Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pages From School of Pe-2
Uploaded by
la0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pagej
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentj
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pagePages From School of Pe-2
Uploaded by
laj
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
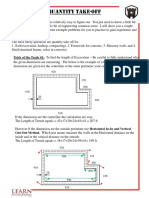
EEE of PE
Shrinkage: A soil decreases in volume when it is compacted
Shrinkage Shrinkage
Density Volume
Shrinkage%)= [7 BankDensiy 4) xT00) | Vesnsoaes™ [100% = Ye shrinkage) Veen
‘Shrinkage factor = 1 — Shrinkage (% decimal) Compacted Volume =
Bank volume x Shrinkage factor
The preceding can be applied to an example of an earthwork operator excavating wet
clay. Assume its initial bank density to be 3,500 pounds per cubic yard and its
excavated loose density to be 2,800 pounds per cubic yard. One ton of this soil (2,000
pounds) would occupy 0.57 (2000-Ib / 3500-Ib = .57) bank cubic yard in the ground
while its hauled or stockpiled volume would be 0.74 (2000 / 2800 = .71) loose cubic
yard. This analysis results in a swell factor of 25% (2800 / 3500 = 0.80; 0.80 “= 25%).
Its related load factor would be 0.80 (remember that 0.80 x 3500 = 2800).
Suppose further that this clay is used to construct a landfill cover using compaction as
described above thereby reducing its volume to 0.53 cubic yard (given). The shrink
factor, then, would be 0.93 (0.53 / 0.57 = 0.93).
For planning purposes, the earthwork contractor will have to assume that for every 100
cubic yards he excavates he will need to haul 125 cubic yards so that he will be able to
place 93 cubic yards. All of these numbers affect his bottom line. The first determines
the amount of the excavation effort, the second determines his hauling requirements
and the third determines the overall cost of the finished project.
Thitial Converted to:
Soil Type_|Soil Condition| Bank | Loose [Compacted|
(Clay Bank 1001.27 0.90
Loose 0791.00 O74
‘Compacted 711 Tat 1.00
[Common Earth Bank. 4001.25 0.90 The TABLE illustrates
Loose 0.20 1.00 072
Conpaced aT 35 TOT] Soil in a variety of states.
[Rock (Blasted) Bank 1001.50 7.30
Loose 0671.00 0.87
‘Compacted O77 1.15 1.00
Sand Bank 1.00 1-12, 0.95
Loose 0.89 1.00 0.85
‘Compacted 1051.18 7.00)
Ea Chapter 1 — Surveying |
ris copy is given to the flowing student as par of School af
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The 25 Most Difficult Questions You'll Be Asked On A Job InterviewDocument6 pagesThe 25 Most Difficult Questions You'll Be Asked On A Job InterviewNakul SehgalNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- ACI 304R-00 Guide For Measuring, Mixing, Transporting, and Placing ConcreteDocument41 pagesACI 304R-00 Guide For Measuring, Mixing, Transporting, and Placing Concretebonnico75% (4)
- The Steps Involved in Cost Estimating AreDocument4 pagesThe Steps Involved in Cost Estimating ArelaNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint, PresentationDocument8 pagesPowerPoint, PresentationlaNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint Present,,AtionDocument7 pagesPowerPoint Present,,AtionlaNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint P, ResentationDocument3 pagesPowerPoint P, ResentationlaNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint Prese,,,NtationDocument6 pagesPowerPoint Prese,,,NtationlaNo ratings yet
- PowerPkoint PresentationDocument4 pagesPowerPkoint PresentationlaNo ratings yet
- ASD LRFD Structural Wood Design Solved Example Problems 2005 EditionDocument452 pagesASD LRFD Structural Wood Design Solved Example Problems 2005 EditionTABIBI1150% (4)
- PowerPkoint PresentationDocument4 pagesPowerPkoint PresentationlaNo ratings yet
- Soil Classification PDFDocument11 pagesSoil Classification PDFSivadol VongmongkolNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint PresentationDocument16 pagesPowerPoint PresentationlaNo ratings yet
- 2Document37 pages2laNo ratings yet
- E WW GS/ (Ws S)Document1 pageE WW GS/ (Ws S)laNo ratings yet
- Civ STR April 2015 With Design Standards - Rev4Document6 pagesCiv STR April 2015 With Design Standards - Rev4laNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 - 001Document26 pagesExam 1 - 001Jose Carlos ArgeñalNo ratings yet
- Pages From SCHOOL OF PE-2 PDFDocument1 pagePages From SCHOOL OF PE-2 PDFlaNo ratings yet
- Act Act: M KG LL M KG DLDocument4 pagesAct Act: M KG LL M KG DLlaNo ratings yet
- Act Act: M KG LL M KG DLDocument4 pagesAct Act: M KG LL M KG DLlaNo ratings yet
- 1 Slab 6Document3 pages1 Slab 6laNo ratings yet
- Engineering Properties-State of Connecticut New HavenDocument7 pagesEngineering Properties-State of Connecticut New HavenlaNo ratings yet
- Kani Method .Document8 pagesKani Method .laNo ratings yet
- Act Act: M KG LL M KG DLDocument4 pagesAct Act: M KG LL M KG DLlaNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Risk Assessment and Hazard MitigationDocument1 pageEarthquake Risk Assessment and Hazard MitigationlaNo ratings yet
- Chap 0Document7 pagesChap 0laNo ratings yet
- Pages From School of PeDocument1 pagePages From School of PelaNo ratings yet
- Homework 1Document1 pageHomework 1laNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabuslaNo ratings yet