Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Common Quarterly QP Answer Key
Common Quarterly QP Answer Key
Uploaded by
Senthilkumar KadirveluOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Common Quarterly QP Answer Key
Common Quarterly QP Answer Key
Uploaded by
Senthilkumar KadirveluCopyright:
Available Formats
www.kalvikural.
com
QUARTERLY PHYSICS KEY ANSWERS SEPTEMBER-2016
PART-I
Sl. Answers Sl. Answers
No No
1 a) 16 a)0.4H
2 d) zero 17 c) slip rings
3 c) H = VIt 18 b) 30 A
4 d) electric potential 19 b) power is transmitted in a
direction perpendicular to the
both fields
5 d) 24 pF 20 a)contracts
6 a)C2N-1m-2 21 a)pure line spectrum
7 b) n2 : 1 22 Mere attempt
8 a) drift velocity 23 a)plane
9 b) increases 24 c) sommerfeld
10 c) velocity of the particle 25 c)1:4:9
11 b) 20 26 c)
12 d) infinite resistance 27 b) absorbs green light
13 a)1.732 28 c)opposite to the direction of
motion of oil droplet
14 c) unchanged 29 a)K
15 b) room heater 30 c)capacitor
Important Note:
1. For answers in Part II , Part-III, and Part- IV like reasoning , explanation, narration,description
and listing the points, students may write in their own words but without changing the concepts
and without skipping any point.
2. Answers written only in BLACK or BLUE should be evaluated.
3. For graphical representation, X and Y variables must be mentioned . If not , reduce mark.
4. Marks should be given to the unit, only if the answer is correct for problems.
PART-II
Q.No Descrbtion MAR TOTAL
K
31 Electric Polarisation Correct definition 3 3
(or)
1
PE 1
32 Capacitors Any 3 Applications (3x1) 3 3
33 =pEsin 1 3
substitution 1
B.KANNAN M.Sc., B.Ed., GHSS MUDUR, VELLORE-631 003| Ph:7871748594
www.kalvikural.com
= 8.5x10-26 Nm (correct answer +unit) +
34 Electrochemical Equivalent correct definition 2 3
Unit = kg C-1 1
35 Kirchoffs Voltage Law- Correct statement 3 3
(Closed circuit if not mentioned reduce 1 mark )
36 Emf and potential difference ( any two 2x1) 3 3
37 I = or I = ( related formula) 1 3
substitution 1
t = 80 s (correct answer +unit) +
38 Seebeck Effect correct statement 3 3
39 Amperes circuital law correct statement 3 3
(or)
= o Io 1
40 Any 3 characteristics of Nichrome (3x1) 3 3
41 Three methods of producing induce emf(3x1) 3 3
42 Q factor correct statement 3 3
(or)
Q= (or) Q = 1
43 e = - M or any related formula 1 3
1
substitution
+
t = 6.25 x 10-3 H (or) 6.25 mH (correct answer +unit)
44 Any 3 conditions for obtaining clear and broad interference bands 3 3
45 Optic axis correct statement 3 3
(Particular direction if not mentioned reduce 1 mark )
46 S=- or C = 1 3
1
substitution
+
t = 0.0833 g / cc (correct answer +unit)
47 Any 3 applications of Moseleys Law 3 3
48 Characteristics of Laser (any 3 ) (3x1) 3 3
49 Hard X-rays and Soft X-rays ( any 3 differences) (3x1) 3 3
50 2d sin = n 1 3
substitution 1
max = 5.64 x 10 -10 m(correct answer +unit) +
PART-III
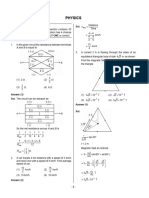
51 Electri potential energy of dipole placed in electric field 5
Diagram 1
Explanation 1
=pEsin
dw = d
W = - pE cos (or) U = - pE cos 1 2
= 0 , U = - pE 1
52 Principle of capacitors 5
Diagram 1
B.KANNAN M.Sc., B.Ed., GHSS MUDUR, VELLORE-631 003| Ph:7871748594
www.kalvikural.com
Explanation ( potential decreases capacitance increases not mentioned 2
reduce 1 mark)
Capacitance depends geometry of the conductor and nature of the medium 1
Capacitors storing electric charges 1
53 Wheatstone Bridge
Diagram 1
Applying kirchoffs first law
Junction B I1-Ig-I3 = 0
Junction d I2+Ig-I4 = 0
For closed circuit network ABDA , I1P+IgG-I2R = 0
For closed circuit network ABCDA, I1P+I3Q-I2R-I4S = 0
For balancing condition Ig = 0 1
= 1
54 a) R = and related formula 2 5
Substitution 2
1
Change in resistance percentage = 0.2%
(or)
1
b) =
Substitution 1
X = 9.305
= 1
Substitution
= 1.082 x 10-6 m (correct answer +unit) 1
55 Thermopile 5
Principle 1
Diagram 1
Explanation 2
Deflection in the galvanometer is directly proportional to the intensity of 1
radiation
56 Conversion galvanometer into an ammeter 5
Diagram 1
Connecting low resistance in parallel to the galvanometer 1
Explanation 1
IgG = ( I-Ig)S or S = G( Ig/ I-Ig) 1
Ra = GS/G+S 1
57 Energy losses in Transformer 5
Hysteresis loss 1
Copper loss 1
Eddy current loss ( iron loss) 1
Flus loss 1
(or)
Mere mentioning the names of losses (4 x =2) 2 3
58 Average power in an a.c circuit 5
Explanation 1
e = Eosint
B.KANNAN M.Sc., B.Ed., GHSS MUDUR, VELLORE-631 003| Ph:7871748594
www.kalvikural.com
I = Iosin(t+)
Upto Pav = cos 1
Pav = Erms Irms cos
The average power of an ac circuit is also called the true power of the 1
circuit 1
59 Sin = Nm 1 5
Substitution of R
R = 45 1
Substitution of B
B = 30 1
Angular separation( R - B ) = 15 1
60 Polaroids any 5 applications (5x1) 5 5
61 Spectral series of Hydrogen atom 5
Explanation of five series 2
Formula 2
(or)
Mere mentioning the names of spectral series only 2
62 =R ( - ) 1 5
1
=R ( - ), = 1
=R ( - ), =
1
Substitution and calculation
1
2= 6563 (correct answer +unit)
PART - IV
63 Electric potential due a dipole 10
Diagram 1
Explanation 1
V1 =
V2 =
V= ( ) 1
1
Upto ( 1 + cos ) 1
Upto ( 1 - cos )
1
V=
Special cases
4
(i) , V= 1
1
(ii) ,V=
B.KANNAN M.Sc., B.Ed., GHSS MUDUR, VELLORE-631 003| Ph:7871748594
www.kalvikural.com
(iii) ,V=0 1
64 Electric field due to charged spherical shell 10
Case (i) outside the shell
Diagram 1
Explanation 1
= E (4r2 ) 1
E= 1
Case(ii) on the surface
1
E= (r=R)
Case(iii) inside the shell 1
Diagram 1
Explanation 1
= E (4r2 ) 1
E=0
The field due to a uniformly charged thin shell is zero at all points inside the 1
shell
65 Magnetic induction due a circular coil 10
Diagram 2
Explanation 1
dB =
1
=90 dB =
Explanation for two components of dB 1
B= 1
B= 1
1
B= 2a
Upto 2
66 Eddy current 10
Definition 2
Direction of eddy current Lenz law 1
Explanation any 3 applications (3x2) 6
( for mere mentioning the headings mark each)
Eddy current can be minimized by using thin laminated sheets instead of 1
solid metal
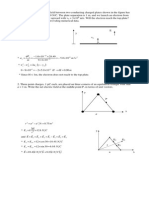
67 RLC Circuit 10
Explanation 1
RLC Series circuit diagram 1
Voltage phase diagram
Impedance diagram
VR = IR
VL = IXL 5
VC = IXC
VL and VC are 180 out of phase with each other
V2 =VR2 +( VL-VC)2 1
B.KANNAN M.Sc., B.Ed., GHSS MUDUR, VELLORE-631 003| Ph:7871748594
www.kalvikural.com
V= -IXc)2 1
=Z= 1
1
tan= =
=tan-1( 1
68 Raman effect 10
Raman effect explanation 1
Diagram (3x1) 3
Explanation of stokes and Anti-stokes lines with respect to frequency 1
Explanation of Raman effect (3x1) 3
Explanation for = o-s 1
is positive for stoke line
is negative for Anti-stoke line
Intensity of stoke line is always greater than antistoke line 1
69 Youngs double slit experiment: Bandwidth 10
Diagram 2
Explanation 2
(reduce mark if the waves arrive inphase or out of phase depending
upon the path difference between two waves is not mentioned)
Upto path difference 2
Condition for bright fringes for bright band X= (+) 1
Condition dark fringes for = (+) 1
Definition for Bandwidth 1
1
Upto
70 J.J Thomson Experiment 2 10
Diagram 1
Explanation 2
Derivation upto V =
1
t= 2
y1 = | 2
Y=k y1 1
= 1
PREPARED BY
B.KANNAN M.Sc., B.Ed., 6
BT ASST IN SCIENCE ,GHSS,
MUDUR, VELLORE 631 003
B.KANNAN M.Sc., B.Ed., GHSS MUDUR, VELLORE-631 003| Ph:7871748594
You might also like
- En 16432 1 2017 - Ballastless TrackDocument38 pagesEn 16432 1 2017 - Ballastless TrackSatish Kumar100% (1)
- Test PDFDocument6 pagesTest PDFRodrigo Civetta Martinez100% (1)
- H2 Physic 2008 A Level SolutionsDocument21 pagesH2 Physic 2008 A Level Solutionsonnoez40% (5)
- ExpertTA AnswersDocument25 pagesExpertTA AnswersJohn Ndambuki0% (1)
- Eddy-Current-Brakes Seminar Report PDFDocument21 pagesEddy-Current-Brakes Seminar Report PDFprashanta padhiary50% (4)
- TUBE INSPECTION by RFETDocument8 pagesTUBE INSPECTION by RFETTusar Kole100% (1)
- 30th Jan Shift 2Document15 pages30th Jan Shift 2Ralph SemisterNo ratings yet
- +2 PHY EM Common Half Yearly Examination Key PDFDocument8 pages+2 PHY EM Common Half Yearly Examination Key PDFAbdul BasithNo ratings yet
- Physics Question PaperDocument5 pagesPhysics Question Papervasudevan m.vNo ratings yet
- 2910 - Enthusiast - Pre - Score - Phase - TOAS, TNAS, TAAS - TTAS - Paper - 2 - E - JA Pages 2 - 19Document18 pages2910 - Enthusiast - Pre - Score - Phase - TOAS, TNAS, TAAS - TTAS - Paper - 2 - E - JA Pages 2 - 19Shubham JainNo ratings yet
- IIT-JEE Paper 1 SolutionsDocument9 pagesIIT-JEE Paper 1 SolutionsSrinivasulu KonetiNo ratings yet
- MATA33 W23 Test 02 Practice 01Document11 pagesMATA33 W23 Test 02 Practice 01Braden DawsonNo ratings yet
- BBSR Jee Ent RT01 Ja Paper-2 23-04-2023Document24 pagesBBSR Jee Ent RT01 Ja Paper-2 23-04-202310D 31 Aditya HotaNo ratings yet
- JEE-Main-18-03-2021-Shift-2 (Memory Based) Physics: Question: A Proton Cannot Split Into A Neutron:-OptionsDocument39 pagesJEE-Main-18-03-2021-Shift-2 (Memory Based) Physics: Question: A Proton Cannot Split Into A Neutron:-OptionsRamacharyuluNo ratings yet
- HW 2Document4 pagesHW 2beepeNo ratings yet
- CBSE-Physcis 12-SP 13Document8 pagesCBSE-Physcis 12-SP 13Gursimrat KaurNo ratings yet
- Akash Shift 2 PDFDocument15 pagesAkash Shift 2 PDFvivekNo ratings yet
- Ioqjs (Part 1) 2021 SolutionDocument13 pagesIoqjs (Part 1) 2021 SolutionAnindita GhoshSatpathiNo ratings yet
- SHORT PRACTICE TEST SERIES - No-006 - NEET - 2022-08-21 - 2022 - ADocument6 pagesSHORT PRACTICE TEST SERIES - No-006 - NEET - 2022-08-21 - 2022 - APLABAN DASNo ratings yet
- 2-50 CC (Key & Sol) 08.07.2022Document8 pages2-50 CC (Key & Sol) 08.07.2022mocoking007No ratings yet
- JEE Main 26 02 2021 Shift 1Document37 pagesJEE Main 26 02 2021 Shift 1ShivaNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2023 30 January Shift 2Document14 pagesJEE Main 2023 30 January Shift 2barnwalk367No ratings yet
- Paper 47Document6 pagesPaper 47KaustubhNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2022 (June 25 Morning Shift) Question Paper With Solutions (PDF)Document24 pagesJEE Main 2022 (June 25 Morning Shift) Question Paper With Solutions (PDF)avaneesh khadyeNo ratings yet
- Phys Sample GDocument11 pagesPhys Sample GAbhijit SanjeevNo ratings yet
- Mock - Test 05 Jee Advanced - PaperDocument19 pagesMock - Test 05 Jee Advanced - PaperGanesha Dattatraya Gaonkar CFALNo ratings yet
- Phpa 339 U9Document22 pagesPhpa 339 U9iiojnjnNo ratings yet
- 07 08 II ms1Document5 pages07 08 II ms1Mahmoud FariedNo ratings yet
- Jee 26 July Morning Answer KeyDocument13 pagesJee 26 July Morning Answer KeyKISHORE GNo ratings yet
- Paper A93Document25 pagesPaper A93MP12No ratings yet
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper Solutions 24 February MorningDocument39 pagesJEE Main 2021 Question Paper Solutions 24 February MorningTanishq KaushikNo ratings yet
- PHYS-30021J-ElectronsInCrystals-Exam-2012-2013-Jan-final 2Document5 pagesPHYS-30021J-ElectronsInCrystals-Exam-2012-2013-Jan-final 2jrigg055No ratings yet
- Exam1 Solutions F15 PDFDocument13 pagesExam1 Solutions F15 PDFHuy QuangNo ratings yet
- Exercises 03Document5 pagesExercises 03davyjones1147No ratings yet
- Solutions Code 0 JEEAdvanced2013 VMC SolvedDocument28 pagesSolutions Code 0 JEEAdvanced2013 VMC SolvedShashank ShekharNo ratings yet
- Mock Test 3 Jee MainDocument49 pagesMock Test 3 Jee MainrethwikeshsriramojuNo ratings yet
- Airforce Group X: Previous Y Ear P AperDocument15 pagesAirforce Group X: Previous Y Ear P Apervikashrajrn10No ratings yet
- JEE-Main-18-03-2021-Shift-1 (Memory Based) PhysicsDocument40 pagesJEE-Main-18-03-2021-Shift-1 (Memory Based) PhysicsRamacharyuluNo ratings yet
- Lower 6Document9 pagesLower 6Tinotenda MazhakataNo ratings yet
- 31st Jan Morning Shift (Memory Based Questions)Document5 pages31st Jan Morning Shift (Memory Based Questions)Mohd TousifNo ratings yet
- Jest QuestionDocument16 pagesJest QuestionThirumugam SNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 2 (2022)Document3 pagesMathematics 2 (2022)Andriya BijuNo ratings yet
- Answers & Solutions JEE (Main) - 2022 (Online) Phase-2: Memory BasedDocument14 pagesAnswers & Solutions JEE (Main) - 2022 (Online) Phase-2: Memory BasedAyush NagarNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/42Document24 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/42Ramadhan AmriNo ratings yet
- Ala'a Nabil-Solved Re-TestDocument2 pagesAla'a Nabil-Solved Re-TestMoh'd AlsalhiNo ratings yet
- Uhorwfvnuohrafvn 8 Honvrf 8 UDocument24 pagesUhorwfvnuohrafvn 8 Honvrf 8 Uk24xnzp2qyNo ratings yet
- Excel-Apex (SRG) - JA - Paper-2 - Web FileDocument33 pagesExcel-Apex (SRG) - JA - Paper-2 - Web FileRohan VayaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Particle Physics PH5811 - End SemesterDocument4 pagesAdvanced Particle Physics PH5811 - End SemesterAviteshNo ratings yet
- Airforce Group X: Previous Year PaperDocument15 pagesAirforce Group X: Previous Year PaperInvincible HeroNo ratings yet
- Physics 9702 Paper 4Document32 pagesPhysics 9702 Paper 4Alvin VictorNo ratings yet
- NJC 2022 H2 Physics Prelim P1 AnsDocument7 pagesNJC 2022 H2 Physics Prelim P1 AnsYong JieNo ratings yet
- JEE-Main-17-03-2021-Shift-1 (Memory Based) PhysicsDocument40 pagesJEE-Main-17-03-2021-Shift-1 (Memory Based) PhysicsSuvigya YadavNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems in PhysicsDocument22 pagesSolved Problems in Physicsvasudevan m.vNo ratings yet
- 350 Fall 12 FinalDocument10 pages350 Fall 12 Finalchuck212No ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/43Document24 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/43agnesasus123No ratings yet
- 15 Maths in PhysicsDocument6 pages15 Maths in PhysicsmvhokoNo ratings yet
- 7230 HW2 PDFDocument3 pages7230 HW2 PDFAnonymous 5bQS8ErIoNo ratings yet
- On the Tangent Space to the Space of Algebraic Cycles on a Smooth Algebraic Variety. (AM-157)From EverandOn the Tangent Space to the Space of Algebraic Cycles on a Smooth Algebraic Variety. (AM-157)No ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Beams and Framed Structures: Structures and Solid Body MechanicsFrom EverandBeams and Framed Structures: Structures and Solid Body MechanicsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Tables of Coefficients for the Analysis of Triple Angular Correlations of Gamma-Rays from Aligned NucleiFrom EverandTables of Coefficients for the Analysis of Triple Angular Correlations of Gamma-Rays from Aligned NucleiNo ratings yet
- The Plasma Dispersion Function: The Hilbert Transform of the GaussianFrom EverandThe Plasma Dispersion Function: The Hilbert Transform of the GaussianRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Hysteresis Loop Tracer.: TitleDocument7 pagesHysteresis Loop Tracer.: TitleSubhrajit SamantaNo ratings yet
- MS 5800 EN 201803 Web PDFDocument5 pagesMS 5800 EN 201803 Web PDFWalter TrajadaNo ratings yet
- RFT ProcedureDocument15 pagesRFT ProcedureShahid Khan100% (2)
- Karnataka 2PU-PCMB - Model Question Paper 2014-15Document134 pagesKarnataka 2PU-PCMB - Model Question Paper 2014-15rahul1060% (1)
- CEC-GE-CT-EN-001 - Citadel General EN CatalogueDocument37 pagesCEC-GE-CT-EN-001 - Citadel General EN CatalogueAlmustafa SabeehNo ratings yet
- Eddy Current BrakesDocument18 pagesEddy Current BrakesAjoy RsNo ratings yet
- Iso 2360 2017Document13 pagesIso 2360 2017leonardoNo ratings yet
- Seminar NDT Introduction Short TostudentsDocument17 pagesSeminar NDT Introduction Short TostudentsJohn doeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 MACHINESDocument30 pagesChapter 1 MACHINESalia khanNo ratings yet
- Yang SHEN PHD Thesis-revised-FinalDocument241 pagesYang SHEN PHD Thesis-revised-FinalCazimir BostanNo ratings yet
- Moving Iron Type InstrumentsDocument6 pagesMoving Iron Type InstrumentsAbhishek KatreNo ratings yet
- 206 - EE8391, EE6302 Electromagnetic Theory - 2marksDocument22 pages206 - EE8391, EE6302 Electromagnetic Theory - 2marksBALAKRISHNANNo ratings yet
- SHM MitDocument90 pagesSHM MitSãröj ShâhNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NDTDocument33 pagesIntroduction To NDTnaganathanNo ratings yet
- CRGO History, DetailsDocument11 pagesCRGO History, DetailskasyapreddyNo ratings yet
- Empt Forming Welding Crimping and CuttingDocument13 pagesEmpt Forming Welding Crimping and CuttingEmil MariusNo ratings yet
- Tsi FinalDocument41 pagesTsi FinalAnand KumarNo ratings yet
- Eddycurrentbrakes 140401105112 Phpapp01Document23 pagesEddycurrentbrakes 140401105112 Phpapp01umangNo ratings yet
- Eddy Corrent PrubeDocument20 pagesEddy Corrent Prubeeloymark2No ratings yet
- Remote Field Eddy Current Technique For In-Service Inspection of Ferromagnetic TubesDocument2 pagesRemote Field Eddy Current Technique For In-Service Inspection of Ferromagnetic TubesassurendranNo ratings yet
- HP Heater # 3 TopDocument68 pagesHP Heater # 3 TopKuppan SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Lemaire Et Al 2020Document20 pagesLemaire Et Al 2020Dilman CzNo ratings yet
- 2nd PUC Physics Most Important Questions Parivartan PhysicsDocument14 pages2nd PUC Physics Most Important Questions Parivartan Physicsbharatesht42No ratings yet
- Paper ID-47201638Document5 pagesPaper ID-47201638Deepak ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- GEIT 50013US Vector22Document4 pagesGEIT 50013US Vector22vrapciudorianNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Losses in Power TransformerDocument8 pagesDesign and Analysis of Losses in Power Transformerbechir mettaliNo ratings yet