Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Implementing and Evaluating Change Using Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA)
Uploaded by
Rock BandOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Implementing and Evaluating Change Using Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA)
Uploaded by
Rock BandCopyright:
Available Formats
Implementing and evaluating change using Plan-Do-
Study-Act (PDSA)
A summary of
How to cite this NCCMT summary:
National Collaborating Centre for Methods and Tools (2017). Implementing and
evaluating change using Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA). Hamilton, ON: McMaster University.
(Updated 01 September, 2017) Retrieved from
http://www.nccmt.ca/resources/search/273.
Categories: Date posted: Date updated:
Tool, Implement, Evaluate, Organizational change February 27, 2017 September 1, 2017
Tool
Relevance For Public Health
Originally, the PDSA approach was developed by the Associates in Process Improvement as a general
framework. The PDSA cycle can be used, for example, to optimize the implementation of an automated cancer
screening outreach program as part of standard health care (See Supplementary resources: "Applying the plan-
do-study-act (PDSA) approach in pragmatic research with safety net health centers."
Description
The Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) framework is a model for testing change to evaluate whether a series of decisions
or activities have resulted in improvement.
The PDSA framework, also known as the Model for Improvement, is at the core of the Institute for Healthcare
Improvement's approach to quality improvement (IHI-QI).
The PDSA framework is based on experiential learning and guiding purposeful action. It outlines three clarifying
questions and the PDSA cycle. The PDSA framework is intended to help implement and evaluate a desired
change. The process typically involves conducting several different "tests of change" followed by systematically
documenting, optimizing, re-testing, and re-evaluating the iterative PDSA cycles (those that are predicted to
lead to sustained improvement) using the PDSA worksheet as a tool.
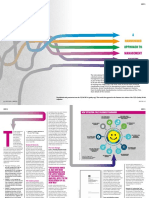
The PDSA cycle includes the following stages:
Plan: Develop a plan to test the desired change
Do: Carry out the test
Study: Observe and learn from the consequences
Act: Determine what modifications should be made to the test
Though the PDSA is at the core of the IHI-QI it is not synonymous with its efforts. Other notable quality
improvement methods include the method of "Lean." A document that compares Lean and quality improvement
is provided here.
Implementing the Tool
Who is Involved?
Implementing this framework could involve program leads, project leads, managers and staff.
Steps for Using Tool
The PDSA framework outlines an algorithm that is designed to help achieve an aim at any scale. As users work
through the PDSA steps, the algorithm can be used as a tool for gaining practical knowledge. Moreover, it helps
users to dissect their perceived understanding of how to accelerate improvement in clinical health care settings
while also allowing immediate, sequential testing of changes.
The main ideas of the PDSA approach are as follows:
Questions are at the root of testing change.
Success of small changes can lead to wide-spread implementation of change.
Informed action drives improved results.
These summaries are written by the NCCMT to condense and to provide an overview of the resources listed in the Registry of Methods and Tools and to give suggestions
for their use in a public health context. For more information on individual methods and tools included in the review, please consult the authors/developers of the original
resources.
National Collaborating Centre for Methods and Tools | www.nccmt.ca Page 1
Conditions for Use
Need to register (free).
2017 Institute for Healthcare Improvement
Evaluation and Measurement Characteristics
Evaluation
Information not available
Validity
Not applicable
Reliability
Not applicable
Methodological Rating
Not applicable
Tool Development
Developers
Associates in Process Improvement
Website: www.apiweb.org
Method of Development
Release Date
Contact Person
Institute for Healthcare Improvement
20 University Road, 7th Floor
Cambridge, USA 02138
Phone: (617) 301-4800 and toll-tree: (866) 787-0831
Fax: (617) 301-4848
Email: info@ihi.org
Resources
Title of Primary
PDSA worksheet for testing change
Resource
File Attachment None
Web-link http://www.ihi.org/resources/Pages/Tools/PlanDoStudyActWorksheet.aspx
Reference
Type of Material Document
Format On-line Access
Cost to Access None.
Language English
Need to register (free).
Conditions for Use
2017 Institute for Healthcare Improvement
These summaries are written by the NCCMT to condense and to provide an overview of the resources listed in the Registry of Methods and Tools and to give suggestions
for their use in a public health context. For more information on individual methods and tools included in the review, please consult the authors/developers of the original
resources.
National Collaborating Centre for Methods and Tools | www.nccmt.ca Page 2
Title of Supplementary
Institute for Healthcare Improvement
Resource
File Attachment None
Web-link http://www.ihi.org/Pages/default.aspx
Reference
Type of Material Website
Format On-line Access
Cost to Access None.
Language English
Conditions for Use 2017 Institute for Healthcare Improvement
Title of Supplementary Applying the plan-do-study-act (PDSA) approach in pragmatic research with safety
Resource net health centers
File Attachment 51727_Plan-Do-Study-Act_Petrik-Rev.pdf
Web-link https://www.kpchr.org/stopcrc/
Petrik, A.F., Coury, J., Schneider, J.L., Rivelli, J.S., Seibel, E., D'Agostini, B., et al.
Reference (2016). Applying the plan-do-study-act (PDSA) approach in pragmatic research with
safety net health centers (poster presentation). 9th Annual Conference on the
Science of Dissemination and Implementation. December 14-16, 2016.
Type of Material Poster presentation
Format Pdf
Cost to Access None.
Language English
Conditions for Use 2016 Kaiser Permanente Center for Health Research
Title of
Supplementary Comparing Lean and quality improvement
Resource
File
None
Attachment
Web-link https://www.med.unc.edu/pediatrics/quality/documents/IHIComparingLeanandQIWhitePaper.pdf
Reference Scoville, R. & Little, K. (2014). Comparing Lean and quality improvement. IHI White Paper.
Cambridge, Massachusetts: Institute for Healthcare Improvement; 2014.
Type of
Document
Material
Format On-line Access
Cost to Access None.
Language English
Conditions for
Use 2014 Institute for Healthcare Improvement
These summaries are written by the NCCMT to condense and to provide an overview of the resources listed in the Registry of Methods and Tools and to give suggestions
for their use in a public health context. For more information on individual methods and tools included in the review, please consult the authors/developers of the original
resources.
National Collaborating Centre for Methods and Tools | www.nccmt.ca Page 3
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- ISO/IEC Directives, Part 1Document76 pagesISO/IEC Directives, Part 1Rock BandNo ratings yet
- List of ContributorsDocument485 pagesList of ContributorsRock BandNo ratings yet
- Annex SL (Normative) Harmonized Approach For Management System StandardsDocument5 pagesAnnex SL (Normative) Harmonized Approach For Management System StandardsRock BandNo ratings yet
- Harmonized Approach To MSS - ANEXO SLDocument3 pagesHarmonized Approach To MSS - ANEXO SLRock BandNo ratings yet
- 107 388 1 PBDocument98 pages107 388 1 PBevelineNo ratings yet
- 4604 9444 1 SMDocument14 pages4604 9444 1 SMyulianitaNo ratings yet
- Culpeper Sport & Fitness Group Fitness Schedule June 2018Document2 pagesCulpeper Sport & Fitness Group Fitness Schedule June 2018Rock BandNo ratings yet
- CSF For ERP (Thesis) PDFDocument313 pagesCSF For ERP (Thesis) PDFRock BandNo ratings yet
- CSF Society Meeting Amsterdam June 7 8Document3 pagesCSF Society Meeting Amsterdam June 7 8Rock BandNo ratings yet
- June 2018 Monthly MemoDocument2 pagesJune 2018 Monthly MemoRock BandNo ratings yet
- CSF Implementing Business Inteligence in SME (Article) PDFDocument22 pagesCSF Implementing Business Inteligence in SME (Article) PDFRock BandNo ratings yet
- Model For Selection of Business Process Improvement MethodologiesDocument15 pagesModel For Selection of Business Process Improvement MethodologiesRock BandNo ratings yet
- Background of Critical Success Factor Research: Working Paper No. 2/2005Document12 pagesBackground of Critical Success Factor Research: Working Paper No. 2/2005mwronkaNo ratings yet
- Charles CorrieDocument35 pagesCharles CorrieRock BandNo ratings yet
- Brouwer 2008Document8 pagesBrouwer 2008Rock BandNo ratings yet
- Company BrochureDocument23 pagesCompany BrochureRock BandNo ratings yet
- Gii Full Report 2017Document463 pagesGii Full Report 2017Andi PionNo ratings yet
- PDCA To Present The 18th Annual Design and Installation of Cost-Efficient Piles (DICEP) ConferenceDocument2 pagesPDCA To Present The 18th Annual Design and Installation of Cost-Efficient Piles (DICEP) ConferenceRock BandNo ratings yet
- InvestigacionDocument98 pagesInvestigacionRock BandNo ratings yet
- Modelling Business ProcessDocument156 pagesModelling Business ProcessRock BandNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Chapter 41: Genitourinary Disorders Garzon Maaks: Burns' Pediatric Primary Care, 7th EditionDocument6 pagesChapter 41: Genitourinary Disorders Garzon Maaks: Burns' Pediatric Primary Care, 7th EditionHelen UgochukwuNo ratings yet
- Oet Speakingr PDFDocument133 pagesOet Speakingr PDFAlphonsa Thomas100% (1)
- Health Sector StrategyDocument11 pagesHealth Sector StrategyRaymunda Rauto-avilaNo ratings yet
- FMXX SpriggsDocument10 pagesFMXX Spriggssuresh2250No ratings yet
- Nursing Research Position StatementDocument3 pagesNursing Research Position StatementFranck Duprey MvogoNo ratings yet
- Pengetahuan Ibu Tentang Mobilisasi Dini Pasca Persalinan Normal Pervaginam Di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Labuhan Rasoki Kecamatan Padangsidimpuan Tenggara Tahun 2018Document6 pagesPengetahuan Ibu Tentang Mobilisasi Dini Pasca Persalinan Normal Pervaginam Di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Labuhan Rasoki Kecamatan Padangsidimpuan Tenggara Tahun 2018Geuman ChajgoNo ratings yet
- Standar Alat AmbulanceDocument4 pagesStandar Alat AmbulanceDonny LogantaraNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Symptoms Campbell All ChapterDocument67 pagesRespiratory Symptoms Campbell All Chaptermelanie.grant662100% (11)
- Bonded Composites Versus Ceramic Veneers PDFDocument7 pagesBonded Composites Versus Ceramic Veneers PDFAnnaAffandieNo ratings yet
- PHD Thesis Public Health PDFDocument7 pagesPHD Thesis Public Health PDFangelicaortizpaterson100% (2)
- NCP - Acute Pain Stomach CancerDocument2 pagesNCP - Acute Pain Stomach CancerJohn Michael TaylanNo ratings yet
- Indraprastha Apollo Hospital: Project DetailsDocument3 pagesIndraprastha Apollo Hospital: Project DetailsSumitKhannaNo ratings yet
- Barriers To Effective Nursing LeadershipDocument14 pagesBarriers To Effective Nursing LeadershipTristan CunananNo ratings yet
- Emergency Neurological Life Support: Fourth Edition, Updates in The Approach To Early Management of A Neurological EmergencyDocument5 pagesEmergency Neurological Life Support: Fourth Edition, Updates in The Approach To Early Management of A Neurological Emergencyalejandro montesNo ratings yet
- Medical Tourism: A Study of Kerala: Project SynopsisDocument2 pagesMedical Tourism: A Study of Kerala: Project SynopsisbhatiaharryjassiNo ratings yet
- Happy Nurses' Day!Document2 pagesHappy Nurses' Day!Pierce ChowNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Public Health NursingDocument3 pagesEvolution of Public Health NursingJavie Bryant RedilNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - SOP ON DispensingDocument4 pagesMicrosoft Word - SOP ON DispensingPalawan Baptist HospitalNo ratings yet
- 'No Evidence That CT Scans, X-Rays Cause Cancer' - Medical News TodayDocument3 pages'No Evidence That CT Scans, X-Rays Cause Cancer' - Medical News TodayDr-Aditya ChauhanNo ratings yet
- SURGICAL SITE INFECTION. - Prevention and CareDocument68 pagesSURGICAL SITE INFECTION. - Prevention and Caretummalapalli venkateswara rao50% (2)
- List of HospitalsDocument13 pagesList of HospitalsRajeev VenegallaNo ratings yet
- Straight WireDocument1 pageStraight Wiresvetaine.ltNo ratings yet
- Medical Reimbursement PDFDocument3 pagesMedical Reimbursement PDFOrlando WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Canadian Personal Care Provider Canadian 1st Edition Wolgin Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesCanadian Personal Care Provider Canadian 1st Edition Wolgin Solutions Manualampyxprimei5136100% (15)
- Joric M. Magusara, RN: Teacher / InstructorDocument5 pagesJoric M. Magusara, RN: Teacher / InstructorJoric MagusaraNo ratings yet
- Nicholas C. Reithmaier: University of South FloridaDocument5 pagesNicholas C. Reithmaier: University of South FloridaNick ReithmaierNo ratings yet
- Knowledge and Practices of Mothers On Nigeria PDFDocument11 pagesKnowledge and Practices of Mothers On Nigeria PDFalfinNo ratings yet
- Higher Education of RizalDocument3 pagesHigher Education of RizaltrinabagueNo ratings yet
- KPD 13 1 14 22Document9 pagesKPD 13 1 14 22aylinsangurhanNo ratings yet
- C-SSRS - HebrewDocument6 pagesC-SSRS - HebrewYosefNo ratings yet