Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Scoliosis: Can It Be Prevented?
Uploaded by
Samiha Torrecampo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesftsrdt
Original Title
Zion
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentftsrdt
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesScoliosis: Can It Be Prevented?
Uploaded by
Samiha Torrecampoftsrdt
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
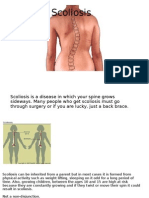
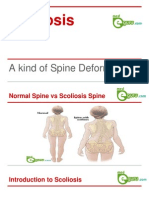
When a person has scoliosis, their backbone curves to the side.
The
angle of the curve may be small, large or somewhere in between.
But anything that measures more than 10 degrees is considered
scoliosis. Doctors may use the letters “C” and “S” to describe the
curve of the backbone.
Scoliosis without a known cause is what doctors call “idiopathic.”
Family history and genetics can also be risk factors for idiopathic
scoliosis. If you or one of your children has this condition, make
sure your other kids are screened regularly. Some kinds of
scoliosis do have clear causes. Doctors divide those curves into two
types -- structural and nonstructural. In nonstructural scoliosis, the
spine works normally, but looks curved. In structural scoliosis, the
curve of the spine is rigid and can’t be reversed.
Scoliosis shows up most often during growth spurts, usually when
kids are between 10 and 15 years old. About the same number of
boys and girls are diagnosed with minor idiopathic scoliosis. But
curves in girls are 10 times more likely to get worse and may need
to be treated.
Scoliosis diagnosed during the teen years can continue into
adulthood. The greater the angle of the spine curve, the more likely
it is to increase over time.
Can It Be Prevented?
No. So forget the rumors you may have heard, such as,
“Childhood sports injuries can cause scoliosis But it can be operated
by means of surgery
You might also like
- NCP ScoliosisDocument4 pagesNCP ScoliosisCharley DegamoNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis, (Updated) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandScoliosis, (Updated) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis 2Document2 pagesScoliosis 2api-264893632No ratings yet
- Adult Scoliosis: A Beginner's 2-Week Quick Start Guide on Managing Adult Scoliosis Through Diet and Other Natural Methods, With Sample Recipes and a Meal PlanFrom EverandAdult Scoliosis: A Beginner's 2-Week Quick Start Guide on Managing Adult Scoliosis Through Diet and Other Natural Methods, With Sample Recipes and a Meal PlanNo ratings yet
- ScoliosisDocument4 pagesScoliosisDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- Yoga for Scoliosis: A Beginner's 3-Step Quick Start Guide on Managing Scoliosis Through Yoga and the Ayurvedic Diet, with Sample RecipesFrom EverandYoga for Scoliosis: A Beginner's 3-Step Quick Start Guide on Managing Scoliosis Through Yoga and the Ayurvedic Diet, with Sample RecipesNo ratings yet
- ScoliosisDocument1 pageScoliosisKimberly Loide TimtimNo ratings yet
- Yoga for Scoliosis: A Beginner’s 3-Step Quick Start Guide on Managing Scoliosis Through Yoga and the Ayurvedic Diet, with Sample RecipesFrom EverandYoga for Scoliosis: A Beginner’s 3-Step Quick Start Guide on Managing Scoliosis Through Yoga and the Ayurvedic Diet, with Sample RecipesNo ratings yet
- About Scoliosis PDFDocument7 pagesAbout Scoliosis PDFNiessha ZuhrotulNo ratings yet
- ScoliosisDocument9 pagesScoliosisapi-302888135No ratings yet
- Scoliosis in Children and Teens enDocument8 pagesScoliosis in Children and Teens enEva-Lena RehnströmNo ratings yet
- Kyphosis Lordosis: What Causes Scoliosis?Document3 pagesKyphosis Lordosis: What Causes Scoliosis?Jian LadaoNo ratings yet
- How Does Scoliosis Affect The Spine?Document11 pagesHow Does Scoliosis Affect The Spine?Eddy ZayasNo ratings yet
- ScolioDocument2 pagesScolioJester de ChavezNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis Tcm75 464820Document2 pagesScoliosis Tcm75 464820Mohamed MagdyNo ratings yet
- Of Every 1,000 Children, 3 To 5 Develop Spinal Curves That Are Considered Large Enough To NeedDocument7 pagesOf Every 1,000 Children, 3 To 5 Develop Spinal Curves That Are Considered Large Enough To NeedEmily SankyNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis Fact SheetDocument3 pagesScoliosis Fact SheetTSRHCNo ratings yet
- ScolioDocument2 pagesScolioJonahh2012No ratings yet
- Scoliosis and KyphosisDocument5 pagesScoliosis and KyphosisEufrasia VictaNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis: Spinal Curvature, KyphoscoliosisDocument3 pagesScoliosis: Spinal Curvature, Kyphoscoliosisiamweena17No ratings yet
- ScoliosisDocument9 pagesScoliosisLorebell80% (5)
- ScoliosisDocument3 pagesScoliosisWilliam D. NarvaezNo ratings yet
- SP SkoliosisDocument19 pagesSP SkoliosisSantosa OkaNo ratings yet
- Adolescent Idiopathic ScoliosisDocument8 pagesAdolescent Idiopathic ScoliosismoechielmoechieNo ratings yet
- C-Shaped Curve: Presented By: Elorde, Charisma CDocument6 pagesC-Shaped Curve: Presented By: Elorde, Charisma CCharisma ElordeNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis: Laguna College San Pablo CityDocument5 pagesScoliosis: Laguna College San Pablo CitychristianjomariNo ratings yet
- Scolio SIS: Submitted ToDocument10 pagesScolio SIS: Submitted Tojean thereseNo ratings yet
- Severe Scoliosis in An Adolescent Benefits of EarlDocument7 pagesSevere Scoliosis in An Adolescent Benefits of EarlNEUROLIVROS NEUROLIVROSNo ratings yet
- Updateonevaluationand Treatmentofscoliosis: Ron El-Hawary,, Chukwudi ChukwunyerenwaDocument19 pagesUpdateonevaluationand Treatmentofscoliosis: Ron El-Hawary,, Chukwudi Chukwunyerenwacarla grauNo ratings yet
- Adolescent Idiopathic ScoliosisDocument5 pagesAdolescent Idiopathic ScoliosisJezabel MascioNo ratings yet
- ScoliosisDocument5 pagesScoliosisIbe JulienneNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis, Lordosis, and KyphosisDocument41 pagesScoliosis, Lordosis, and Kyphosischrisamaria100% (3)
- Scoliosis: By: Manilyn B. Lin Bsn-IiiDocument13 pagesScoliosis: By: Manilyn B. Lin Bsn-IiiWillie100% (1)
- Scoliosis: Aka: Idiopathic Scoliosis, Adolescent ScoliosisDocument12 pagesScoliosis: Aka: Idiopathic Scoliosis, Adolescent ScoliosisLei Coloma SissonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of ScoliosisDocument6 pagesAnatomy of ScoliosisDaniel MañalacNo ratings yet
- Fatima Sehar-699Document6 pagesFatima Sehar-699Fatima SeharNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis PDFDocument19 pagesScoliosis PDFdallas100% (1)
- ScoliosisDocument18 pagesScoliosisAnkit Tonger AnkyNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis, Lordosis, and KyphosisDocument40 pagesScoliosis, Lordosis, and KyphosisRati W. PaneseNo ratings yet
- ScoliosisDocument19 pagesScoliosisMia Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Idiopathic Scoliosis AdolescentsDocument10 pagesIdiopathic Scoliosis AdolescentscahyaningarumNo ratings yet
- Mehu525 - U2 - T9 - Evaluation and Treatment of Developmental Hip DysplasiaDocument13 pagesMehu525 - U2 - T9 - Evaluation and Treatment of Developmental Hip DysplasiaJorge OtoyaNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis - DR P K Sahoo PDFDocument3 pagesScoliosis - DR P K Sahoo PDFManish MauryaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Disorders Lec # 6Document43 pagesGenetic Disorders Lec # 6MISS. COMNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis Charper12Document122 pagesScoliosis Charper12Simón Pérez LópezNo ratings yet
- Pilates For ScoliosisDocument13 pagesPilates For ScoliosisIoan-Alexandru CodarceaNo ratings yet
- Department of Orthopaedic and Traumatology Faculty of Medicine - Hasanuddin University Makassar 2017Document24 pagesDepartment of Orthopaedic and Traumatology Faculty of Medicine - Hasanuddin University Makassar 2017aritrisnawatiNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis Aimee Morse Professor Bradford BIO 254 H1Document7 pagesScoliosis Aimee Morse Professor Bradford BIO 254 H1amNo ratings yet
- What Are Knock Knees?Document2 pagesWhat Are Knock Knees?thet waiNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis: A Kind of Spine DeformityDocument6 pagesScoliosis: A Kind of Spine DeformityAnvitatoursNo ratings yet
- Scoliosi 1Document5 pagesScoliosi 1Hazel Lyn Valdoz Gongora-CardozaNo ratings yet
- LP Scoliosis Kel.3Document19 pagesLP Scoliosis Kel.3Yanti Puspita SariNo ratings yet
- ScoliosisDocument5 pagesScoliosisIbe JulienneNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis (Curved Spine)Document7 pagesScoliosis (Curved Spine)Chow Mun FaiNo ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument25 pagesDefinitiondjustiela karrangNo ratings yet
- ArticleDocument8 pagesArticleLusian VissNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis Surgery IannnDocument8 pagesScoliosis Surgery IannnAnie ZacariasNo ratings yet
- ScoliosisDocument2 pagesScoliosisweruNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis - DR LanangDocument52 pagesScoliosis - DR LanangDandi PremaNo ratings yet
- Relationship InitiationDocument10 pagesRelationship InitiationSamiha TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- Salita vs. SalveDocument4 pagesSalita vs. SalveAustine CamposNo ratings yet
- Document 4Document1 pageDocument 4Samiha TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- Dear Hahaksisnkakzneh Two Less Lonely People in The World and Im So Tired - Confused. HahsjwisnelwzhnhdndbhdemnshkznksmxnekbnnjkxnsnDocument1 pageDear Hahaksisnkakzneh Two Less Lonely People in The World and Im So Tired - Confused. HahsjwisnelwzhnhdndbhdemnshkznksmxnekbnnjkxnsnSamiha TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- Sps Concepcion vs. Atty Dela RosaDocument5 pagesSps Concepcion vs. Atty Dela RosaSamiha TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- BAR MATTER 1153 Estelito MendozaDocument21 pagesBAR MATTER 1153 Estelito MendozaSamiha TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- As You Gaze Up Into The Night SkyDocument3 pagesAs You Gaze Up Into The Night SkySamiha TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- Kinder Curriculum 2016 PDFDocument32 pagesKinder Curriculum 2016 PDFBonjovi Verdejo100% (8)
- RHYS MURILLO - Insurance Reviewer - Ateneo Law SchoolDocument102 pagesRHYS MURILLO - Insurance Reviewer - Ateneo Law Schoollex libertadore94% (31)
- By Observing and Analyzing Actions of Lawyers and Judges in The Courtroom, Students Experience Different Advocacy TechniquesDocument1 pageBy Observing and Analyzing Actions of Lawyers and Judges in The Courtroom, Students Experience Different Advocacy TechniquesSamiha TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- 1 Parent - Teacher Conference: Grade 2 - Maalalahanin Afternoon Session 12:00 NOON - 5:30 P.MDocument1 page1 Parent - Teacher Conference: Grade 2 - Maalalahanin Afternoon Session 12:00 NOON - 5:30 P.MSamiha TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- Bar Matter No. 1153Document1 pageBar Matter No. 1153Megan ManahanNo ratings yet
- Sunnah (PDF Library)Document99 pagesSunnah (PDF Library)Mohamad Syamsul HizhamNo ratings yet
- Cursive Words A PDFDocument1 pageCursive Words A PDFSamiha TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- Fataawa Al-Lajnah Ad-Daa'imahDocument4 pagesFataawa Al-Lajnah Ad-Daa'imahSamiha TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- Fataawa Al-Lajnah Ad-Daa'imahDocument4 pagesFataawa Al-Lajnah Ad-Daa'imahSamiha TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- How Is The Taraweeh Prayer Performed: 1. The Number of RakahsDocument8 pagesHow Is The Taraweeh Prayer Performed: 1. The Number of RakahsSamiha TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- AqeedahOfTheImamsOfAhl Us Sunnahwww - Islam .GQDocument240 pagesAqeedahOfTheImamsOfAhl Us Sunnahwww - Islam .GQSamiha TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Hadith and SunnaDocument6 pagesThe Difference Between Hadith and SunnaSimoneNo ratings yet
- WitrDocument2 pagesWitrSamiha TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- BM 2012 and BM 850Document17 pagesBM 2012 and BM 850Samiha TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- WitrDocument2 pagesWitrSamiha TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- Andamo Vs IACDocument2 pagesAndamo Vs IACSamiha TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- Bar Matter No. 1153Document1 pageBar Matter No. 1153Megan ManahanNo ratings yet
- Republic Vs Monuz GR#151910Document10 pagesRepublic Vs Monuz GR#151910Jose Salve CabilingNo ratings yet
- B.M. No. 1154Document4 pagesB.M. No. 1154Patrick Jorge SibayanNo ratings yet
- 2004 Rules On Notarial ActDocument12 pages2004 Rules On Notarial ActSamiha Torrecampo100% (1)
- 2004 Rules On Notarial ActDocument2 pages2004 Rules On Notarial ActSamiha TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- Bar Matter No. 1153Document1 pageBar Matter No. 1153Megan ManahanNo ratings yet
- 2004 Rules On Notarial ActDocument12 pages2004 Rules On Notarial ActSamiha Torrecampo100% (1)