Professional Documents
Culture Documents
15-27 (Genap)
Uploaded by
Imam Ridwan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views2 pagesElemen Mesin 3
Original Title
15-27 (genap)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentElemen Mesin 3
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views2 pages15-27 (Genap)
Uploaded by
Imam RidwanElemen Mesin 3
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
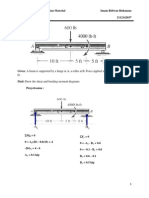
SOLUTION (15.27)
Known: Three spur gears transmit power from a motor shaft to a machine shaft in a
given geometric arrangement. The middle gear acts as an idler and is supported by
‘two bearin
gs.
Find:
(a)
)
(©)
Determine the radial load on idler shaft bearings for a given direction of motor
shaft rotation.
Determine the radial load on the bearings for the motor shaft rotation opposite to
(a).
Give an explanation as to why answers to (a) and (b) are different.
Schematic and Given Data:
Assumptions:
iG
‘The gears mesh along their pitch circles.
2. _ All the gear tooth loads are static and are transmitted at the pitch point.
3. Friction losses in the gears and bearings are negligible.
4. Shaft bending deflections can be neglected.
Analysis:
(@)
Pitch diameter of idler
100 tb tan 20°= 36.4 Ib
100b-in motor orgue__
100%n, motor pinion ras ~ 100
364 tb
100 1b
V¥'136.474 136.47 = 1929
192.9 Ib
Bearing radial loads: Ra = 289 Ib, Rp = 96.1 Ib
(b) Bearing loads are reduced by factor of 90/192.9 to give:
Ra = 135 Ib, Re = 45 Ib
364 1b
1001
364 1b
1001
163.6°+ 63.67 =90b
(©) Reversing direction of rotation reversed tangential forces, causing
tangential and radial components to subtract, rather than add.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Elmes GanjilDocument8 pagesElmes GanjilImam RidwanNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Perancangan Mesin pencacah limbah gelas plastik kapasitas 25 kg/jamDocument50 pagesPerancangan Mesin pencacah limbah gelas plastik kapasitas 25 kg/jamImam RidwanNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Makalah Teknik PemeliharaanDocument26 pagesMakalah Teknik PemeliharaanImam RidwanNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Tugas 2 MKM - Imam Ridwan Rukmana (2112142037)Document11 pagesTugas 2 MKM - Imam Ridwan Rukmana (2112142037)Imam RidwanNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Perpindahan Panas - Imam Ridwan Rukmana - UASDocument12 pagesPerpindahan Panas - Imam Ridwan Rukmana - UASImam RidwanNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Pendekatan MatematikaDocument53 pagesPendekatan MatematikaImam RidwanNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- PorosDocument12 pagesPorosImam RidwanNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Disain Kolektor SuryaDocument43 pagesDisain Kolektor SuryaImam RidwanNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Tugas 4 MKM - Imam Ridwan Rukmana (2112142037)Document10 pagesTugas 4 MKM - Imam Ridwan Rukmana (2112142037)Imam RidwanNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- Modul PPN DTSD PajakDocument0 pagesModul PPN DTSD PajakDesi Purnamasari HadibrataNo ratings yet
- Faktor XDocument10 pagesFaktor XImam RidwanNo ratings yet
- Sambungan ULIR Baut dengan Beban EksentrikDocument11 pagesSambungan ULIR Baut dengan Beban EksentrikpenxBpresidentNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- CVDocument3 pagesCVImam RidwanNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- TraktorDocument9 pagesTraktorMochammad Immam DNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Book 4: Alternating Current Electric CircuitDocument566 pagesBook 4: Alternating Current Electric CircuitMAT JIBRUD100% (3)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Modul Vi Gerak Dan Gaya Dinamika Bagian 2Document10 pagesModul Vi Gerak Dan Gaya Dinamika Bagian 2Destriayu VasistaNo ratings yet
- WeldingDocument3 pagesWeldingImam RidwanNo ratings yet
- 311 830 1 PBDocument7 pages311 830 1 PBAyi UlenNo ratings yet
- 2 03 051 V01Document27 pages2 03 051 V01Imam RidwanNo ratings yet
- TroubleshootingDocument18 pagesTroubleshootingImam RidwanNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- General RemarksDocument1 pageGeneral RemarksImam RidwanNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Check Sheet Inspection Cartoning C2404Document6 pagesCheck Sheet Inspection Cartoning C2404Imam RidwanNo ratings yet
- Langkah Operasi Mesin Bubut Retrofit GSK980TDDocument41 pagesLangkah Operasi Mesin Bubut Retrofit GSK980TDImam Ridwan90% (10)
- Check Sheet Lubricating&Tightening Cartoning C2404Document4 pagesCheck Sheet Lubricating&Tightening Cartoning C2404Imam RidwanNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- LoaderDocument18 pagesLoaderImam Ridwan80% (5)
- 2 00 001 TOC Basic SettingDocument1 page2 00 001 TOC Basic SettingImam RidwanNo ratings yet
- Cartoning C2024Document70 pagesCartoning C2024Imam RidwanNo ratings yet
- Cartoning C2024Document70 pagesCartoning C2024Imam RidwanNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)