0% found this document useful (0 votes)
840 views28 pagesMobile Android Hacking
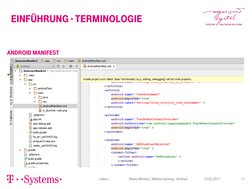
This document provides an overview of mobile hacking on Android devices. It introduces key Android concepts like activities, services, content providers, and broadcast receivers. It explains how these components interact through intents and how they are declared in the Android manifest. It then discusses common vulnerabilities like exported activities, unsecured broadcast receivers, insecure content providers, and intent sniffing. It also mentions sensitive data stored in hardcoded strings or insecure local storage. The document recommends tools for static and dynamic analysis and decompiling apps to find issues. Finally, it provides examples of mobile hacking research from security conferences.
Uploaded by
KhairiBudayawanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
840 views28 pagesMobile Android Hacking
This document provides an overview of mobile hacking on Android devices. It introduces key Android concepts like activities, services, content providers, and broadcast receivers. It explains how these components interact through intents and how they are declared in the Android manifest. It then discusses common vulnerabilities like exported activities, unsecured broadcast receivers, insecure content providers, and intent sniffing. It also mentions sensitive data stored in hardcoded strings or insecure local storage. The document recommends tools for static and dynamic analysis and decompiling apps to find issues. Finally, it provides examples of mobile hacking research from security conferences.
Uploaded by
KhairiBudayawanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Einleitung
- Schwachstellen
- Tools