Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Finance Chap 6 Notes
Uploaded by
thebfiles0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageStrategic Financial Management
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentStrategic Financial Management
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageFinance Chap 6 Notes
Uploaded by
thebfilesStrategic Financial Management
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
FIN 427
Chapter 6
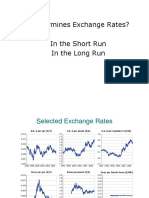
Production Opportunities Yield Curve
the investment opportunities in productive (cash- a graph showing the relationship between bond yields
generating) assets and maturities
Time Preferences for Consumption Normal Yield Curve
the preferences of consumers for current an upward-sloping yield curve
consumption as opposed to saving for future
consumption Inverted Abnormal Yield Curve
a downward-sloping yield curve
Risk
in a financial market context, the chance that an Humped Yield Curve
investment will provide a low or negative return a yield curve where interest rates on intermediate-
term maturities are higher than rates on both short-
Inflation and long-term maturities
the amount by which prices increase over time
Pure Expectations Theory
Real Risk-Free Rate of Interest, r* a theory that states that the shape of the yield curve
the rate of interest that would exist on default-free depends on investors expectations about future
U.S. Treasury securities of no inflation were expected interest rates
Nominal (Quoted) Risk-Free Rate, rRF Foreign Trade Deficit
the rate of interest on a security that is free of all risk; the situation that exists when a country imports more
rRF is proxied by the T-bill rate or the T-bond rate. than it exports
rRF includes an inflation premium
Inflation Premium (IP)
a premium equal to expected inflation that investors
add to the real risk-free rate of return
Default Risk Premium (DRP)
the difference between the interest rate on a U.S.
Treasury bond and a corporate bond of equal maturity
and marketability
Liquidity Premium (LP)
a premium added to the equilibrium interest rate on a
security if that security cannot be converted to cash
on short notice and at close to its fair market value.
Interest Rate Risk
the risk of capital losses to which investors are
exposed because of changing interest rates
Maturity Risk Premium (MRP)
a premium that reflects interest rate risk
Reinvestment Rate Risk
the risk that a decline in interest rates will lead to
lower income when bonds mature and funds are
reinvested
Term Structure of Interest Rates
the relationship between bond yields and maturities
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Research in Public AdministrationDocument14 pagesResearch in Public AdministrationthebfilesNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Theories For Research in Public Administration: January 2018Document28 pagesTheories For Research in Public Administration: January 2018thebfilesNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Evaluating Satisfaction of Citizens On Quality of Public Administration Services in The Central Highlands of VietnamDocument7 pagesEvaluating Satisfaction of Citizens On Quality of Public Administration Services in The Central Highlands of VietnamthebfilesNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Commercial LawDocument61 pagesCommercial LawthebfilesNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- PSA Hiring Area of Assignment PDFDocument13 pagesPSA Hiring Area of Assignment PDFthebfilesNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Exchange RatesDocument34 pagesExchange RatesthebfilesNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Balance Sheet: AssetsDocument6 pagesBalance Sheet: AssetsthebfilesNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Taxation Chapter 7Document13 pagesTaxation Chapter 7thebfilesNo ratings yet
- Taxation Chapter 3Document5 pagesTaxation Chapter 3thebfilesNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- LPS Conservatorship HandboodDocument313 pagesLPS Conservatorship Handboodadrucker100% (1)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Artesianaustralianventurecapitalfund 170819143939Document31 pagesArtesianaustralianventurecapitalfund 170819143939xxNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Aoi TemplateDocument4 pagesAoi TemplateAm MartinNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- How To Download Fundamentals of Investing Pearson Series in Finance Ebook PDF Version Ebook PDF Docx Kindle Full ChapterDocument36 pagesHow To Download Fundamentals of Investing Pearson Series in Finance Ebook PDF Version Ebook PDF Docx Kindle Full Chapterannie.root658100% (27)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- First Security Islami Bank LTD/ Ratio AnalysisDocument22 pagesFirst Security Islami Bank LTD/ Ratio AnalysisManzurul KarimNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Renbud Computer Services CoDocument7 pagesRenbud Computer Services CoMonica Rosa LinaNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Advanced Auditing Final Exam-Group QuestionsDocument12 pagesAdvanced Auditing Final Exam-Group QuestionsAnna FlemingNo ratings yet
- Investment in Equity - MCDocument5 pagesInvestment in Equity - MCLeisleiRago100% (1)
- Afwijzing MylanDocument10 pagesAfwijzing MylanAnonymous Hnv6u54HNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Shivangi Digant ShahDocument10 pagesShivangi Digant ShahSabari Nathan MariappanNo ratings yet
- Athleta Memo V1 DraftDocument5 pagesAthleta Memo V1 Draftuygh gNo ratings yet
- K (D1/P0) + G: WockhardtDocument2 pagesK (D1/P0) + G: WockhardtYYASEER KAGDINo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Pre Quali 2019Document9 pagesPre Quali 2019Haidie DiazNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Slides s06 2Document50 pagesWeek 1 Slides s06 2Pallavi ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Concept Questions: Chapter Five Accrual Accounting and Valuation: Pricing Book ValuesDocument40 pagesConcept Questions: Chapter Five Accrual Accounting and Valuation: Pricing Book ValuesMd MirazNo ratings yet
- BankruptcyDocument18 pagesBankruptcySheila Mae MalesidoNo ratings yet
- Basic Requirements and Procedure in Registering A CorporationDocument3 pagesBasic Requirements and Procedure in Registering A CorporationAnnie Lara BarzagaNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Chapter Fourteen: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument26 pagesChapter Fourteen: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinAdityaPutriWibowoNo ratings yet
- Loan Amortization Schedule1Document9 pagesLoan Amortization Schedule1api-354658624No ratings yet
- Instapdf - in Hindenburg Research Adani Report 192Document137 pagesInstapdf - in Hindenburg Research Adani Report 192Fasi HaiderNo ratings yet
- Air Products Ar2018 PDFDocument148 pagesAir Products Ar2018 PDFTrường TùngNo ratings yet
- Adjusting Entries v1Document7 pagesAdjusting Entries v1mpro61640% (5)
- QuestionairDocument5 pagesQuestionairpavangoldNo ratings yet
- Features of Stock ExchangeDocument19 pagesFeatures of Stock ExchangeTarn JeetNo ratings yet
- 11th Annual Real Estate Investment World Asia 2012Document15 pages11th Annual Real Estate Investment World Asia 2012LfaFerrariNo ratings yet
- Inner Circle Trader - TPDS 4Document2 pagesInner Circle Trader - TPDS 4Felix Tout CourtNo ratings yet
- FRM Part I - VAR & Risk ModelsDocument17 pagesFRM Part I - VAR & Risk Modelspradeep johnNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Cbse Accountancy Question Paper 2007Document23 pagesClass 12 Cbse Accountancy Question Paper 2007Sunaina RawatNo ratings yet
- Strategy Index 10 UpdateDocument1 pageStrategy Index 10 UpdateChanuka PrabhashNo ratings yet
- Advanced Accounting 7e Hoyle - Chapter 6Document13 pagesAdvanced Accounting 7e Hoyle - Chapter 6Leni RosiyaniNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)