Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1
Uploaded by
Bianca Mihaela Samuil0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pagedeutsch
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentdeutsch
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 page1
Uploaded by
Bianca Mihaela Samuildeutsch
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
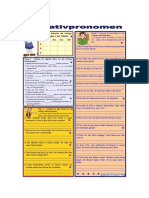
The Case System:
nominative, accusative, genitive, dative
All languages have ways of showing what role cach notin ix playing in a particular acntence,
for example who (or what) i doing what to whom. In English, we how this mainly by the
position of the noun in the sentence. German speakers, on the ather hand, show the sale of
42 noun mainly by adding endings co any determiners of adjectives which accompany the
oun (and sometimes tothe notin ice).
When they arc used in a sentence, sonns have one of four cases, depending on thee role ix
the sentence: nominative (subject), accusative (direct object). genitive (genitive object)
and dative (indirect object). In this cours: you will only necd to use the nominative,
accustive, and dative; the genitive sles frequently used, but we have included it in this
grammar cecion fr the ake of completeness
‘As we suid above, the cam af'a noun is signaled by the endings of any articles andlor
adjectives that are used with it. Here are some exemples, using only maculine nouns:
Der Hind beife den Mern, ‘The dog bites the man.
‘nominative accusative
De Mann, beitt en Hund “The man bites the Ang.
‘nominative ‘accusative
De Mann pt em Hund den Kuchen. “The man gives the cag the ke.
‘nominative dative aerusative (ives the eake tothe dg).
De Hand des Bickers int den Kuchen. “The bakers dag eats the cake
‘nominative geri caecurstive
Use of the Cases
Nominative: the subject of the sentence is ways in the nominative case. Asa rule of
thumbs, the subject is the person or thing performing the action of the verb. Tp take one of
the examples ftom above, in che sentence Der Hund beift-den Mann, the dog is the one
doing the biting: he is the subject of the senvence.
Accusative: the direct object of che seacence & always in the accusative caw. The direct
‘object i the Jing direcly affected by the action of the verb. So in the sentence Der
Hund beibt den Mann, che man i the direct object, because bee is the one who gets bitten,
(Gonisiver the penitive case is used to indicate possession. The person or thing which
posexcs isin the genitive cae. For example, in the phrase: der Hund des Bickers, it's the
baker who pomemes the dog, ao i’ the baker whois in the genitive case.
‘Dative: the indirect object of the sentence is always in the dative case. Think of the
indirect object ar the person or thing indirectly affected by the action of the verb. So in the
sentence Der Mann gibt dem Hund den Kuchen, the dog is the indirect object, the one ta
whom the man gives the eake. The cake is the direct object, the thing which is given. IF
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Adjective Endings: Dieser Wein Ist Billig, Dieser Da Ist Billiger, Aber Dieser Hier Ist Am BilligstenDocument1 pageAdjective Endings: Dieser Wein Ist Billig, Dieser Da Ist Billiger, Aber Dieser Hier Ist Am BilligstenBianca Mihaela SamuilNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1Bianca Mihaela SamuilNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1Bianca Mihaela SamuilNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1Bianca Mihaela SamuilNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1Bianca Mihaela SamuilNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1Bianca Mihaela SamuilNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument1 pageNew Microsoft Word DocumentBianca Mihaela SamuilNo ratings yet
- FCE WritingDocument5 pagesFCE WritingBianca Mihaela SamuilNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument1 pageNew Microsoft Word DocumentBianca Mihaela SamuilNo ratings yet