0% found this document useful (0 votes)
154 views1 pageDirect Instruction
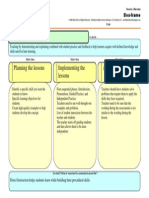
Direct instruction is a classroom teaching model that uses explicit curriculum design and delivery, often including scripted teaching that focuses on developing students' skills. It assesses learning. Direct instruction can benefit low-achieving students, English learners, and those from diverse backgrounds. It has three key components: program design to develop necessary skills; instructional organization for content delivery; and student-teacher interactions for learning content.
Uploaded by
api-366876366Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
154 views1 pageDirect Instruction
Direct instruction is a classroom teaching model that uses explicit curriculum design and delivery, often including scripted teaching that focuses on developing students' skills. It assesses learning. Direct instruction can benefit low-achieving students, English learners, and those from diverse backgrounds. It has three key components: program design to develop necessary skills; instructional organization for content delivery; and student-teacher interactions for learning content.
Uploaded by
api-366876366Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd