Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3dworld Anatomy Tips Eaton PDF
Uploaded by
yahe32sOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3dworld Anatomy Tips Eaton PDF
Uploaded by
yahe32sCopyright:
Available Formats
TUTORIALS | Anatomy tips
● An image from the author’s Anatomy for Digital
Artists course. The archer is posed to illustrate the
complexity of the back muscles under tension. The
model was originally a rigged, low-resolution mesh,
posed in Maya. The musculature was sculpted in
ZBrush and the model was rendered back in Maya.
The écorché was composited over the original render
TIPS & TRICKS
Anatomy for 3D artists
However far technology advances, anatomical knowledge will still form the basis of good character
design. Follow this set of expert tips to get better results from your own work BY SCOTT EATON
n aspiring character artist might ask: “How little opportunity to learn these anatomical fundamentals in art
Our expert
this issue…
A is anatomy important to my work?” The
emphatic answer is that as a character artist,
anatomy should inform every aspect of your
schools today. Like most of the knowledge of the great masters,
the subject has fallen out of favour in education and, as a
result, there are currently very few people who are qualified to
work! Anatomy is the structural foundation that grounds teach the subject. This makes finding good instruction difficult
characters in the physical world and makes them believable, and it transfers the responsibility of learning anatomy onto the
even if they are cartoons or imaginary creatures. artists themselves.
Of course, every CG artist needs to know how to This collection of tips will help you on your way towards the
use software applications, but what really separates an mastery of these fundamentals. Once you’ve finished, why not
accomplished artist from a mere operator is artistic vision and check out the list of recommended books on anatomy so you
a firm grounding in the fundamentals of human form. Artistic can increase your skills even more?
vision can’t easily be taught, but the enterprising artist will find These tips are intended to provide a foundation for your
Scott Eaton
is Creative Technical Director that there’s a wealth of resources available that will help them own learning. Some relate to muscles, some to bones and
at Escape Studios, where he discover more about anatomy. others to proportion. If you can assimilate these principles and
founded and now teaches
Anatomy for Digital Artists. Fortunately for us, the fundamentals of artistic anatomy combine them with your own anatomy study, your character
He has consulted for many have been known for thousands of years. Unfortunately, there’s work will go from strength to strength.
companies, including Sony,
The Mill and Double Negative
www.escapestudios.co.uk
052 | 3D WORLD March 2006
Anatomy tips | TUTORIALS
IN FOCUS | Écorché
This word is French for ‘flayed’ and
it describes the practice of drawing
or sculpting a figure without the
skin. Drawing écorché figures dates
back to the 15th century and is a
great way of learning anatomy. The
technique is simple. Start with a
● A quick silhouette check of a work in progress. Even though the base reference image showing good
model is very low-resolution, this helps assess proportional difficulties
muscular detail and tape a piece of
tracing paper over it. Now find the
bony landmarks on the figure and
APPROACH BIG SHAPES LIKE use these as reference points to
A SCULPTOR locate and place the muscle groups
Always subordinate small details to the big shapes. In computer
in the surrounding areas. Draw in
graphics, especially in newer programs that let you sculpt fine
the muscles, taking care to indicate
details quickly and easily, it’s simple to start right into the details
the direction of the muscle fibres,
(wrinkles, texture, veins and so on) of a character before the larger
and continue until it’s complete.
shapes are correctly established. If you approach the task of making
a CG model like the sculptors of old approached working in stone, it ● Écorché image by the author, showing the
will help to structure the construction process. back muscles. This image also highlights the
smoothing effect of skin and fat over the
Think of how a stone sculptor has to carve a chunk of stone into underlying muscles
a blocky model first, taking care to establish the correct proportions
and big shapes. Only once this stage is complete do the actual
muscular shapes and details get carved in.
CHECK SILHOUETTES
Checking the silhouette of your model is a good way to assess examined in detail, but it’s enough for the artist to understand the
the larger proportions and gesture of your model, without being large masses of these forms and use them to establish the large
distracted by the lack of finer details, which will be established later. shapes and planes of the figure. Both Bammes and Loomis present
Set your model to a flat, unshaded colour and zoom out to where excellent simplifications of the main masses of the skeleton – see
it’s small but still readable on the screen. Check the outline of the ‘Further reading’ on page 55. 1
model, looking for the big shapes and proportions. A dark, unshaded
colour helps you concentrate on the big shapes and ignore the fact PUT MASSES IN YOUR MODEL
that the model isn’t finished. There should always be a sense of underlying structure in your
models. This is achieved by maintaining your mass conceptions as 2
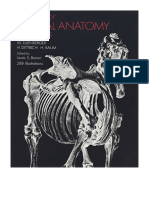
STUDYING A SKELETON you start to place the muscles onto the body. A simple technique
The skeleton is the foundation of any character – human, animal or in CG is to actually create simplified mass conceptions underneath 3
otherwise – and must be understood before the muscles will make the skin of your model. These will serve as a reference for both 4
sense. Say a client asks you to model a coat hanging in a closet. modelling the muscular forms on top, and also a reference during
Being a dutiful artist, you would have to ask two questions to make rigging to make sure the deformations don’t violate what’s meant to
sure the client gets what he or she was looking for: most obviously, be the rigid skeleton underneath.
what kind of coat is it? However, perhaps more importantly, you’d
also ask, what’s the shape of the hanger? Just as the hanger dictates THE BONY POINTS
the shapes of the hanging jacket, the skeleton dictates the shape of We acknowledge the importance of the skeleton and understand
the body and hanging muscles. Besides being the scaffolding that the simplification of the big masses of the pelvis and rib cage, but
establishes the proportion of the body, the skeleton serves as the what next? Well, you need to learn the key bony points on the ● An image showing a few of
start point and end point for all of the skeletal muscles. surface of the body. These are the places where the skeleton lies the critical bony points of the
skeleton: 1. Acromion process;
directly underneath the skin. They’re great reference markers for 2. Lateral epicondyle of the
MASS CONCEPTIONS establishing the proportions of the body and for accurately placing humerus; 3. Olecranon;
4. Anterior superior iliac spine
It ‘s important to have a mental simplification of the large shapes the surrounding muscle groups. Not only that, but these are the
of the skeleton. With a simple mass conception of the skull, rib cage places on your model that, when you’re rigging, shouldn’t deform
and pelvis, a figure can be sketched quickly to show balance and at all – they should only move rigidly with the joint. Some of the
▲
proportion. Each of these masses is decidedly complicated when most important are the point of the shoulder (acromion process),
March 2006 3D WORLD | 053
TUTORIALS | Anatomy tips
the spine of the scapula, the seventh cervical vertebra, the points of
the hip (anterior and posterior superior iliac spines), and the elbow
(olecranon and the epicondyles of the humerus). See the diagram on
the previous page.
ORIGINS AND INSERTIONS
What are the bony points good for? Well, like the coat hanger
example, they dictate how and where the muscles originate and
insert. Understanding these muscular attachments will help you to ● Even aliens have anatomy! This character design borrows from human
determine the direction of pull of the muscle, no matter what pose anatomy, modifying the proportions for a creature of this stature
the figure is in. This dictates how edge flow should be laid out.
attaching into the forearm. The principle of interlocking holds true
PULLING POWER right across the body, so emphasising this will make your models
One of the most important structural aspects to understand about become much more powerful.
muscles is that they must span at least one joint to function. This
simple mechanical principle gives muscles their pulling power. They THE FOREARM
originate on one bone and insert on another bone further down the The two most complicated areas of the body are the forearm and
hierarchy. It’s a simple concept, but it makes the interplay of muscles the scapula. Both owe their complexity to the number of muscles
across joints both dynamic and believable. and the numerous directions in which they pull. Mastery of these
● A study highlighting the
At the elbow, for example, there’s considerable interlocking areas will require additional study, so do pay attention to them.
complexity of the muscles of the
back. Note the interlocking of the between the upper and lower arm muscles. The forearm muscles When it comes to the arm muscles, the origins and insertions of
shoulder muscles onto the upper
extend well above the elbow, attaching onto the upper arm bone the biceps and triceps are relatively simple, but the muscles of the
arm, and the interplay of the
upper arm and forearm muscles (humerus). Likewise, the biceps and triceps extend below the elbow, forearm are much more complex.
As a roadmap to help you in your study, begin by understanding
the structure of the lower end of the upper arm bone (humerus).
There are two important bumps there (epicondyles): one on the
outside and one on the inside. From these two bumps respectively,
the extensors and flexors of the hand originate. The flexors then
IN FOCUS | Observe variation travel on the inside of the forearm, while the extensors travel over
the outside.
THE SCAPULA
● A drawing from life. A long pose Much of the complexity of the back – which beginners often
in front of a model gives an artist
incorrectly approximate with a few arbitrarily placed lumps and
the time to carefully study the
anatomy and proportions of the bumps – is due to the scapula (shoulderblade) and all its muscles
figure. Life drawing classes with
sliding to and fro over the rib cage. Again, to tackle this complicated
extended poses are difficult to
find, but are very useful for area, start by understanding the bony form of the scapula. The
carefully studying figures shape of the bone is like a guide map for placing the muscle. The
spine of scapula is an important bony landmark that will give away
the orientation of the bone and the disposition of the muscles that
reside there. Approach this area like a detective.
THE SKIN AND FAT
Your investigation of anatomy will certainly have you studying from
reference plates. These plates show every muscle in fine dissected
detail, but it’s important to remember that this is what the muscles
look like without their top layer of fat and skin. This layer acts to
soften and, in some cases, entirely obscure the muscular detail.
The effect of skin and fat on the underlying muscles is like
It must be understood that the figures presented in anatomy books are often limited to a single
looking through a piece of frosted glass – you can still see the
idealised human figure. In reality, though, the marvellous unpredictability of the gene pool creates
remarkable variations from this ideal. This is where direct observation becomes important. Take
shapes and masses behind the glass, but the edges are blurred and
every opportunity to study these individual variations. If you commute using public transport, many of the details are lost. Always cross-reference what you see
there’s no better opportunity to study the differences in facial structure and features. Buy a small on the muscular plate with photos or drawings of what the area
sketchbook and make notes – the variation will astonish you. looks like in real life.
054 | 3D WORLD March 2006
Anatomy tips | TUTORIALS
LIFE DRAWING
There’s no substitute for
studying anatomy on a live
figure, so find a life drawing
course near you and drop in. The
poses in classes are often too
quick to complete an entire figure
study accurately, so here’s a
recommended technique: during
any one pose, focus your drawing
on a specific part of the body and
take your time studying the bony
and muscular forms in that area.
Do a finished study of that small
section. With this method, you’ll
have more time to observe the
forms and details of the muscles
in the area, rather than putting
down a slapdash drawing of the
entire figure. It’s time better
spent and will accelerate your
anatomical learning.
● A collage of drawings from life.
These illustrate the softness of the
body due to skin and fat
accumulation. Even on athletic
figures, skin and fat still have a
softening effect on muscular details
ANIMAL ANATOMY FURTHER READING | Anatomy reference books
Once you have human anatomy under your belt, it’s quite easy to
learn animal anatomy. You may be surprised to learn that animals
have anatomy that’s very similar to humans, varying mostly in Even a casual glance in your local bookstore • A contemporary reference
• Encyclopedic coverage of the individual muscles
proportion. They have scapulae, flexors, extensors and all the things will reveal that there are shelves full of • An essential resource
we’ve talked about, only in a different size and shape. The wing of a anatomy books available to the eager
Title: Anatomy Lessons from the Great Masters
bat, for example, has the exact same bone hierarchy as a human arm student. There are some great titles out Author: Robert Beverly Hale & Terence Coyle
and hand, right down to the smallest digits of the fingers – only the there, but there are also lots of bad ones ISBN: 0823002810
• Uses master drawings to explain a range of
proportions and function are different. Learn human anatomy well too. A student of anatomy should study
anatomical concepts
and you’ll soon be able to understand animal anatomy. from only the best, so here’s a list of • Exhaustive coverage of the body
• Highly recommended for intermediate and
recommended anatomy books:
advanced students of anatomy
PLAUSIBLE ANATOMY
Title: Artistic Anatomy Title: Die Gestalt des Menschen
The principles outlined above can and should be applied to
Author: Dr Paul Richer & Robert Beverly Hale Author: Gottfried Bammes
fantasy creatures as well. Given that a creature is situated in a ISBN: 0823002977 ISBN: 3473610992
• The authoritative reference in the field • Constructionist approach to the skeleton
world with physics similar to our own, it will have evolved similar
• Difficult text, but well worth the effort and figure
mechanisms for dealing with gravity, mass and momentum. Use • Clear, extremely accurate plates • Excellent simplification of forms
your knowledge of human anatomy to imagine how the creature • Recommended for its illustrations, even if
Title: Atlas of Human Anatomy for the Artist you don’t read German!
might be constructed with muscles and bones so that it can react Author: Stephen Rogers Peck
to the environment around it. Take into consideration all the points ISBN: 0195030958 Title: Figure Drawing For All It’s Worth
• A classic, must-have reference Author: Andrew Loomis
mentioned here. Make note of an underlying skeleton, its bony • Many illustrations that explain difficult concepts ISBN 067031255X
points, muscular origins and insertions. Consider the interlocking of • Lucid text • Quality introduction to anatomy, proportions and
figure drawing from a master illustrator
muscles and tendons across joints. Borrow from human anatomy Title: Human Anatomy for Artists • Text is extremely readable
but change the proportions and functions as necessary. ● Author: Eliot Goldfinger • Not in print, but second-hand copies can be found
ISBN: 0195052064 online from specialist stores or sites like eBay
March 2006 3D WORLD | 055
You might also like
- Morpho: Muscled Bodies: Anatomy for ArtistsFrom EverandMorpho: Muscled Bodies: Anatomy for ArtistsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- How to Create Manga: Drawing the Human Body: The Ultimate Bible for Beginning Artists (With Over 1,500 Illustrations)From EverandHow to Create Manga: Drawing the Human Body: The Ultimate Bible for Beginning Artists (With Over 1,500 Illustrations)Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (3)
- John WatkissDocument74 pagesJohn WatkissRembert Montald100% (2)
- Drawing The Female Form - Bridgman, George B., Pinchot, BDocument69 pagesDrawing The Female Form - Bridgman, George B., Pinchot, BBurakcan Kocer100% (1)
- Big Bad World of Concept Art For Video Games: An Insider's Guide For Students - Study & TeachingDocument4 pagesBig Bad World of Concept Art For Video Games: An Insider's Guide For Students - Study & Teachingwykizoda0% (3)
- Animated Performance Sample Chapter 'Design For Living'Document28 pagesAnimated Performance Sample Chapter 'Design For Living'AVAAcademiaNo ratings yet
- 3D Total Anatomy of The Human Head - Mario AngerDocument28 pages3D Total Anatomy of The Human Head - Mario AngerDiego100% (2)
- Classic Human Anatomy in Motion PRDocument1 pageClassic Human Anatomy in Motion PRhhhNo ratings yet
- How To Draw Background With Character by Betsy Lun TaoDocument202 pagesHow To Draw Background With Character by Betsy Lun TaoAnne Teodora100% (2)
- Free Chapter bgts2 PDFDocument21 pagesFree Chapter bgts2 PDFSơn Nguyễn100% (2)
- Sketching Men: How to Draw Lifelike Male Figures, A Complete Course for Beginners (Over 600 Illustrations)From EverandSketching Men: How to Draw Lifelike Male Figures, A Complete Course for Beginners (Over 600 Illustrations)No ratings yet
- Anatomy For 3D Artists The Essential GuiDocument7 pagesAnatomy For 3D Artists The Essential GuiSalsoul Choi0% (2)
- 3dtotal Anatomical CollectionDocument2 pages3dtotal Anatomical CollectiontutorphilNo ratings yet
- How To Draw Manga Eyes 9pDocument9 pagesHow To Draw Manga Eyes 9pBui Nguyen Hoang HaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Construction of the Human FigureFrom EverandAnatomy and Construction of the Human FigureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Bahi JD InterviewDocument9 pagesBahi JD InterviewArturo Hernández Correas100% (2)
- 04a ConteanimatedDocument228 pages04a ConteanimatedBurcuylmzz100% (1)
- Creating A Stylised Male PortraitDocument4 pagesCreating A Stylised Male PortraitenveroxaNo ratings yet
- How To Draw Manga - Anime Clothing and Folds DrawingDocument8 pagesHow To Draw Manga - Anime Clothing and Folds DrawingPanagiotidis Tasos100% (2)
- A Sketchy Past - The Art of Peter de Seve Ipad Android KindleDocument7,720 pagesA Sketchy Past - The Art of Peter de Seve Ipad Android KindleEliCash0% (2)
- 3dworld Animal Anatomy EatonDocument5 pages3dworld Animal Anatomy Eatonmelanieloo100% (2)
- Anatomy, Perspective and Composition for the ArtistFrom EverandAnatomy, Perspective and Composition for the ArtistRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Morpho: Fat and Skin Folds: Anatomy for ArtistsFrom EverandMorpho: Fat and Skin Folds: Anatomy for ArtistsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Morpho: Face, Head, and Neck: Anatomy for ArtistsFrom EverandMorpho: Face, Head, and Neck: Anatomy for ArtistsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Goldfinger Human Anatomy For Artists PDFDocument4 pagesGoldfinger Human Anatomy For Artists PDFSamuelNo ratings yet
- Scott Eaton Anatomy Tutorial - 3D Artist - Animation, Models, Inspiration & Advice - 3DArtist MagazineDocument11 pagesScott Eaton Anatomy Tutorial - 3D Artist - Animation, Models, Inspiration & Advice - 3DArtist MagazineMohammed SalihNo ratings yet
- Syn Studio Concept Art Diploma: Application GuideDocument6 pagesSyn Studio Concept Art Diploma: Application Guidebharat0072No ratings yet
- Figure Drawing David Sequeira TutorialDocument14 pagesFigure Drawing David Sequeira Tutorialabhinav Verma100% (1)
- 10 Steps To Improve Your Figure Drawing - Creative BloqDocument16 pages10 Steps To Improve Your Figure Drawing - Creative BloqMohammed SalihNo ratings yet
- Takuji Kawano - Soul CaliburDocument2 pagesTakuji Kawano - Soul CaliburMatthew MeleadyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy-Master-Class AboutDocument10 pagesAnatomy-Master-Class AboutNóra Pintér100% (1)
- Art Rocket - Drapery and FoldsDocument17 pagesArt Rocket - Drapery and FoldsKian SantaeNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Head Drawing For Character Design - Ron LemenDocument17 pagesTutorial - Head Drawing For Character Design - Ron Lemeno_dimitrov100% (2)
- How To Draw Manga Vol. 42 Drawing Yaoi - Decrypted.r PDFDocument149 pagesHow To Draw Manga Vol. 42 Drawing Yaoi - Decrypted.r PDFpaola100% (3)
- Cookie Concept Art PDFDocument10 pagesCookie Concept Art PDFNesshi S. OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Figure DrawingDocument3 pagesFigure DrawingKrishna DhyaniNo ratings yet
- Mitch LeeuweCVDocument3 pagesMitch LeeuweCVDenisse CardozaNo ratings yet
- BGTDP Characters Free ChapterDocument12 pagesBGTDP Characters Free ChapterBarry Fry100% (3)
- Cartoon Character DesignDocument4 pagesCartoon Character DesignLeiliane Alencar100% (1)
- Anatomy April HANDY HINTS PDFDocument37 pagesAnatomy April HANDY HINTS PDFlaurent capoeiraNo ratings yet
- Character Art: Getting Into The Industry... and Staying in It: by John DeriggiDocument8 pagesCharacter Art: Getting Into The Industry... and Staying in It: by John DeriggiAhmad TantawyNo ratings yet
- Composition For Comic ArtistsDocument22 pagesComposition For Comic Artistskingsleyclementakpan100% (2)
- Art: Charles Hu Figure Drawing Lecture Updated 4:21:2011Document86 pagesArt: Charles Hu Figure Drawing Lecture Updated 4:21:2011albin_grau100% (2)
- 1lib - Eu-Force Animal Drawing Animal Locomotion and Design Concepts For AnimatorsDocument13 pages1lib - Eu-Force Animal Drawing Animal Locomotion and Design Concepts For AnimatorsTeresa Arteaga0% (2)
- An Atlas of Animal Anatomy For Artists - W. EllenbergerDocument4 pagesAn Atlas of Animal Anatomy For Artists - W. Ellenbergercawyrysa0% (1)
- Heads, Features and Faces (Dover Anatomy For Artists) by George B. BridgmanDocument8 pagesHeads, Features and Faces (Dover Anatomy For Artists) by George B. Bridgmanchrisitna jones0% (3)
- Total04 Digital Version PDFDocument52 pagesTotal04 Digital Version PDFbeatriz matos50% (4)
- Head LukasDocument43 pagesHead LukasSergent Khaos100% (1)
- ArtStation - 6 Months of Learning To Draw, Andrew PriceDocument38 pagesArtStation - 6 Months of Learning To Draw, Andrew PriceMrinal K Mahato100% (1)
- SPARKLITE Digital ArtbookDocument52 pagesSPARKLITE Digital ArtbookRamiro Miguel Torrente Pita100% (2)
- Creating Stylized Characters Using The Collage TechniqueDocument17 pagesCreating Stylized Characters Using The Collage TechniqueEdwin Acosta100% (2)
- Character DesignDocument4 pagesCharacter DesignMark Rous50% (4)
- Basics Animation 03 Drawing For Animation-SlicerDocument194 pagesBasics Animation 03 Drawing For Animation-SlicermarjaaaaaNo ratings yet
- (YiM - Ebook) Sketch Workshop Characters 3dtotal PublishingDocument3 pages(YiM - Ebook) Sketch Workshop Characters 3dtotal PublishingEmmanuel Chadee0% (2)
- Comic Artist39s Photo Reference People Amp Poses PDFDocument3 pagesComic Artist39s Photo Reference People Amp Poses PDFMichael0% (2)
- Go Berserk in PhotoshopDocument3 pagesGo Berserk in Photoshopk2ngdraNo ratings yet