Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Harmonics
Uploaded by
tatyarao6538Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Harmonics
Uploaded by
tatyarao6538Copyright:
Available Formats
Harmonics
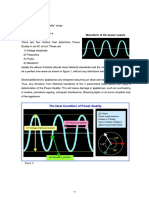
Fundamental Wave
The waveform in a non-sinusoidal wave having frequency at which the system is designed and is
expected to run and/or is being operated is known as fundamental wave. The corresponding
frequency is called fundamental frequency. Fundamental wave is a pure sine wave having
fundamental frequency. In some part of the world like India fundamental frequency is 50 Hz and
other existing value is 60 Hz. Let f be the fundamental frequency in current waveforms, then
fundamental component of current will be
where, I1 is amplitude of fundamental component of current.
Harmonics
Waveforms in a non-sinusoidal wave having frequencies other than fundamental frequency are
called harmonics. The frequency of each harmonic component is known as harmonic frequency. In
most of the cases of periodic and well dened waves, where waveform can be expressed by Fourier
series, harmonic frequencies are integer multiple of fundamental frequency (however it may be
fractional). The integer
factor is known as the order of harmonic component. Let n be the order, then n will be 1, 2, 3, ...,
etc. Harmonic component of current of order n can be represented as
Where In is the amplitude of harmonic component of order n. Integer harmonics are divided into
two categories: odd harmonics and even harmonics. Other than integer harmonics there are sub and
inter harmonics where n is fractional.
Odd Harmonics Integer harmonics having frequencies which are odd integer multiple of
fundamental frequency are known as odd harmonics. Odd harmonics may be expressed as
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Mobile Beat - Top 200Document30 pagesMobile Beat - Top 200HawaiishamanNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- French Canadian Folk MusicDocument3 pagesFrench Canadian Folk MusicClaudia Lorena Duque Villa33% (3)
- Battle of The Bands Mechanics and FormDocument3 pagesBattle of The Bands Mechanics and FormRenjiro Sahn100% (2)
- Laments in The Early Operas of FrancescDocument67 pagesLaments in The Early Operas of FrancescSergio VittadiniNo ratings yet
- WrightDocument2 pagesWrighttatyarao6538No ratings yet
- How To Book LPG Gas From Whatsapp: by 9scroob TeamDocument6 pagesHow To Book LPG Gas From Whatsapp: by 9scroob Teamtatyarao6538No ratings yet
- Breakdown Voltage and Its in Uencing FactorsDocument1 pageBreakdown Voltage and Its in Uencing Factorstatyarao6538No ratings yet
- DesignDocument1 pageDesigntatyarao6538No ratings yet
- Ed195793 PDFDocument5 pagesEd195793 PDFtatyarao6538No ratings yet
- Schedule of Rates: Nagpur & Amravati RegionDocument3 pagesSchedule of Rates: Nagpur & Amravati Regiontatyarao6538No ratings yet
- Lectromagnetic TransientDocument2 pagesLectromagnetic Transienttatyarao6538No ratings yet
- System EnggDocument2 pagesSystem Enggtatyarao6538No ratings yet
- Marcel ApplicationsDocument2 pagesMarcel Applicationstatyarao6538No ratings yet
- Methos in AnalysisDocument2 pagesMethos in Analysistatyarao6538No ratings yet
- ControlDocument2 pagesControltatyarao6538No ratings yet
- Quality 6310 MonitorDocument2 pagesQuality 6310 Monitortatyarao6538No ratings yet
- Introduction SystemsDocument2 pagesIntroduction Systemstatyarao6538No ratings yet
- Introduction SystemsDocument2 pagesIntroduction Systemstatyarao6538No ratings yet
- Practice Vol 2 Warigton PDFDocument1 pagePractice Vol 2 Warigton PDFtatyarao6538No ratings yet
- Relaying TheoryDocument3 pagesRelaying Theorytatyarao6538No ratings yet
- Powystem IngDocument3 pagesPowystem Ingtatyarao6538No ratings yet
- January February March April May June July August September October November DecemberDocument1 pageJanuary February March April May June July August September October November Decembertatyarao6538No ratings yet
- Advanced Power SystemDocument1 pageAdvanced Power Systemtatyarao6538No ratings yet
- Electrical in Power SystemsDocument3 pagesElectrical in Power Systemstatyarao6538No ratings yet
- Canon ImageCLASS MF244dwDocument2 pagesCanon ImageCLASS MF244dwtatyarao6538No ratings yet
- Power SystemDocument1 pagePower Systemtatyarao6538No ratings yet
- Advanced Power System ProtectionDocument1 pageAdvanced Power System Protectiontatyarao6538No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Music 1Document7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Music 1Maria Victoria Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- R&P Guitar Grade 3 - Session Skills SamplesDocument3 pagesR&P Guitar Grade 3 - Session Skills SamplesNischal PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Interchange5thEd IntroLevel Unit11 Listening WorksheetDocument2 pagesInterchange5thEd IntroLevel Unit11 Listening Worksheethugo_mcNo ratings yet
- Chopsticks - Euphemia Allen Easy PianoDocument1 pageChopsticks - Euphemia Allen Easy Pianovelizdevillacruz091110No ratings yet
- Do You KNow Where You'Re Going ToDocument4 pagesDo You KNow Where You'Re Going ToANNLNo ratings yet
- Paradisi Sonata No6 ToccataDocument2 pagesParadisi Sonata No6 ToccataClaudio PerelliNo ratings yet
- Trumpet Quartet - Fugue in G Minor Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart Con Clarin e Flauti Prova 01Document38 pagesTrumpet Quartet - Fugue in G Minor Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart Con Clarin e Flauti Prova 01felix.gNo ratings yet
- In The Hall of The Mountain King - 3 - 3 - Score and PartsDocument11 pagesIn The Hall of The Mountain King - 3 - 3 - Score and PartsOliviaWienertNo ratings yet
- Categorical Auditory Working Memory in CrowsDocument17 pagesCategorical Auditory Working Memory in CrowsStacey KrellerNo ratings yet
- Ragheb AlamaDocument1 pageRagheb AlamaMiami's L Word تNo ratings yet
- Europe Week: A Journey Through Albania's Cultural Heritage and Natural Wonders ProgrammeDocument8 pagesEurope Week: A Journey Through Albania's Cultural Heritage and Natural Wonders ProgrammeAndi PilinciNo ratings yet
- Samba Dees - Alto 2 PartDocument3 pagesSamba Dees - Alto 2 Part_hypermusicNo ratings yet
- Ahmed Saad Session 3-1Document3 pagesAhmed Saad Session 3-1Ahmed GamalNo ratings yet
- Diddy Kong Racing - Frosty VillageDocument2 pagesDiddy Kong Racing - Frosty VillageAustin StoddardNo ratings yet
- Apologize Guitar TabDocument4 pagesApologize Guitar TabWill HarrisonNo ratings yet
- Para Diddle FunkDocument2 pagesPara Diddle Funkscribdpintor100% (2)
- Hum 01 UNIT 5 Lessons 12 and 3Document17 pagesHum 01 UNIT 5 Lessons 12 and 3Bj Apostol QuejaNo ratings yet
- The Girl at Midnight by Melissa GreyDocument24 pagesThe Girl at Midnight by Melissa GreyRandom House Teens80% (5)
- Communication Skills Ii: PEL 131 UNIT-4Document30 pagesCommunication Skills Ii: PEL 131 UNIT-4boltNo ratings yet
- Orient-Occident 1200 - 1700, 2006. Ensemble Hesperion XXI, Direction Jordi Savall. LabelDocument1 pageOrient-Occident 1200 - 1700, 2006. Ensemble Hesperion XXI, Direction Jordi Savall. LabelJuan Sebastian CorreaNo ratings yet
- Advent & Christmas Songs (COMPLETE)Document222 pagesAdvent & Christmas Songs (COMPLETE)Anima PurpleNo ratings yet
- Patapon WalkthroughDocument31 pagesPatapon Walkthroughdp_paulNo ratings yet
- Nights in White Satin ChordsDocument3 pagesNights in White Satin Chordsfralab3132No ratings yet
- 21st Century ReportDocument21 pages21st Century ReportJecellaEllaServanoNo ratings yet
- BINISLAKAN (Done)Document8 pagesBINISLAKAN (Done)Amata, Basha Marie L.50% (2)