Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bigdataposter PDF
Bigdataposter PDF
Uploaded by
santa2121Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bigdataposter PDF
Bigdataposter PDF
Uploaded by
santa2121Copyright:
Available Formats
Do you know Big Data?
What is big data? How big is big data?
v.1 *
Dr. Dan Law, Charlie Greenbacker,
John Eberhardt ( )
What are leading big data tools?
Many definitions…! • Wikipedia: “Big data is the term for a collection of data It can be REALLY BIG!:! • Big data tools fall along a “stack” spanning infrastructure to visualization!
sets so large and complex that it becomes difficult to – Internet traffic is now ~5 Zettabyte per year (IBM)! – Current iPhone 5s: 76 Gigaflops!
• The Multiple V’s: Data that brings challenges in Volume process using on-hand database management tools or – 1 Zettabyte = 1 billion terabytes! – Fastest supercomputer: 50 Petaflops! Open Source COTS
(size), Velocity (speed), Variety (formats), Veracity traditional data processing applications”! – Visa processes 150 Million transactions per day (VISA)! – Interesting Comparison: Human Brain has 100 Billion
Stack Element Used For Examples Examples
(accuracy), as well as Visualization, Value, Vendors, etc.! • Adam Jacobs, 1010data: “Data whose size forces us – Library of Congress holds 3.2 Petabytes of data! Neurons (100 Giga-Neurons), 100 Trillion Synapses (100
• User Interface • Tableau, Centrifuge,
• McKinsey: “Datasets whose size is beyond the ability of to look beyond the tried-and-true methods that are – 207 Terabytes of video loaded daily on YouTube (2012)! Tera-Synapses), neurons “fire” 1-1000 times/second (100 Visualiza(on • Web-‐based tools
• D3js, 3js, Gephi, Ozone
Visual AnalyCcs
typical database software tools to capture, store, manage, prevalent”! – 50 billion devices connected to the Internet by 2020 (IDC)! Giga-fires to 100 Tera-fires per second)!
and analyze.”! • – 50 Billion photos on Facebook in 2010! • Machine learning • R, Mahout, Titan, OpenCV, • SAS, SPSS, MapR,
• Economist: “Society has more information than ever
Dan Law, Altamira: “Data of any type with potential
value that exceeds the analytic capabilities of traditional – 400 Million Tweets per day (Washington Post)! Analy(cs • StaCsCcal tools Lumify, Hive, Pig, Spark PalanCr
before and we can do things when we have a large body of stand-alone solutions”! – Seagate sold 330 Exabytes of hard drives in 2011!
information that simply we could not do when we only have • – LHC produces 500 Exabytes of particle collision data per • Data & Metadata • HDFS, Accumulo, MongoDB,
John Eberhardt, Altamira: “Any data collection that • Oracle, Marklogic,
smaller amounts”! cannot be managed as a single instance.”!
day CERN! ! Data Store • Source Data Cassandra, Titan, Neo4j,
YarcData, Teradata
• Indexes MySQL
• TransformaCon /
What types of data are in big data? What is a data scientist? NormalizaCon • Splunk, SAS, Oracle,
• Structured Data! • Semi-structured! • Streaming Data! • Geospatial Data! Ingest • Ingest / Streams
• Storm, Hadoop/MapReduce
IBM
People or teams that possess a special Data Science
! Tables, Relational Data, ! Hybrid data, such as! Data that moves across ! Data that includes Processing
mix of skills:!
etc. with semantics! documents with tables!networks at high speed! information on positions
Social Network Analysis
– They are "T-shaped” (see graphic at right)! • CM, Scheduling,
• Unstructured Data! • Metadata! • Temporal Data! in space (regions,
Statistical Analysis
Data Visualization
Natural Language
Machine Learning
– They have mastered all foundational areas of Monitoring
• AWS,
Azure,
Data Mining
• Linux,
OpenShiW,
OpenStack,
! Raw Text, Images, ! Structured data about ! Data including trends / points, tracks, shapes)!
Infrastructure
Processing
data science (horizontals in the graphic)! • ApplicaCon
Cloudera,
Red
Hat,
• And many others…! Puppet,
Zookeeper,
Oozie,
etc.
Video, Audio! data, e.g. from/to! activities in time! • Computer Programming! OperaCng
Systems
Rackspace,
vendor
• Mathematics & Analytic Methodology (Stats)! (IaaS,
PaaS)
• Computers,
HDFS,
KaZa,
JBoss,
Xymon
specific
• Big Data Technologies!
• Communications Skills! Networks
How do we extract knowledge from big data? – They possess deep expertise in at least one
Domain Knowledge & Communication Skills • Select key components of Hadoop Ecosystem:!
specialty area (verticals in the graphic)!
• By teaching computers to extract knowledge:! Distributed Computing & Big Data – HDFS (Storage), MapReduce (Distributed Processing), Accumulo (Secure data store, Indexing)!
Popular data scientist tools:!
! By agreeing upon and defining semantic concepts of knowledge in one or more “knowledge representations” (for
example, a fixed ontology, auto-generated ontology, user-defined tags)! – R, Python, Mahout, Pandas, Many Others…! Mathematics & Analytic Methodology
– See http://oss4ds.com! Computer Programming
! By building transforms to map semantic content from structured data into knowledge representations!
! By building classifiers to extract semantic content from unstructured data and to map that extracted content into
What Questions shoulD we ask about Databases?
knowledge representations! • What type of data do can we store?! • Can we perform analytics using the
! By building analytics to correlate / fuse / perform reasoning on extracted semantic content to generate even more ! Structured, unstructured, relational, graphs,
semantic content, and to map that information into a knowledge representations! How do we implement big data solutions? entities…!
database?!
! e.g. MapReduce?!
• And by doing this on a large scale…! Follow a process, that considers:! ! Big Files (e.g. imagery)? Small files (e.g. text)?!
• What is the latency for queries? Or for
! By dividing a problem into pieces and executing in parallel (e.g. MapReduce)! – Team Skills! • How is data ingested into the database?! analytics?!
! By building clever indexes of knowledge, so that you can search it quickly…! Problem ! – Problem Definition!
Definition and ! Streaming? Batch?! ! e.g. milliseconds? days?!
! By using high performance computers (HPCs) or other fast electronics (e.g. FPGAs, ASICs, Optics)! – Experimental Design!
! A mixture of the above… (e.g. Netezza, YarcData, Next Generation Oracle)!
Experimental • What does the database cost?! • Is it optimized for particular features?!
Design! Collection, – Success/Evaluation Criteria!
Evaluation! Storage and ! License costs? O&M costs? License restrictions?! ! Fast writes? Fast reads? Ease of use?!
– Data, Curation & QA!
Retrieval!
– Solution Design! • What hardware is required?! • How many users can the system
What do we do with knowledge we extract? • Infrastructure! ! Commodity? Proprietary?! support?!
• We can estimate and visualize parameters in data using statistics! • Ingest & Storage! • How scalable is the database?! ! Scaling for data does not necessarily imply
• Analytics! ! Gigabytes? Terabytes? Petabytes? Exabytes? scaling for a large number of users!
! We can describe data, explore correlations, discover patterns, predict outcomes, etc. through “observational studies”!
Data Curation • Visualization! Yottabytes?! • Is the database secure?!
! We need to account/correct for Bias and Confounding, for example by introducing elements of chance!!
Visualization! and Quality • Security! • Is the database fault tolerant?!
!We need to consider selection bias, measurement bias, analysis bias, error, confounding variables! ! Does it provide access controls? Has it been
Assurance! • Privacy & Ethics! ! Does it need to be? What about COOP?!
• We can implement rules to trigger actions in response to discovered knowledge! Analysis! accredited? To what level?!
• Budget & Schedule!
Not a linear process!
– Try an agile approach…!
What types of Visual techniques are there? What questions... about predictive tools?
Type Utility Pros Cons • How does this tool perform prediction?! • Does the tool correct for, or enable one
Spreadsheets! Viewing tabular data! Simple/Common! Can’t see patterns! How do we address privacy & ethics in big data? ! answers should list algorithms used (refer to table to correct for potential bias or
at left for descriptions/pros/cons…)!
Common Charts! Viewing numeric data! See Patterns/Trends! Hard to pivot/explore! confounding variables?!
Graphs! Exploring networks! Powerful analysis! Complex / Intensive! Privacy. Be sure to comply with:! Ethics. Consider:! • What types of data does the tool ! e.g. by introducing elements of chance or by
Geospatial views! Viewing data in space! Intuitive maps! Graphics intensive! – The 4th Amendment to the Constitution! 1. Respect for Persons / informed consent!
– Electronic Communications Privacy Act! 2. Beneficence!
analyze?! counting everything!
Temporal views! Viewing data in time! Find patterns/trends! Not all data temporal!
– Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act! 3. Justice! ! e.g. structured, unstructured, hybrid (are these ! if not, you should be skeptical of the predictions a
Spatiotemporal! Both space & time! Powerful analysis! Uncommon, Intensive!
– The Privacy Act! 4. Respect for Law and Public Interest! right for your mission?). Petabytes of data?! tool makes!!
3D Views! Viewing complex data! More immersive! Graphics Intensive!
Spatiotemporal! Immersive visualization! Intuitive / Powerful! Specialized Hardware! – Executive Order 12333!
– USA PATRIOT Act! !
Want to Learn More?
What types of statistical algorithms are there?
Algorithm Utility Pros Cons How do we secure big data? • George Mason University! • Explore integrated open source
Not qualitative, high curation
! GMU has both full semester graduate-level analytic platforms at www.lumify.io!
Linear! Providing point estimates! High precision, easy!
burden! • By addressing the notorious nine:! • By using big data to secure big data! courses and two day certificate course in Big ! Learn about open-source ingest, knowledge
! 1. Data Breaches! ! Collect & analyze activity data, network data, Data Practices! extraction, and link analysis from structured and
Supports more complex data, Limited inference, high 2. Data Loss! audits, provenance, pedigree, lineage!
Non-Linear! Processing complex systems! • Learn about Data Science and Big unstructured big data!
complex decisions! supervision needed! 3. Account Hijacking! • And by using:!
! 4. Insecure APIs! Data Tools at www.oss4ds.com! • Learn more about big data
! Risk Management: ICD 503! ! The instructors are part of a broader data
Fuzzy Logic /Neural!
Representing highly complex,
Complex inference, messy data!
Lower precision, seed value 5. Denial of Service! ! Access controls, IDAM, biometrics, PKI,
implementations at
qualitative systems! bias!
6. Malicious Insiders! science team that publishes open source www.altamiracorp.com!
physical security, cell-level security, smart resources to help you learn about Data Science
Complex dependencies, fuzzy Lower precision, no point 7. Abuse and Nefarious Use!
Probabilistic! Distribution, probability oriented! data, encryption!
decisions! estimates, see value bias!
8. Insufficient Due Diligence! and Big Data!
Represent large sets, easy Limited inference,
! CND, Anti-Malware, anti-virus!
Graph! Representation of data! 9. Shared Technology Issue!
interaction! computationally challenging!
A few Useful Contacts *Please email Dan Law if you have comments or suggest any improvements to this poster
Altamira: Dan Law, dan.law@altamiracorp.com Cloudera: 866-843-7207 Koverse: info@koverse.com Oracle: 800-633-0738
Amazon: http://aws.amazon.com/federal/
Centrifuge: info@centrifugesystems.com
Datastax: info@datastax.com
IBM: 800-333-6705
MarkLogic: info@marklogic.com
MongoDB: 866-237-8815
Splunk: 866-438-7758
Yarcdata: 925-264-4700
©2014 Altamira Technologies Corporation
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The CROW (1994-2005) - Complete Movie and TV Series - 480p-720p x264Document2 pagesThe CROW (1994-2005) - Complete Movie and TV Series - 480p-720p x264Asad RanaNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesLesson Plancooljexsan0% (1)
- Amy LowellDocument4 pagesAmy LowellRatnakar KoliNo ratings yet
- The Mental and Physical Healing of Dance Kaya Buschke ERWC Period 3 October 13, 2016Document14 pagesThe Mental and Physical Healing of Dance Kaya Buschke ERWC Period 3 October 13, 2016api-341952629No ratings yet
- MEM601 - Assessment - 1 - Brief - Short Answer Questions - FINALDocument6 pagesMEM601 - Assessment - 1 - Brief - Short Answer Questions - FINALArun pandiyanNo ratings yet
- Ithihasa&AbbreviationsDocument17 pagesIthihasa&AbbreviationsSree DivyaNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Training and Development in Banking and Other Sector With Special Reffernce To MumbaiDocument45 pagesEffectiveness of Training and Development in Banking and Other Sector With Special Reffernce To MumbaisnehaamhatreNo ratings yet
- Order of AdjectivesDocument5 pagesOrder of AdjectivesJanine EspinedaNo ratings yet
- ARTS8 Q3 LAS1 Final1Document11 pagesARTS8 Q3 LAS1 Final1Edrian Cubon VillodresNo ratings yet
- WBv12.1 Emag Tutorial4 Transformer PDFDocument38 pagesWBv12.1 Emag Tutorial4 Transformer PDFAraz SNo ratings yet
- Public Holidays 2009 - Government of Tamil NaduDocument5 pagesPublic Holidays 2009 - Government of Tamil NaduDr.SagindarNo ratings yet
- Letter of Authorization: To Whom It May ConcernDocument2 pagesLetter of Authorization: To Whom It May ConcernAvinash NandaNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: 1. Damon Is The Lessee in Connection With A Type A Lease. Under The New ASU, Damon WouldDocument4 pagesThis Study Resource Was: 1. Damon Is The Lessee in Connection With A Type A Lease. Under The New ASU, Damon WouldDaniella Mae ElipNo ratings yet
- Hansel and Gretel HandsoutDocument4 pagesHansel and Gretel Handsoutचौधरीखड़कNo ratings yet
- 15 Joint VentureDocument11 pages15 Joint VentureJanani PriyaNo ratings yet
- Practice Examination in Auditing TheoryDocument28 pagesPractice Examination in Auditing TheoryGabriel PonceNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Rev. Sheet Ans. KeyDocument12 pagesGrade 10 Rev. Sheet Ans. KeyKuunVoTAmNo ratings yet
- 1111 Portal ActivationDocument12 pages1111 Portal ActivationVeronica MerabishviliNo ratings yet
- Designer Baskets Inc V Air Sea TransportDocument38 pagesDesigner Baskets Inc V Air Sea TransportJan Igor GalinatoNo ratings yet
- Georgicsbooksiii 00 VirguoftDocument166 pagesGeorgicsbooksiii 00 VirguoftMarius AlexandruNo ratings yet
- Garh - Siyana Road, Katira Jafrabad (Hapur) : Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument16 pagesGarh - Siyana Road, Katira Jafrabad (Hapur) : Physics Investigatory ProjectRohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Socioemotional Development in Late AdulthoodDocument15 pagesSocioemotional Development in Late Adulthoodsonali mishraNo ratings yet
- Comminution PDFDocument10 pagesComminution PDFKhana Rizki MaulanaNo ratings yet
- MCQ 2Document5 pagesMCQ 2hbusyNo ratings yet
- 2021 CGV LPU REM 2 THQ No. 4Document2 pages2021 CGV LPU REM 2 THQ No. 4Susannie AcainNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2 - Descriptive WritingDocument4 pagesLesson Plan 2 - Descriptive Writingapi-301142304No ratings yet
- Annotated BibliographyDocument7 pagesAnnotated Bibliographyjenicaq820No ratings yet
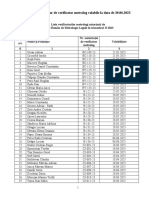
- Lista Verif Metrol Aut Trim II 2023Document25 pagesLista Verif Metrol Aut Trim II 2023Monica GusaNo ratings yet
- Recursive Functions DescriptionDocument3 pagesRecursive Functions DescriptionRaya RevanzaNo ratings yet
- PetrifiedDocument13 pagesPetrifiedMarta GortNo ratings yet