Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cyfctgkjb 05
Uploaded by
Ali Mubarack CK0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageOnce you upload an approved document, you will be able to download the document
Original Title
cyfctgkjb05
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentOnce you upload an approved document, you will be able to download the document
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageCyfctgkjb 05
Uploaded by
Ali Mubarack CKOnce you upload an approved document, you will be able to download the document
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
there will be additional stresses in the case of redundant structures where as.
determinate structures are not affected by support settlement.
The analysis of indeterminate structure differs mainly in two aspects as
compared to determinate structure.
a) To evaluate stresses in indeterminate structures, apart from sectional
properties (area of cross section and moment of inertia), elastic properties are
also required.
b) Stresses are developed in indeterminate structure due to support settlements,
temperature change and fabrication errors etc
Instructional Objectives
After reading this chapter the student will be
1. Able to analyse statically indeterminate structure of degree one.
2. Able to solve the problem by either treating reaction or moment as redundant.
3. Able to draw shear force and bending moment diagram for statically
indeterminate beams.
4, Able to state advantages and limitations of force method of analysis.
7.1 Introduction.
In this lesson, a general introduction is given to the force method of analysis of
indeterminate structure is given. In the next lesson, this method would be applied
to statically indeterminate beams. Initially the method is introduced with the help
of a simple problem and subsequently it is discussed in detail. The flexibility
method of analysis or force method of analysis (or method of consistent
deformation) was originally developed by J. Maxwell in 1864 and O. C. Mohr in
1874, Since flexibility method requires deflection of statically determinate
structure, a table of formulas for deflections for various load cases and boundary
conditions is also given in this lesson for ready use. The force method of analysis.
is not convenient for computer programming as the choice of redundant is not
unique. Further, the bandwidth of the flexibility matrix in the force method is much
larger than the stiffness method. However it is very useful for hand computation.
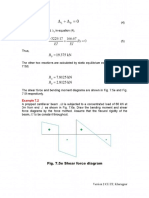
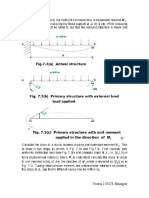
7.2 Simple Example
Consider a propped cantilever beam (of constant flexural rigidity £7 , and span
L), Which is carrying uniformly distributed load of w kNim., as shown in Fig.
7.2a. The beam is statically indeterminate ie. its reaction cannot be evaluated
from equations of statics alone. To solve the above problem by force method
proceeds as follows.
Version 2 CE IIT, Kharagpur
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Rcfgbgvbne 03Document1 pageRcfgbgvbne 03Ali Mubarack CKNo ratings yet
- Xtgdvhokije 19Document1 pageXtgdvhokije 19Ali Mubarack CKNo ratings yet
- ZVJDSFSN 12Document1 pageZVJDSFSN 12Ali Mubarack CKNo ratings yet
- Etdfse 17Document1 pageEtdfse 17Ali Mubarack CKNo ratings yet
- Zytrgfd 16Document1 pageZytrgfd 16Ali Mubarack CKNo ratings yet
- Ibujke 02Document1 pageIbujke 02Ali Mubarack CKNo ratings yet
- Kkkkge 05Document1 pageKkkkge 05Ali Mubarack CKNo ratings yet
- Pftgde 01Document1 pagePftgde 01Ali Mubarack CKNo ratings yet
- Evysbdrthfg 09Document1 pageEvysbdrthfg 09Ali Mubarack CKNo ratings yet
- Sdijaeryp 07Document1 pageSdijaeryp 07Ali Mubarack CKNo ratings yet
- DfdsrfrefDocument1 pageDfdsrfrefAli Mubarack CKNo ratings yet
- Hailll Page 02Document1 pageHailll Page 02Ali Mubarack CKNo ratings yet
- FB Va Aaaaaaa Feb 08Document1 pageFB Va Aaaaaaa Feb 08Ali Mubarack CKNo ratings yet
- GGFRDC 04Document1 pageGGFRDC 04Ali Mubarack CKNo ratings yet
- Wrftgvkuy 06Document1 pageWrftgvkuy 06Ali Mubarack CKNo ratings yet
- Dfdfasrf 03Document1 pageDfdfasrf 03Ali Mubarack CKNo ratings yet
- 500 Matrix Force MethodDocument19 pages500 Matrix Force MethodSarah SullivanNo ratings yet
- (IRFCA) Indian Railways FAQ Permanent WayDocument24 pages(IRFCA) Indian Railways FAQ Permanent WayAli Mubarack CKNo ratings yet
- Asmo2 Uk ScreenDocument8 pagesAsmo2 Uk ScreenAli Mubarack CKNo ratings yet
- 500 Matrix Force MethodDocument19 pages500 Matrix Force MethodSarah SullivanNo ratings yet
- Hailll Page 02 PDFDocument1 pageHailll Page 02 PDFAli Mubarack CKNo ratings yet
- Idges 1973Document506 pagesIdges 1973hcabanillaspNo ratings yet
- 500 Matrix Force MethodDocument19 pages500 Matrix Force MethodSarah SullivanNo ratings yet
- A New Safety Philosophy For CWR: Professor of Railway Engineering TU DelftDocument6 pagesA New Safety Philosophy For CWR: Professor of Railway Engineering TU DelftAli Mubarack CKNo ratings yet
- Blanck Froorkee FormatormatDocument1 pageBlanck Froorkee FormatormatAli Mubarack CKNo ratings yet
- Track Structures in An Urban Environment: Prof - Dr.ir. C. EsveldDocument23 pagesTrack Structures in An Urban Environment: Prof - Dr.ir. C. EsveldAli Mubarack CKNo ratings yet
- 4 Load & Load CombinationDocument10 pages4 Load & Load CombinationAnonymous b9fkTYfEoRNo ratings yet
- NonLinearAnalysis SAP2000Document11 pagesNonLinearAnalysis SAP2000Javier VidalNo ratings yet