Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hartley Oscillator
Uploaded by
kartika_krazeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hartley Oscillator
Uploaded by
kartika_krazeCopyright:
Available Formats
hartley oscillator
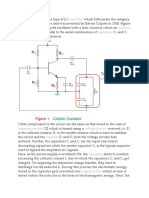
The Hartley oscillator is as popular as Colpitt’s os cillator and is widely used as local oscillator
in radio receivers. The circuit arrangement is shown in figure. Hartley oscillator circuit is similar
to Colpitt’s oscillator circuit, except that phase-shift network consists of two inductors Lr and
L2 and a capacitor C instead of two capacitors and one inductor. The output of the amplifier is
applied across inductor Lx and the voltage across inductor L2 forms the feedback voltage. The coil
L1 is inductively cou pled to coil L2, the combination functions as an auto-transformer. However,
because of direct connec tion, the junction of L1 and L2 cannot be directly grounded. Instead,
another capacitor CL is used. The operation of the circuit is similar to that of the Colpitt’s
oscillator circuit.
Considering the fact that there exists mutual inductance between coils L1 and L2 because the coils
are wound on the same core, their net effective inductance is increased by mutual inductance M.
So in this case effective inductance is given by the expression
L = L1 + L2 + 2 M and resonant or oscillation frequency is given by the expression
F = 1 / 2∏√[C (L1 + L2 + 2M)]
Hartley oscillator can also be suitably used for generating RF signals. The frequency can be easily
varied by varying the inductances which can be done by making the core movable. Another
method of varying frequency is of varying capacitance. Hartley’oscillator is not suitable for low
frequency work because at low frequency, the value of inductance required becomes large.
You might also like
- Ćuk ConverterDocument4 pagesĆuk ConverterSuneet Kumar RathNo ratings yet
- Transformer LabDocument8 pagesTransformer LabAshi GargNo ratings yet
- RF OscillatorsDocument11 pagesRF OscillatorsMohammad Irani0% (1)
- OscillatorsDocument45 pagesOscillatorsAliAbbasNo ratings yet
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsFrom EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Types of Oscillator CircuitsDocument10 pagesTypes of Oscillator CircuitsSam XingxnNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - Oscillator PDFDocument26 pagesCHAPTER 2 - Oscillator PDFMuhd Deen0% (2)
- Colpitts OscillatorDocument11 pagesColpitts Oscillatordinesh189No ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Hartley OscillatorreportDocument8 pagesHartley OscillatorreportirishjoymartinNo ratings yet
- Hartley and Colpitt - S OscillatorDocument7 pagesHartley and Colpitt - S OscillatorT BlackNo ratings yet
- Hartley OscillatorDocument3 pagesHartley OscillatorMoses Phiri100% (1)
- Colpitts OscillatorDocument17 pagesColpitts Oscillatorjerricalday100% (2)
- Analog Mini Project: Topic: Hartley OscillatorDocument4 pagesAnalog Mini Project: Topic: Hartley OscillatorMananRajputNo ratings yet
- Hartley Oscillator WorkingDocument1 pageHartley Oscillator Workingkhairasaab100% (1)
- RF Sine Wave OscillatorsDocument3 pagesRF Sine Wave Oscillatorsmohammed229No ratings yet
- Magnetically Coupled CircuitsDocument53 pagesMagnetically Coupled Circuitsmohsensharifi787980No ratings yet
- Oscillator We Looked at in The Previous Tutorial. Just Like The Hartley Oscillator, The TunedDocument6 pagesOscillator We Looked at in The Previous Tutorial. Just Like The Hartley Oscillator, The TunedXercxis Buendia MolanoNo ratings yet
- PC Chapter 32Document58 pagesPC Chapter 32ultimuNo ratings yet
- 2 3 OscillatorsDocument32 pages2 3 Oscillatorsrobiah zakariaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Tuned OscillatorsDocument25 pagesLesson 3 Tuned OscillatorsOdoch HerbertNo ratings yet
- Colpitts Oscillator Is A Type of LCDocument3 pagesColpitts Oscillator Is A Type of LCVishal BasugadeNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document13 pagesExperiment 1cluj48No ratings yet
- Name: - Edward Felton - SectionDocument10 pagesName: - Edward Felton - SectionedNo ratings yet
- Tuned Collector OscillatorDocument3 pagesTuned Collector OscillatorArvind SharmaNo ratings yet
- Electronics - What Is LC Circuit and Its ApplicationsDocument3 pagesElectronics - What Is LC Circuit and Its ApplicationsJahid TanvirNo ratings yet
- The Buck ConverterDocument6 pagesThe Buck ConverterjiggywiggyNo ratings yet
- Colpitts OscillatorDocument4 pagesColpitts OscillatorAnimesh BhanjaNo ratings yet
- Colpitts Oscillator: Electronic CircuitDocument5 pagesColpitts Oscillator: Electronic CircuitAntonio DiazNo ratings yet
- Unit+14 Electromagnetic+Induction+and+Alternating+Currents PDFDocument17 pagesUnit+14 Electromagnetic+Induction+and+Alternating+Currents PDFSanket PatilNo ratings yet
- RF OSCILLATORS: Colpitts Oscillator Communication Lab تلااصتلاا ر بتخمDocument8 pagesRF OSCILLATORS: Colpitts Oscillator Communication Lab تلااصتلاا ر بتخمAliNo ratings yet
- Hid IgniterDocument6 pagesHid IgniterTNo ratings yet
- RF Oscillators: Experiment 1Document11 pagesRF Oscillators: Experiment 1Emil Eugene DomingoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - LC OscillatorsDocument37 pagesLecture 6 - LC Oscillatorsyoussef hossamNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current Revision Notes - Free PDF DownloadDocument17 pagesJEE Main Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current Revision Notes - Free PDF DownloadVineela SuthakaniNo ratings yet
- 4 OscillatorsDocument12 pages4 OscillatorsTeshale AlemieNo ratings yet
- LC Oscillators: Theory, Design and Trend: ECE 1371 Term PaperDocument15 pagesLC Oscillators: Theory, Design and Trend: ECE 1371 Term Paperaustin_lee_37No ratings yet
- Transformer Lab: Department of Electrical and Systems EngineeringDocument8 pagesTransformer Lab: Department of Electrical and Systems EngineeringKwaku HumbleNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02Document21 pagesLecture 02Abd El-Rahman DabbishNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 7: Name - Nitin Bohra Roll NO. - 13687Document8 pagesExperiment - 7: Name - Nitin Bohra Roll NO. - 13687Mohit RaoNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document49 pagesCH 2meseret sisayNo ratings yet
- Boost Converter ConfigurationDocument7 pagesBoost Converter Configurationultrakill rampageNo ratings yet
- Wireless EnergyDocument21 pagesWireless Energyskysurfer windsurferNo ratings yet
- Tuned Amplifier 1Document11 pagesTuned Amplifier 1Rahul GuhaNo ratings yet
- 1 APC Self InductanceDocument36 pages1 APC Self Inductanceapmishra1000% (2)
- 7 Hartly & Collpit PDFDocument13 pages7 Hartly & Collpit PDFengineerluv100% (1)
- An LC CircuitDocument11 pagesAn LC CircuitHRM, BAPEXNo ratings yet
- RLC NotesDocument4 pagesRLC Noteskerala pscNo ratings yet
- Hartley Oscillator: Project ProposalDocument9 pagesHartley Oscillator: Project Proposal24.Sophiah Resky AnandaNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of The Resonant Converter For Low Output Current RippleDocument9 pagesAnalysis and Design of The Resonant Converter For Low Output Current Rippleroughdraft2020No ratings yet
- Oscillators Module 02Document22 pagesOscillators Module 02ntinaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 28Document2 pagesLesson 28e5865domingoascotbaguioNo ratings yet
- Hartley OscillatorDocument4 pagesHartley OscillatorHRM, BAPEXNo ratings yet
- Hartley OscillatorDocument3 pagesHartley OscillatorJunaid AleemNo ratings yet
- Oscillators Module 02Document20 pagesOscillators Module 02ervaishu5342100% (1)
- Phys 106: General Physics 2: Chapter IV: InductanceDocument63 pagesPhys 106: General Physics 2: Chapter IV: InductancehwuhwuheNo ratings yet
- 4.2.3 Resonant FiltersDocument33 pages4.2.3 Resonant Filtersventricebarrett14No ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Alternating Current Short QuestionDocument3 pagesChapter 16 Alternating Current Short Questiondaniyal.king55No ratings yet
- Battery Eliminator: High Voltage Alternating CurrentDocument12 pagesBattery Eliminator: High Voltage Alternating CurrentAnishka KadiyanNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four InductanceDocument11 pagesChapter Four Inductanceبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Women in ScienceDocument5 pagesWomen in Sciencekartika_krazeNo ratings yet
- Digital Support Systems: Conceptual Model of DssDocument7 pagesDigital Support Systems: Conceptual Model of Dsskartika_krazeNo ratings yet
- Classification of Embedded Systems Three Types of Embedded Systems AreDocument24 pagesClassification of Embedded Systems Three Types of Embedded Systems Arekartika_krazeNo ratings yet
- Embedded System Design: Narina Thakur Bharti Vidyapeeth's College of Engineering Dept of Computer ScienceDocument45 pagesEmbedded System Design: Narina Thakur Bharti Vidyapeeth's College of Engineering Dept of Computer Sciencekartika_krazeNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Systems: - A Brief Run DownDocument28 pagesMicroprocessor Systems: - A Brief Run Downkartika_krazeNo ratings yet
- NE555 Pulse Code ModulationDocument6 pagesNE555 Pulse Code ModulationmihaelklajnerNo ratings yet