Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Demand Supply Ans PDF
Demand Supply Ans PDF
Uploaded by
azmidiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Demand Supply Ans PDF
Demand Supply Ans PDF
Uploaded by
azmidiCopyright:
Available Formats
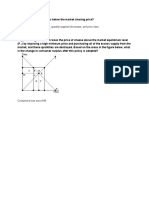
DEMAND, SUPPLY AND EQUILIBRIUM
In a hypothetical market, the buyers will take 20 units of good X if the goods are free. The
marketing department estimates that that for each $1 increase in the price of the good, the
buyers will reduce their purchases by 1.25 units of the good. Construct the demand function
on the graph provided. Complete the table that shows the demand schedule.
Price
(PX)
19
Supply
18
Decrease
17
16
15
14
13
Supply
12
11
10
9
Equilibrium Demand
8
price is Increase
about 7
$7.40 6
5
4
3
2
Demand
1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23
Equilibrium quantity is about 10.8 units
Figure 1.a Quantity
(QX/ut)
1.What is the equation that represents the quantity demanded as a function of price?
Qd = f(P), Qd = 20 1.25P
2.What is the equation that represents the price as a function of the quantity?
P = f(Qd), P = 16 - .8Qd
3.When the Price is $4 what is the Quantity demanded? Qd = 20 1.25(4) = 15 units
4. What is the maximum price that someone is willing and able to pay for the 8th unit of the
good? P = 16 - .8(8) = $9.60
The sellers will not offer any of good X at or below a price of $2. For each additional dollar
the price increases they will offer 2 additional units for sale.
5.What is the supply equation?
Cost = P = f(Qs) P = 2 + .5Qs or Qs = -4 + 2P
6.Construct the supply equation on the graph and complete the schedule in the Table.
7.Using the graph, what is the approximate equilibrium price?About $7.40
8.Using the graph what is the approximate equilibrium quantity? About 10.8 units
Basic Microeconomics - Demand, Supply and Equilibrium
9.What is the equilibrium quantity and price when calculated by using the supply and
demand equations?
Quantity supplied = Quantity demanded
Qs = -4 + 2P = 20 1.25P = Qd
3.25P = 24
P = 24/3.25 = $7.385 (equilibrium Price)
2 +.5Q = 16 - .8Q
1.3Q = 14
Q = 14/1.3 = 10.769 units
More is purchased at each
10.What happens if the demand should increase (decrease)?
possible price; A higher price will be paid for each unit of the good. .
Show an increase (decrease) in demand on the graph? See Demand Increase
in Figure 1.
11. What happens to equilibrium price and quantity when demand increases (decreases)?
Both equilibrium price and quantity would increase (decrease)
12. Show a decrease (increase) in supply. See
Supply Decrease in Figure 1 Demand & Supply
13.What happens to equilibrium price and quantity Quantity X Quantity X
when the supply decreases?Equilibrium Price Demanded Supplied
price will increase while equilibrium (PX) (QD) (QS)
quantity will decrease. Qd = 20 - 1.25P Qs = (-4) + 2P
$20 P = 16 - .8Qd P = 2 + .5Qs
14. What happens when demand increases and
$19
supply decreases? Equilibrium price must
$18
necessarily increase but the change in $17
equilibrium quantity will depend on the $16 0.00 28.00
magnitude of the shifts and the $15 1.25 26.00
relative elasticities of supply and $14 2.50 24.00
demand. $13 3.75 22.00
$12 5.00 20.00
$11 6.25 18.00
$10 7.50 16.00
The supply and demand $9 8.75 14.00
functions intersect
$8 10.00 12.00
between these two
rows, the quantity $7 11.25 10.00
supplied will equal the $6 12.50 8.00
quantity demanded $5 13.75 6.00
$4 15.00 4.00
$3 16.25 2.00
$2 17.50 0.00
$1 18.75 -2.00
$0 20.00 -4.00
Basic Microeconomics - Demand, Supply and Equilibrium
You might also like
- Chapter 2 Complete SolutionsDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Complete SolutionsVictor64% (14)
- Economics for CFA level 1 in just one week: CFA level 1, #4From EverandEconomics for CFA level 1 in just one week: CFA level 1, #4Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- 999 AnswersDocument109 pages999 AnswersZURMAN1No ratings yet
- Managerial Economics: Problem Set 1Document1 pageManagerial Economics: Problem Set 1Asfawosen Dingama100% (2)
- Microeco HW Answers Ch. 3, 4Document7 pagesMicroeco HW Answers Ch. 3, 4pheeyona100% (3)
- Appendix 04Document10 pagesAppendix 04Mudassar ShahidNo ratings yet
- Demand, Supply and Equilibrium: Figure 1.aDocument2 pagesDemand, Supply and Equilibrium: Figure 1.aedysutiarsoNo ratings yet
- Market Equilibrium 1Document55 pagesMarket Equilibrium 1bullet proofNo ratings yet
- Econ 201 Mid Term ReviewDocument7 pagesEcon 201 Mid Term ReviewGeorge DhimaNo ratings yet
- Chap 002 SDocument8 pagesChap 002 SAashima GroverNo ratings yet
- Tugas Ekonomi Manajerial Chapter 2 Market Forces Demand & Supply - Nely Noer Sofwati (2020318320009)Document5 pagesTugas Ekonomi Manajerial Chapter 2 Market Forces Demand & Supply - Nely Noer Sofwati (2020318320009)Nely Noer SofwatiNo ratings yet
- Demand&SupplyDocument66 pagesDemand&SupplySuman PoudelNo ratings yet
- Queens College Department of EconomicsDocument2 pagesQueens College Department of EconomicsConcurseirodorio100% (1)
- Answers To Homework 3 Spring 2011Document10 pagesAnswers To Homework 3 Spring 2011Anh Khoa NguyenNo ratings yet
- AnswerDocument17 pagesAnswerkooruu22No ratings yet
- Answer Key - ElasticityDocument13 pagesAnswer Key - ElasticityAli MehsenNo ratings yet
- bài tập vận dụng chap 1 2 m4bDocument12 pagesbài tập vận dụng chap 1 2 m4bconkienlua2005No ratings yet
- Handout Economy 4 - Equilibrium and Elasticity PriceDocument8 pagesHandout Economy 4 - Equilibrium and Elasticity PriceAndriani GraceNo ratings yet
- Assignment-1 of MicroeconomDocument3 pagesAssignment-1 of MicroeconomTajinder SinghNo ratings yet
- ECON 201 - Problem Set 1Document5 pagesECON 201 - Problem Set 1KemalNo ratings yet
- Curva de EngelDocument3 pagesCurva de EngelRodrigo Romo MuñozNo ratings yet
- Eco 101 EquilibriumDocument15 pagesEco 101 EquilibriumMovie SeriesNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Homew OrkDocument32 pagesMicroeconomics Homew OrkTấn Lộc LouisNo ratings yet
- Google Market Equilibrium ExamplesDocument11 pagesGoogle Market Equilibrium ExamplesAllicamet SumayaNo ratings yet
- Linear Equarions - Economic ApplicationsDocument41 pagesLinear Equarions - Economic Applicationsthrphys1940No ratings yet
- Function On BusinessDocument14 pagesFunction On BusinessPrasetyo HartantoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1-10 QuestionsDocument5 pagesExercise 1-10 QuestionsTam NguyenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MicroeconomicsDocument5 pagesIntroduction To MicroeconomicscyrusNo ratings yet
- Problems Demand AnalysisDocument7 pagesProblems Demand AnalysisKenil ShahNo ratings yet
- Q D 55 75 Q S 50 55 75 - CompressDocument5 pagesQ D 55 75 Q S 50 55 75 - CompressLộc Phạm vănNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 For MAT 2020octDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 For MAT 2020octBrohi ZamanNo ratings yet
- Wiley QuizDocument14 pagesWiley QuizMarcLikesPianoNo ratings yet
- Extra Session-Numerical Problems With CalculusDocument42 pagesExtra Session-Numerical Problems With CalculusAnit DattaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document3 pagesAssignment 3bluestacks3874No ratings yet
- 3070 PSet-7 SolutionsDocument13 pages3070 PSet-7 SolutionsvikasNo ratings yet
- Chapters 1&3 (Supply and Demand)Document3 pagesChapters 1&3 (Supply and Demand)Jim ThiveosNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium pdf-1Document3 pagesEquilibrium pdf-1norshaheeraNo ratings yet
- Eco 401 B1 103143Document5 pagesEco 401 B1 103143Komal IlyasNo ratings yet
- Economics Exercise 4.0Document4 pagesEconomics Exercise 4.0miranazrin6610No ratings yet
- FINAL EXAM PREPARATION (DWL, Surplus)Document2 pagesFINAL EXAM PREPARATION (DWL, Surplus)Шугыла ЕсимханNo ratings yet
- ECON 373 HuqDocument6 pagesECON 373 HuqMarva Nic BranNo ratings yet
- Consumer Surplus and Producer Surplus - Handout PDFDocument4 pagesConsumer Surplus and Producer Surplus - Handout PDFShashank KrrishnaNo ratings yet
- McqsDocument4 pagesMcqsdeepNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics Tutorial 1 SolutionDocument5 pagesManagerial Economics Tutorial 1 SolutionNitish NairNo ratings yet
- Supply Analysis and Determination of Market EquilibriumDocument14 pagesSupply Analysis and Determination of Market EquilibriumZannatun NayeemNo ratings yet
- Demand & SupplyDocument52 pagesDemand & SupplyJessica Adharana KurniaNo ratings yet
- Part 1 - MicroeconomicsDocument79 pagesPart 1 - MicroeconomicsLi Ting NeoNo ratings yet
- 9780199128600Document12 pages9780199128600eibsourceNo ratings yet
- ECON111 Individual Assignment 02 999Document9 pagesECON111 Individual Assignment 02 999tuannguyen.ts2004No ratings yet
- Mathematical EconomicsDocument2 pagesMathematical Economicsmuyi kunleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Market EquilibriumDocument42 pagesChapter 4 Market Equilibriumfarah hanimNo ratings yet
- Demand Theory: Presented By: Melani C. Quilloy, LPT, MBADocument31 pagesDemand Theory: Presented By: Melani C. Quilloy, LPT, MBACamille BagueNo ratings yet
- ME CH 2 Tutorial AnswersDocument6 pagesME CH 2 Tutorial AnswersTabassum AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Micro Assigniment 1Document7 pagesMicro Assigniment 1keting0806No ratings yet
- 14.01 Pset1Document4 pages14.01 Pset1jystdance98No ratings yet
- Lesson 2.2 QuizDocument3 pagesLesson 2.2 QuizKristina NelsonNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandMathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- GCSE Mathematics Numerical Crosswords Foundation Written for the GCSE 9-1 CourseFrom EverandGCSE Mathematics Numerical Crosswords Foundation Written for the GCSE 9-1 CourseNo ratings yet
- The Process of Capitalist Production as a Whole (Capital Vol. III)From EverandThe Process of Capitalist Production as a Whole (Capital Vol. III)No ratings yet
- Money and BankingDocument57 pagesMoney and BankingMohammed RaihanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Demand and SupplyDocument79 pagesLesson 3 - Demand and SupplyRounak TiwariNo ratings yet
- Econ 2106 Principles of MicroeconomicsDocument7 pagesEcon 2106 Principles of MicroeconomicsWalid Asif JanjuaNo ratings yet
- Public GoodsDocument37 pagesPublic GoodsSiti Nur RosifahNo ratings yet
- Economics Class 11 Unit 1 - Basic-Concept-Of-EconomicDocument0 pagesEconomics Class 11 Unit 1 - Basic-Concept-Of-Economicwww.bhawesh.com.np100% (5)
- Tax TheoriesDocument7 pagesTax TheoriesFarhan Ahmed Danial100% (1)
- Differences Between Micro and MacroeconomicsDocument5 pagesDifferences Between Micro and MacroeconomicsCheapestPapers100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Lecture NotesDocument12 pagesChapter 1 Lecture NotesRachel FreemanNo ratings yet
- Prices & Markets Tutorial GuideDocument87 pagesPrices & Markets Tutorial GuideCeline100% (1)
- Economic Chapter 1Document44 pagesEconomic Chapter 1NAPIZEVANSNo ratings yet
- Review QuestionsDocument12 pagesReview QuestionsThanveer KufranNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document12 pagesCH 5ceojiNo ratings yet
- UtilityDocument6 pagesUtilityHemchandra PatilNo ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument19 pagesElasticityaitapNo ratings yet
- Gain From Trade The Theory of Comparative AdvantageDocument2 pagesGain From Trade The Theory of Comparative AdvantageissacvabrahamNo ratings yet
- Micro EcoDocument134 pagesMicro EcoAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- P3 Labour MarketDocument6 pagesP3 Labour Markettaufeek_irawan7201No ratings yet
- Mib12e Pptchapter4Document24 pagesMib12e Pptchapter4JakeNo ratings yet
- Demand AnalysisDocument31 pagesDemand AnalysisMuteeb RainaNo ratings yet
- SPRING 2012 Midterm 1Document11 pagesSPRING 2012 Midterm 1UFECO2023No ratings yet
- Chapter 8/competitive Firms and MarketsDocument19 pagesChapter 8/competitive Firms and Marketsi.abdellah100% (1)
- General Economics With Taxation and EntrepreneurshipDocument55 pagesGeneral Economics With Taxation and EntrepreneurshipZeejnANo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument62 pagesElasticity of DemandVikku AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Deriving Demand Functions ExamplesDocument8 pagesDeriving Demand Functions ExamplesKanika MahajanNo ratings yet
- ECONTWO SyllabusDocument8 pagesECONTWO SyllabusJ GNo ratings yet
- 10e 06 Chap Student WorkbookDocument23 pages10e 06 Chap Student WorkbookMarielle Aria SantosNo ratings yet
- Ragan Chapter5Document34 pagesRagan Chapter5YaraKanawatiNo ratings yet
- Demand & SupplyDocument11 pagesDemand & SupplyHaniNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour and Utility AnalysisDocument36 pagesConsumer Behaviour and Utility Analysisnandini_mba4870No ratings yet