67% found this document useful (6 votes)
4K views9 pagesPractice Strips
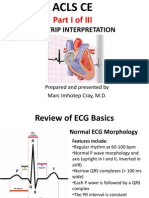
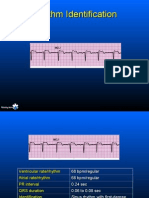
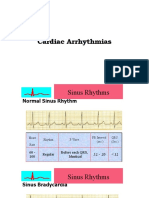
The document provides instructions for analyzing telemetry practice strips and interpreting cardiac rhythms. It lists the 5 steps for rhythm analysis as determining regularity, heart rate, P waves, relationship between P waves and QRS complexes, and interpreting the rhythm. It then provides 20 practice rhythm strips for the user to determine the rate, PR interval, QRS width, rhythm interpretation, and appropriate next steps of care.
Uploaded by
Erica YamamotoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
67% found this document useful (6 votes)
4K views9 pagesPractice Strips
The document provides instructions for analyzing telemetry practice strips and interpreting cardiac rhythms. It lists the 5 steps for rhythm analysis as determining regularity, heart rate, P waves, relationship between P waves and QRS complexes, and interpreting the rhythm. It then provides 20 practice rhythm strips for the user to determine the rate, PR interval, QRS width, rhythm interpretation, and appropriate next steps of care.
Uploaded by
Erica YamamotoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Telemetry Practice Strips: This section provides practice strips for telemetry competency, with instructions on analyzing rhythm, calculating heart rate, and interpreting QRS and PRI intervals.
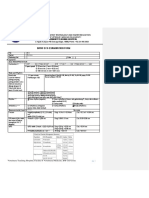
- Answers: Offers answers to the telemetry practice strips, detailing rate, interpretation, and suggested next courses of action.