Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mathematics CCE (P) 2015
Uploaded by
Dhrubajyoti Das0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views16 pagesFgyy
Original Title
Mathematics CCE(P) 2015
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFgyy
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views16 pagesMathematics CCE (P) 2015
Uploaded by
Dhrubajyoti DasFgyy
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
CcECP) - 2015
MATHEMATICS
KTM-20-XV
DO NOT OPEN THIS TEST BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE ASKED TO DO SO
Subject Code: [2/0
Test Booklet No. : ()()92()
e.
TEST BOOKLET
MATHEMATICS
Time Allowed : 2 (Two) Hours Full Marks : 200
INSTRUCTIONS
1. The name of the Subject, Roll Number as mentioned in the Admission Certificate, Test Booklet No.
and Subject Code shall be written legibly and correctly in the space provided on the Answer Sheet
with black ball pen.
Space provided for Series in the Answer Sheet is not applicable for Optional Subject. So the
space shall be left blank.
3. All questions carry equal marks. Your total marks will depend only on the number of correct
responses marked by you in the Answer Sheet.
4. No candidate shall be admitted to the Examination Hall/Room 20 minutes after commencement of
distribution of the paper. The Supervisor of the Examination Hall/Room will be the time-keeper
‘and his/her decision in this regard is final
5. No candidate shall leave the Examination Hall/Room without prior permission of the Supervisor/
Sas See No candidate shall be permitted to hand over his/her Answer Sheet and leave the
Examination Hall/Room before expiry of the full time allotted for each paper.
6. No Mobile Phone, Pager, ete., are allowed to be carried inside the Examination Hall/Room by the
candidates. Any Mobile Phone, Pager, etc., found in possession of the candidate inside the
Examination Hall/Room, even if on off mode, shall be liable for confiscation.
7. No candidate shall have in his/her possession inside the Examination Hall/Room any book,
notebook or loose paper, except his/her Admission Certificate and other. connected paper
permitted by the Commission.
8. Complete silence must be observed in the Examination Hall/Room, No candidate shall copy from
the paper of any other candidate, or permit his/her own paper to be copied, or give, or attempt to
give, or obtain, or attempt to obtain irregular assistance of any kind.
9. After you have completed filling in all your responses on the Answer Sheet and the Examination
has concluded, you should hand over to the Invigilator only the Answer Sheet. You are permitted
to take away with you the Test Booklet.
10. Violation of any of the above Rules will render the candidate liable to expulsion from the
Examination Hall/Room and disqualification from the Examination, and according to the nature
and gravity of his/her offence, he/she may be debarred from future Examinations and Interviews
conducted by the Commission for appointment to Government Service.
11. Smoking inside.the Examination Hall/Room is strictly prohibited.
12. This Test Booklet contains three pages for Rough Work at the end.
DO NOT OPEN THIS TEST BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE ASKED TO DO SO
[ No. of Questions : 100 ]
im he)
@ceCe)-2015—
MATHEMATICS
1. For any two sets Aand B, AN(AUB)”
is equal to
@) 4 (B) B
© ¢ (D) AnB
2. If A and B be two non-empty sets,
then which one of the following is
the result of (AU B)- A?
(a) A-B (B) B-A
cB (D) 4’
3. Consider the function f:W—>W.
defined by
n+1if nis even
Fey) n-1if n is odd
where W is the set of whole
numbers. Then the function f is
(A) one-one
(8) onto
(C) bisective
(D) None of the above
4. If A and B are two sets such that
nA)=2, nlB)=3 then n(P(A xB) is
equal to
(A) 64 (B) 6
Os (D) 12
KTM-20-KV/26
5. With respect to —_ composite
composition, the set A, of all even
permutations of degree n, defined
on a set S forms a finite group of
order
ain ®) Zn
(Q n/2 @) 4n/2
6. If in a group of 65 people, 40 like
cricket, 10 like both cricket and
tennis, then the number of people
who like tennis only and not cricket
is
(a) 15 (8) 25
(© 35 ©) 45
7. If in a group G, a® =e, the identity
element of G and aba =b? for
@ beG then Of) is
(A) 31 8) 29
(C) 23 ©) 19
8. The set Q of rational numbers is not
a group under the operation +
defined by aeb= 2 for
(A) *is not a binary operation inQ
(B) * is not associative in Q
(C) there does not exist identity
element in Q
(D) some elements of Q have no
inverses
9. Let Hand K be two subgroups of a
group G. Then HUK is a subgroup
of G if and only if
(A) either HoK or KCH
©) HoK=6
(Q) Hex and KeH
(D) None of the above
10. Let (Q +, +) be a@ ring of rational
numbers. Then the set of integers Z
is
(A) a subring but not an ideal of @
(8) neither a subring nor an ideal
of O
(C) @ subring as well as an ideal
of Q
(D) not a subring but an ideal of Q
11, The inverse of a symmetric matrix is
(A) symmetric
(B) skew-symmetric
(©) diagonal matrix
(D) None of the above
12. The rank of a mxn matrix whose
every element is unity is
(A) m Bn
(C) mn 1
KTM-20-XV/26
13. The system of lincar equations
AX = B is consistent if and only if
the coefficient matrix A and the
augmented matrix [ABj are of
(A) same rank
(B) different ranks
(C) same number of rows
(D) None of the above
14. Ifx, y ze R* and x9 +y3 +29 =81
then the maximum value of x +y+z
is
(a) 3v3 @®) 3
(C) 27 (Dd) 9
15. The condition in order that the
equation x9 - px? +qx-r=0 may
have a pair of equal roots is
(A) pa=r
(8) pr=q
(C) ar=p
(D) None of the above
16, The infinite series
14214243, 1424344 |
33 43
is
(A) convergent
(8) oscillatory
(©) divergent
(D) None of the above
[P.7.0.
17. The series
Dh Pig?
279" "28
is convergent if
(a) x1
(CG) x=1
(D) None of the above
18, Choose the incorrect statement :
(A) A convergent sequence
determines its limit uniquely.
(B) Every convergent series is
bounded.
(VA monotonic increasing
sequence diverges to + if it is
not bounded above.
(0) A monotonic decreasing
‘Sequence is not convergent.
19. tim(Y txt vx -v%) is equal to
(a) 0 ® 4
(C) log 2 (0) e*
20. The function f defined by
= aS
x
ee
is continuous at x = 0 for
(4) k=0
() k
(©) k=7
(0) no value of k
fee
KTM-20-XV/26
21. If y=logisin.x), then yg is equal to
in. x +cos?
(A)
ats
2cosx
sin? x
()
1+cos? x
()
sin? x
(py sin? x+2cosx
sin? x
22. Suppose the function f satisfies the
conditions
@) flx+y=FeIfly Vx and y
(i) f(x) = 1+ 292) where
lim gx) =1
x30)
Then f’(x) is equal to
(A) fe)
®) fa
(C) 2f(x)- 910)
(D) None of the above
24. Ifu=x?y+ y?z+2?x then the value
Qu, du, au,
poe ate Oe
of = is equal to
a) 0
B® u
(©) x+y+z
(©) (e+ y+2?
25. The point of intersection of the
tangents to the curve y = 2x? at the
points (1, 2) and (-1, 2) is
4) OO (B) 2)
() (@ -2 ©) 29
26. If H is a homogeneous function of x
and y of degree k, then each of
x
and ea is a homogeneous function
in x and y of degree
@ k
(B) k-1
(©) k-2
(D) None of the above
27. The function f(x, y= 2x? +2xy-y?
has
(A) no stationary point
(©) only one stationary point at
(9
(C)_ two stationary points
1
wed (5-3)
(D) two stationary points at (0, 0)
and (1, -1)
t (0, 0}
KTM-20-XV/26
28. ea(+ 2)
jim = is equal to
(a) 0
®) 3
(1
@ -1
x+sinx
T+cosx
then Fr /2) is equal to
29. If F(x)=f
dx and F(Q)=0,
(A) n/2
(8) «/3
(C) x/4
@ «
(C) $loga
(©) mlog2
31. The volume of the solid obtained by
2 42
revolving the ellipse: ~+¥ =1
a2 bs.
about the x-axis is
2
(A) 4na*b
2
(8) 4nab
2,
(C) 3na*b
2
(D) 3nab’
[P7.0.
92. The triangle of maximum area which
can be inscribed in a circle is
(A) scalene
(B) right angled
(C) isosceles
(D) equilateral
83. If flx) = fla-x), x) +. fax) =4and
then L ‘flgixidx is
(ay 1
®) 0
@ -1
(D) None of the above
34, The radius of curvature of the
parabola y? = 4x at the vertex (0, Q)
is equal to
(a) 0 ® 1
© 2 om 3
85. The value of [sin“(cosx)dx is
(Ap eo
2 eit
2
8) a Azo
© es
(D) None of the above
KTM-20-XV/26
36. In the mean value theorem
fle+h)= fle) thf x+0h, 0<8<1
where f(x) = sin, the limiting value
of 6.as h->0+ is
@ 2 ed
1 © -4
37. If fixy= c Vt dt, then at is equal
to
ao @) 1
(©) 2x? (D) ve
38. If at every point of a certain curve,
the slope of the tangent equals ~ a
then the curve is
(A) a straight line
(8) a circle
(C) a parabola
(0) an ellipse
39. If
foot ta-x+ x%)ae = afitan tx ae
then the value of A is equal to
(A) 1 @) 2
( 3 (D) 4
40. The condition /’(q=0 for f(d'to be
an extreme value of the function fis
(A) necessary condition
(B) sufficient condition
(©) necessary and
conditions
sufficient
(D) necessary but not sufficient
condition
41, The degree of the differential
equation
(BE) eh m(Qor-2
is
@) 3
® 2
cq 1
(D) not defined
42. The integrating factor of the
differential equation
yde = (x+2y?)dy=0
is
(a) 1/y
(B) 1/x
Oy
(D) None of the above
KTM-20-XV/26
43. (y-cx)(c~1)=c is a solution of the
differential equation
(A) y= px+ p-p?;
(B) y= px-———
pei
() y= px+
(D) None of the above
44. The particular integral of the
differential equation
(D8 - Dy=e* +e*
is given by
(A) dle +e™*)
(B) dx(e* +e*)
() bx2(e*+e*)
) 4x2(e*-e°*)
45. The differential equation
Mix, ude + Nx, dy =0
is an exact equation if
aM , aN
0 Say?
8)
c
©)
[P-T.0,
46. The general solution of the
differential equation
(D? +6D+9y=2e?*
is
(A) y=(Acos3x + Bsin 3x) +2e?*
(B) y= cre +20°?*
(C) y=(q +egxJe3* +e>*
(D)_ y= (q +eqxe* +2e2*
47. If the straight lines
ax? +2hxy+ by? +29x+2fy+e=0
intersect on the x-axis then
(A) ag= fh
(8) ah= fg
(©) af=gh
(D) None of the above
48. If by transformation from one
rectangular axes to another with
the same origin, the expression
ax + by changes to a’x’+b’y’, then
(A) atb=a'+b’
(B) a’
i)
@)
KTM-20-XV/26
49. The equation ax? +2hxy+by? =0
represents a pair of perpendicular
lines if
(A) a+b=0
(B) h? = ab
(C) nh? >ab
(D) h? 1
(@®) k<1
() k=1
(D) None of the above
82. The series,
vn? 1-1, is
(A) oscillatory
(8) convergent
(©) divergent
(D) None of the above
[P-2.0.
83. The value of & in the mean value
theorem f(b) - fla)=(b-a)f'"@) for
F\x) =x and a=4, b=9, is
3
Wo
te) 78
a
) fe
(D) None of the above
0, oe core
the function f(x) =
in x]in| —
w Aa)
(B) fis not continuous in|
(©) f is not derivable at some
points oe (2a
ne of (5.3)
(D) fis not defined at some points
of [-%. 3
223,
85. If the function f(x) =(x- 3? satisfies
all the conditions of Lagrange’s
mean value theorem, then the point
on the curve where the tangent is
parallel to the chord joining the
points (3, 0) and (4, 1) is
a 4
8) O99
(©) 6/2 1/4)
@) (7/2 1/4)
KTM-20-XV/26
14
86. If uw=log(x® + y*+z5 - 3xyz), then
Uz +Uy +U, is equal to
3
(5 eae
Wye
Ot
°)
(@)
"7. The angle of intersection of the
curves r= all+cos®), r= b(1—cos6)
is
on
(B) x/2
ao
(D) 0/2
88. The maximum value of sin x +cosx is
(A) 2
B) 2
1
(D) 1+V2
89. The value of {tant hae is
+x
1
®) 0
() -1
(D) 2/4
90. The value of the indefinite integral
j a
3+2sinx +cosx
is given by
91. The polar equation of a conic is
$= 3-4c080
r
Then the eccentricity of this conic is
given by
a) 4/3
6) 5/3
(C) 3/4
@) 5/4
KTM-20-XV/26
15
92. The area of the region bounded by
the parabola y? =x and the line
Qy=x is
(4) 1 sq. unit
(8) 4 sq. unit
(C) 2 sq. unit
aks ok
(@)
we
‘sq. unit
93. The slope of the tangent at (x, toa
curve passing through the point
(tty?
@ vis
of the curve is given by
Then the equation
(A) 2x? - y?) = 3x
(B) (x? - y?) = 3y
(©) xc? -y?)=6
(D) x(x? +y?)=10
94, The general solution of the
differential equation
@) y-de%* +a
(C) y=e** +ax+b
See e:
(D) e** sax? +b
Oy
[P.7.0.
95. The solution of the differential
equation
ay yay “
east xe
is given by
(A) e%(q +epx) + x2e*
©) eq +egx)+ Jade
a 20) ae
(©) ele, +eqx) +5 x*e
(D) None of the above
96. The value of 4 for which the two
circles x? + y? +5x +3y+7=Oand
x? + y? -8x+6y+h=0
orthogonal, is
(A)
@) -18
18
(9
@ 0
97. The number of normals which can be
drawn from a given point to a
parabola is
(a) 1
®) 2
() 3
@) 6
KTM-20-XV/26
16
98. For any three vectors d, b, ¢; the
value of (a+b, b+, +d
equal to
@) 2a 5 a
@ tab 4
© ab a
(D) None of the above
99. If a =cosx+isinx, B-cosytisiny,
yecosz+isinz and a+f+y-0,
then the value of +141 ig
apy
(A) 3cos(x+ y+z)
(B) 3sin(x + y+2)
(0
(D) None of the above
100. If a=cos+isin®, b=cos$+ising,
then’ the value of cos(@ + ¢) is
a i
m He)
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Designing and Manufacturing of A Hand-Made Electric MotorcycleDocument6 pagesDesigning and Manufacturing of A Hand-Made Electric MotorcycleArash0% (1)
- Assam Public Service Commission: WWW - Apsc.nic - inDocument6 pagesAssam Public Service Commission: WWW - Apsc.nic - inDhrubajyoti DasNo ratings yet
- BEL announces selection of 480 contract engineers on 8th JulyDocument1 pageBEL announces selection of 480 contract engineers on 8th JulyDhrubajyoti DasNo ratings yet
- DFCCILDocument14 pagesDFCCILTopRankersNo ratings yet
- Department Discipline Qualification No. of Seats UR SC ST OBC (NCL)Document3 pagesDepartment Discipline Qualification No. of Seats UR SC ST OBC (NCL)TopRankersNo ratings yet
- Corrected Answer Key AM 25082015Document4 pagesCorrected Answer Key AM 25082015Dhrubajyoti DasNo ratings yet
- Figure 5.1. Typical Pressure Vs Crank Angle For A Four Stroke EngineDocument5 pagesFigure 5.1. Typical Pressure Vs Crank Angle For A Four Stroke EngineonikNo ratings yet
- BIS Recruitment Detailed Official Notification 2018Document29 pagesBIS Recruitment Detailed Official Notification 2018Kshitija100% (1)
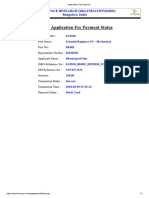
- Isro PaymentDocument1 pageIsro PaymentDhrubajyoti DasNo ratings yet
- Assam Public Service Commission: WWW - Apsc.nic - inDocument6 pagesAssam Public Service Commission: WWW - Apsc.nic - inDhrubajyoti DasNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus, Linear Algebra, and Differential Forms: A Unified ApproachDocument4 pagesVector Calculus, Linear Algebra, and Differential Forms: A Unified ApproachDhrubajyoti DasNo ratings yet
- Gate 2019 PDFDocument18 pagesGate 2019 PDFDhrubajyoti DasNo ratings yet
- SPIL Global Code of Conduct With QA 2016Document32 pagesSPIL Global Code of Conduct With QA 2016Dhrubajyoti DasNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus, Linear Algebra, and Differential Forms: A Unified ApproachDocument4 pagesVector Calculus, Linear Algebra, and Differential Forms: A Unified ApproachDhrubajyoti DasNo ratings yet
- Productflyer - 978 1 84800 390 3Document1 pageProductflyer - 978 1 84800 390 3Dhrubajyoti DasNo ratings yet
- Delhi Metro Rail Recruitment Official Notification 2018Document5 pagesDelhi Metro Rail Recruitment Official Notification 2018Kshitija100% (3)
- Steam and Streak LineDocument3 pagesSteam and Streak LinedurendranNo ratings yet
- Pre PhysicsDocument1 pagePre PhysicsDhrubajyoti DasNo ratings yet
- Detailed Advertisment MGES 2016 17 PDFDocument17 pagesDetailed Advertisment MGES 2016 17 PDFPrateekMittalNo ratings yet
- Notification IDBI Bank Executive Posts PDFDocument17 pagesNotification IDBI Bank Executive Posts PDFTamilNo ratings yet
- DMRC Last Date Extended Official Notification 2018Document1 pageDMRC Last Date Extended Official Notification 2018TopRankersNo ratings yet
- Weekly Pocket Eng 14 Jan 20 Jan 2018Document4 pagesWeekly Pocket Eng 14 Jan 20 Jan 2018Dhrubajyoti DasNo ratings yet
- SBI Clerk Exam Date Postponed Official Notification 2018Document1 pageSBI Clerk Exam Date Postponed Official Notification 2018KshitijaNo ratings yet
- Writtentest and Interview-Venuetming 2017-1 PDFDocument1 pageWrittentest and Interview-Venuetming 2017-1 PDFDhrubajyoti DasNo ratings yet
- SBI Clerk Recruitment 2018Document6 pagesSBI Clerk Recruitment 2018nidhi tripathi100% (1)
- SBI Clerk Recruitment 2018Document6 pagesSBI Clerk Recruitment 2018nidhi tripathi100% (1)
- New Form 15G PDFDocument2 pagesNew Form 15G PDFSoma Sundar50% (2)
- Advt 12018 in WebsiteDocument5 pagesAdvt 12018 in WebsiteDhrubajyoti DasNo ratings yet
- Advt 12018 in WebsiteDocument5 pagesAdvt 12018 in WebsiteDhrubajyoti DasNo ratings yet