Professional Documents
Culture Documents
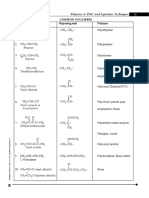
Styrene Butadiene Acrylonitrile
Styrene Butadiene Acrylonitrile
Uploaded by
Ahmad Nuh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views3 pagesABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a terpolymer made by combining the monomers styrene, acrylonitrile, and polybutadiene. There are two main types - blends of acrylonitrile-styrene copolymers with polybutadiene-acrylonitrile rubber, and interpolymers of polybutadiene with styrene and acrylonitrile. ABS has good stress cracking and chemical resistance, is strong and tough, but has poor weathering and flame resistance. Its applications include telephone casings, shower heads, lawn mower covers, vacuum cleaner parts, computer housing, electrical goods, and car bumpers.
Original Description:
Original Title
07ABS.doc
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a terpolymer made by combining the monomers styrene, acrylonitrile, and polybutadiene. There are two main types - blends of acrylonitrile-styrene copolymers with polybutadiene-acrylonitrile rubber, and interpolymers of polybutadiene with styrene and acrylonitrile. ABS has good stress cracking and chemical resistance, is strong and tough, but has poor weathering and flame resistance. Its applications include telephone casings, shower heads, lawn mower covers, vacuum cleaner parts, computer housing, electrical goods, and car bumpers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views3 pagesStyrene Butadiene Acrylonitrile
Styrene Butadiene Acrylonitrile
Uploaded by
Ahmad NuhABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a terpolymer made by combining the monomers styrene, acrylonitrile, and polybutadiene. There are two main types - blends of acrylonitrile-styrene copolymers with polybutadiene-acrylonitrile rubber, and interpolymers of polybutadiene with styrene and acrylonitrile. ABS has good stress cracking and chemical resistance, is strong and tough, but has poor weathering and flame resistance. Its applications include telephone casings, shower heads, lawn mower covers, vacuum cleaner parts, computer housing, electrical goods, and car bumpers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Styrene Butadiene Acrylonitrile
CH2=CH-CH=CH2 CH2=C(CN)H
--- CH2=C
CN
H-bond
(strong)
H
-- CH2=C
CN
- Bulky, irregular - Flexible, - Good solvent
- High Tg, strong weak rubber resistant
Basic building blocks of S, A, and polybutadiene put
together in a variety of ways
Two most important type:
I Blends of SAN copolymers with butadiene-
acrylonitriel rubber
II Interpolymer of polybutadiene, S and A
Blends of acrylonitrile- styrene copolymers with
polybutadiene-acrylonitrile rubber
Blending on a two-roll mill or in an internal mixer
or blending the lattices followed by coagulation
or spray drying
The two materials are compatible, tf little
improvement in impact strength
To improve IS, the rubber is lightly crosslinked by
the use of small quantities of peroxide
Typical blend
70 parts (70:30 styrene AN)
30 parts (65:35 butadiene AN)
Interpolymers of polybutadiene with styrene and
acrylonitrile
Styrene and AN are added to polybutadiene latex
Mixture warmed to about 50C to allow
absorption of the monomers
Water soluble initiators (eg. Potassium
persulphate) added to polymerise styrene and
AN
Resultant mixture of polybutadiene,
polybutadiene grafted with AN and styrene, S-AN
copolymer
Presence of graft polymer is essential for
strength improvement
Properties:
i) Good stress cracking and chemical resistance
ii) Strong (?), tough (?) (high IS), lightweight
iii)Poor weathering resistance & flame resistance
iv) Amorphous, opaque
Applications:
i) Telephone
ii) Shower head
iii)Cover for lawn-mower
iv)Vacuum cleaner
v) PC housing
vi)Electrical goods; TV
vii) Car bumper
You might also like
- Denka Suspending Agent For PVC SynthesisDocument15 pagesDenka Suspending Agent For PVC SynthesisNGUYỄN HOÀNG LINHNo ratings yet
- IR Spectrum Table by Frequency RangeDocument5 pagesIR Spectrum Table by Frequency RangeDiego RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Chemical Compatibility TableDocument28 pagesChemical Compatibility TableBea LubaoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Resistance ChartDocument32 pagesChemical Resistance Chartdalton2004No ratings yet
- Fiitjee: PolymersDocument4 pagesFiitjee: PolymersYash NataniNo ratings yet
- Common Examples and Applications of Copolymers. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)Document4 pagesCommon Examples and Applications of Copolymers. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)Yashi SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Polymer Chemistry - PPT 2Document36 pagesPolymer Chemistry - PPT 2yesheyongdue3No ratings yet
- Resumen MECANISMOS Condensacion Antes Del Video 4Document3 pagesResumen MECANISMOS Condensacion Antes Del Video 4HC RichNo ratings yet
- Organic - Class 9 PDFDocument34 pagesOrganic - Class 9 PDFSajan Singh LUCKYNo ratings yet
- Allen: Common Polymers Monomer Repeatng Unit PolymerDocument3 pagesAllen: Common Polymers Monomer Repeatng Unit PolymerVedang ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Kimia PolimerDocument44 pagesKimia PolimerMitaPermataSariNo ratings yet
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene StyreneDocument5 pagesAcrylonitrile Butadiene StyreneRaguraman RNo ratings yet
- The Phenol + Formaldehyde RXNDocument24 pagesThe Phenol + Formaldehyde RXNIshan PatelNo ratings yet
- Polymers PostDocument42 pagesPolymers Postapi-3767370No ratings yet
- Ratings - Chemical Effect A: No Effect - Excellent B: Minor Effect - Good C: Moderate Effect - Fair D: Severe Effect - Not RecommendedDocument22 pagesRatings - Chemical Effect A: No Effect - Excellent B: Minor Effect - Good C: Moderate Effect - Fair D: Severe Effect - Not RecommendedVarun MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Blocked Isocyanates and Their Usage in Plastic Coatings ApDocument5 pagesBlocked Isocyanates and Their Usage in Plastic Coatings ApalpersakirmetinNo ratings yet
- Polymer Chemistry-1 (Introduction) PDFDocument45 pagesPolymer Chemistry-1 (Introduction) PDFFanny Rahman EkawandiNo ratings yet
- Trimec: Chemical Compatibility ChartDocument12 pagesTrimec: Chemical Compatibility ChartMandiriNo ratings yet
- Suplement oDocument11 pagesSuplement oFernanda AmorimNo ratings yet
- ABC 6kg-Datasheet PDFDocument2 pagesABC 6kg-Datasheet PDFDylan ParkNo ratings yet
- Technical Information Chemical Compatibility: Inspired by ChallengeDocument16 pagesTechnical Information Chemical Compatibility: Inspired by Challengeyrdna nawaiteosNo ratings yet
- Sample: Structure Functional Group Present Peaks (CM)Document2 pagesSample: Structure Functional Group Present Peaks (CM)MUHAMMAD USMANNo ratings yet
- Sample: Structure Functional Group Present Peaks (CM)Document2 pagesSample: Structure Functional Group Present Peaks (CM)MUHAMMAD USMANNo ratings yet
- Topic 3: Major Bulk Organic Major Bulk Organic Chemicals From PropyleneDocument9 pagesTopic 3: Major Bulk Organic Major Bulk Organic Chemicals From PropyleneYong LiNo ratings yet
- Compatibilitate ChimicaDocument24 pagesCompatibilitate ChimicafpanazanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Compatibility Chart Hypalon: Page 1 of 10 Kelco 15/12/2008Document10 pagesChemical Compatibility Chart Hypalon: Page 1 of 10 Kelco 15/12/2008Jagdish PatelNo ratings yet
- Nylon Chemical Compatibility ChartDocument14 pagesNylon Chemical Compatibility Chartteban09No ratings yet
- Chemical Compatibility GuideDocument12 pagesChemical Compatibility GuideMeuMundoMinecraftNo ratings yet
- Chlorinated Polyethylene Data SheetDocument2 pagesChlorinated Polyethylene Data SheetwestmoonintNo ratings yet
- FTIR Infrared Spectroscopy Absorption TableDocument4 pagesFTIR Infrared Spectroscopy Absorption TablePankaj Kumar PalNo ratings yet
- 20 DQ Halo and HaloDocument15 pages20 DQ Halo and HaloAyushi KapoorNo ratings yet
- If You Already Know The Frequency Range Use This IR Spectrum Chart. If You Already Know The Frequency Use The AboveDocument11 pagesIf You Already Know The Frequency Range Use This IR Spectrum Chart. If You Already Know The Frequency Use The AboveAdza LuailikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document10 pagesChapter 5XuânNo ratings yet
- Infrared Spectroscopy Absorption Table - Chemistry LibreTexts PDFDocument7 pagesInfrared Spectroscopy Absorption Table - Chemistry LibreTexts PDFNurhayati HasanahNo ratings yet
- Ban Salclasses: CH MistryDocument7 pagesBan Salclasses: CH MistryApoorv RastogiNo ratings yet
- Acetal (Polyoxymethylene) Chemical Compatibility ChartDocument14 pagesAcetal (Polyoxymethylene) Chemical Compatibility Chartteban09No ratings yet
- Polymers and Reinforced PlasticsDocument27 pagesPolymers and Reinforced PlasticsKoduru ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chemical ResistanceDocument12 pagesChemical ResistancegusunNo ratings yet
- 5 IR Analisis KualitatifDocument38 pages5 IR Analisis KualitatifPAHTMA PURNAMA SARI DEWINo ratings yet
- Literature Preempt Material CompatibilityDocument2 pagesLiterature Preempt Material CompatibilityNatalia AlmaguerNo ratings yet
- Stahl - PUDSDocument29 pagesStahl - PUDSsusanasusana_No ratings yet
- Aluminum Chemical Compatibility ChartDocument14 pagesAluminum Chemical Compatibility Chartteban09No ratings yet
- Viacryl SC 303/65Xb: Technical Datasheet Liquid Coating Resins and AdditivesDocument2 pagesViacryl SC 303/65Xb: Technical Datasheet Liquid Coating Resins and AdditivesFadi MagdyNo ratings yet
- Valve Material SelectionDocument8 pagesValve Material Selectionerovho100% (1)
- ModuleIV - PART I NotesDocument5 pagesModuleIV - PART I NotesNoel DennisNo ratings yet
- IR Analisis KualitatifDocument38 pagesIR Analisis KualitatifRetno SulistyaningrumNo ratings yet
- IR Spectrum TableDocument17 pagesIR Spectrum TableAndres Felipe MNo ratings yet
- Chemical Resistance List2Document8 pagesChemical Resistance List2Jean Paul Pamo ValdiviaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Compiled by Saya Minn ThantDocument80 pagesOrganic Chemistry Compiled by Saya Minn ThantKaung Si ThuNo ratings yet
- Aplikasi Infra Merah Dalam Bidang Farmasi: Abdul Rohman Laboratorium Kimia Analisis Fakultas Farmasi UGMDocument38 pagesAplikasi Infra Merah Dalam Bidang Farmasi: Abdul Rohman Laboratorium Kimia Analisis Fakultas Farmasi UGMKhumairah MohtarNo ratings yet
- Sikagard® - 62Document7 pagesSikagard® - 62Aquasoul CoNo ratings yet
- Compound Selection and Conversion ChartsDocument6 pagesCompound Selection and Conversion ChartsRolando DoderoNo ratings yet
- Polymers PDFDocument6 pagesPolymers PDFAnusia ThevendaranNo ratings yet
- Infrared Spectroscopy: WWU ChemistryDocument34 pagesInfrared Spectroscopy: WWU ChemistryTrung HoNo ratings yet
- Ic103: Materials Chemistry-I: Institute Core Course For Btech ProgramDocument23 pagesIc103: Materials Chemistry-I: Institute Core Course For Btech ProgramAkash LikharNo ratings yet