ratings yet
- Os FS-20Document4 pagesOs FS-20Raúl MuñizNo ratings yet