Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 8 Risk and Rate of Return
Uploaded by
Alice Loren0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views2 pagesok
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentok
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views2 pagesChapter 8 Risk and Rate of Return
Uploaded by
Alice Lorenok
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
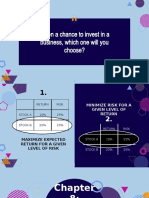
CHAPTER 8 RISK AND RATE OF RETURN
Generally, higher return, higher risk;
In order to make investors invest in risky investments this usually entails higher returns
Common forms of investments: Risk Return
Bonds low Low
Stocks high high
Risk – Chance that some unfavorable events will occur
Risks are always expected when doing investments; analysis (stand-alone basis & portfolio basis) is more on
which is riskier/which risk are you more willing to bet on?
No investment should be undertaken unless rate of return is high enough to compensate for the
perceived risk
STAND ALONE RISK VS. PORTFOLIO RISK
STAND ALONE RISK PORTFOLIO RISK
users Small business Financial institutions (required by
law), investors with larger
investment capabilities
definition The risk an investor would face if
he/she held only in one asset.
Putting your eggs in only one
basket. Thus, when loss is
acquired it is 100% loss. If profit
1000%
statistical measurement Probability distribution
Expected rate of return
Historical, or past realized, rates
of return
Standard deviation
Coefficient of variation
Risk free – when expected return can be measured precisely
Expected rate of return ≠actual rate of return ( thus, usually comes in ranges)
You might also like
- Risk and Rate of ReturnDocument5 pagesRisk and Rate of ReturnKrazy ButterflyNo ratings yet
- Risk Damodaran PDFDocument55 pagesRisk Damodaran PDFMiguel RevillaNo ratings yet
- Module 5 RiskDocument8 pagesModule 5 RiskZergaia WPNo ratings yet
- 10 - Chapter 4 PDFDocument14 pages10 - Chapter 4 PDFNithin DanielNo ratings yet
- Summary of Part 4 (Risk and Returns)Document3 pagesSummary of Part 4 (Risk and Returns)Justz LimNo ratings yet
- Risk, Return, & The Capital Asset Pricing ModelDocument19 pagesRisk, Return, & The Capital Asset Pricing ModelElyza BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Risk and Return PDFDocument14 pagesRisk and Return PDFluv silenceNo ratings yet
- G5 Risk Return Trade OffDocument14 pagesG5 Risk Return Trade Offlorraine barrogaNo ratings yet
- Risk and ReturnDocument32 pagesRisk and Returnmogibol791No ratings yet
- Financial Markets - Chapter 5 - Overview of Risk and ReturnDocument29 pagesFinancial Markets - Chapter 5 - Overview of Risk and ReturnCharrise BechaydaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document27 pagesUnit 4RAJNo ratings yet
- Business Studies ProjectDocument19 pagesBusiness Studies ProjectArpita SiddhpuriaNo ratings yet
- Group D RISK AND THE REQUIRED RATE OF RETURNDocument28 pagesGroup D RISK AND THE REQUIRED RATE OF RETURNgellie villarinNo ratings yet
- Mansci 01: Risks and Returns: The Smaller The Standard Deviation, The Tighter The ProbabilityDocument2 pagesMansci 01: Risks and Returns: The Smaller The Standard Deviation, The Tighter The ProbabilityMichelle ManglapusNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Portfolio TheoryDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Portfolio TheorySaish ChavanNo ratings yet
- Finance PPT - Ahmad AmanDocument9 pagesFinance PPT - Ahmad AmanHarshit Wardhan PrasadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 PDFDocument90 pagesLecture 5 PDFsyingNo ratings yet
- Risk and ReturnDocument5 pagesRisk and ReturnJose Emmanuel Ca�eteNo ratings yet
- Risk and The Required Rate of ReturnDocument31 pagesRisk and The Required Rate of Returngellie villarinNo ratings yet
- Financial Management: Topic: Risk & ReturnDocument4 pagesFinancial Management: Topic: Risk & ReturnIris FenelleNo ratings yet
- MidtermDocument16 pagesMidtermNicole ReintegradoNo ratings yet
- Risk Measurement and Its ApplicationsDocument12 pagesRisk Measurement and Its Applicationsishmeetkaur14No ratings yet
- Risk Neutral DefinitionDocument6 pagesRisk Neutral Definitionselozok1No ratings yet
- Security Analysis - IntroductionDocument20 pagesSecurity Analysis - IntroductionAnanya Ghosh100% (1)
- Week07 Workshop AnswersDocument10 pagesWeek07 Workshop Answersneok30% (1)
- Risk Return RelationshipDocument10 pagesRisk Return RelationshipJunaid PantheeranNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2.1 (Risk and Return)Document40 pagesLecture 2.1 (Risk and Return)Devyansh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets Book SummaryDocument50 pagesFinancial Markets Book SummaryDarby HertogsNo ratings yet
- EC3333 NotesDocument25 pagesEC3333 Notesxqhuang99No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Risks and ReturnsDocument20 pagesLecture Notes On Risks and ReturnsAngelica AllanicNo ratings yet
- Risk:: The Two Major Types of Risks AreDocument16 pagesRisk:: The Two Major Types of Risks AreAbhishek TyagiNo ratings yet
- Risk Return Analysis Analysis of Banking and FMCG StocksDocument93 pagesRisk Return Analysis Analysis of Banking and FMCG StocksbhagathnagarNo ratings yet
- Risk and ReturnDocument14 pagesRisk and ReturnShafaq Khurram100% (1)
- Risk and Rates of ReturnDocument33 pagesRisk and Rates of ReturnLeyla MalijanNo ratings yet
- Cap. Mark. Midterm NotesDocument14 pagesCap. Mark. Midterm NotesMJ NuarinNo ratings yet
- Finman Written ReportDocument9 pagesFinman Written ReportRanie MonteclaroNo ratings yet
- 08 Handout 124Document11 pages08 Handout 124bernadette soteroNo ratings yet
- Financial Mathematics NotesDocument3 pagesFinancial Mathematics NotesJackNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Theory - Ses2Document82 pagesPortfolio Theory - Ses2Vaidyanathan Ravichandran100% (1)
- Risk Return Trade of - Invesment RisksDocument44 pagesRisk Return Trade of - Invesment RisksKhelly MargaretteNo ratings yet
- 2 23Document3 pages2 23an scNo ratings yet
- Micro III - Risk and Undertainty 2023Document17 pagesMicro III - Risk and Undertainty 2023uihgfhjjhghNo ratings yet
- The Investment Principle: Risk and Return Models: " You Cannot Swing Upon A Rope That Is Attached Only To Your Own Belt."Document23 pagesThe Investment Principle: Risk and Return Models: " You Cannot Swing Upon A Rope That Is Attached Only To Your Own Belt."syamdsp5479No ratings yet
- Risk and Rates of ReturnDocument2 pagesRisk and Rates of ReturnLiana Monica LopezNo ratings yet
- 2 FM LECTURE 2 Risk and ReturnDocument20 pages2 FM LECTURE 2 Risk and Returnnida buttNo ratings yet
- Volatility Standard Deviation 2. Variance (Standard Deviation) 3. Standard Deviation VarianceDocument4 pagesVolatility Standard Deviation 2. Variance (Standard Deviation) 3. Standard Deviation VarianceLeo SaimNo ratings yet
- Introduction Investment PlanningDocument5 pagesIntroduction Investment Planningapi-3770163No ratings yet
- CH8 Financial ManagementDocument12 pagesCH8 Financial ManagementSyed ShafanNo ratings yet
- The Meaning and Measurement of Risk and Return: All Rights ReservedDocument35 pagesThe Meaning and Measurement of Risk and Return: All Rights ReservednikowawaNo ratings yet
- CH-2 Risk ReturnDocument1 pageCH-2 Risk ReturnRahel asfawNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Portfolio ManagementDocument7 pagesUnit 4 - Portfolio ManagementAlyana GeriNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Risk Analysis - Nikita - PPT PDFDocument28 pagesPortfolio Risk Analysis - Nikita - PPT PDFNikita Aggarwal100% (1)
- MFCF - Session 3Document47 pagesMFCF - Session 3Ondřej HengeričNo ratings yet
- RISK RETURN ANALYSIS bgjQOpyjCSDocument22 pagesRISK RETURN ANALYSIS bgjQOpyjCSAnisha MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Security Analysis: Chapter - 1Document47 pagesSecurity Analysis: Chapter - 1Harsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Modern Portfolio TheoryDocument129 pagesModern Portfolio TheoryKUZIWAOLIVIANo ratings yet
- Sample QuestionsDocument13 pagesSample Questionsisrael adesanyaNo ratings yet
- Beating the Market, 3 Months at a Time (Review and Analysis of the Appels' Book)From EverandBeating the Market, 3 Months at a Time (Review and Analysis of the Appels' Book)No ratings yet
- Janeyuuu chapIVDocument9 pagesJaneyuuu chapIVAlice LorenNo ratings yet
- RealismDocument1 pageRealismAlice LorenNo ratings yet
- BusinessDocument1 pageBusinessAlice LorenNo ratings yet
- PrinciplesDocument1 pagePrinciplesAlice LorenNo ratings yet
- Mini Research: Goal: To Determine If Students of BEED 3 Exhibit Personal Growth and Are Equipped With TheDocument1 pageMini Research: Goal: To Determine If Students of BEED 3 Exhibit Personal Growth and Are Equipped With TheAlice LorenNo ratings yet
- Controlling NatureDocument22 pagesControlling NatureAlice LorenNo ratings yet
- ConformityDocument2 pagesConformityAlice LorenNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Property DamagesDocument11 pagesDeterminants of Property DamagesAlice LorenNo ratings yet
- Potential ApplicationDocument2 pagesPotential ApplicationAlice LorenNo ratings yet
- National Income DeterminationDocument31 pagesNational Income DeterminationAlice LorenNo ratings yet
- What Are The Four Most Fundamental Factors That Affect The Cost of MoneyDocument1 pageWhat Are The Four Most Fundamental Factors That Affect The Cost of MoneyAlice Loren50% (2)
- I Just Want To Receive Free Content From Scribd. Thanks!Document1 pageI Just Want To Receive Free Content From Scribd. Thanks!Alice LorenNo ratings yet
- Lecture NotesDocument100 pagesLecture NotesAlice LorenNo ratings yet
- MS WordDocument1 pageMS WordAlice LorenNo ratings yet