Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic DT Questions
Uploaded by
shripalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic DT Questions
Uploaded by
shripalCopyright:
Available Formats
Radio Network Controller
The Radio Network Controller (or RNC) is a governing element in the UMTS radio access network
(UTRAN) and is responsible for controlling the Node Bs that are connected to it. The RNC carries
out radio resource management, some of the mobility management functions and is the point
where encryption is done before user data is sent to and from the mobile. The RNC connects to
the Circuit Switched Core Network through Media Gateway (MGW) and to the SGSN (Serving
GPRS Support Node) in the Packet Switched Core Network.
1 Interfaces
2 Protocols
3 RNC roll
RNC Interfaces
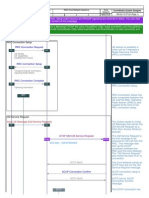
The logical connections between the network elements are known as interfaces. The interface
between the RNC and the Circuit Switched Core Network (CS-CN) is called Iu-CS and between the
RNC and the Packet Switched Core Network is called Iu-PS. Other interfaces include Iub
(between the RNC and the Node B) and Iur (between RNCs in the same network). Iu interfaces
carry user traffic (such as voice or data) as well as control information (see Protocols), and Iur
interface is mainly needed for soft handovers involving 2 RNCs though not required as the
absence of Iur will cause these handovers to become hard handovers.
Until 3gpp R4, all the interfaces in the UTRAN are implemented using ATM only, except the Uu
(air) interface which uses WCDMA technology. Starting R5, IP bearers can be used over Ethernet
instead. Physically, these interfaces can be carried over SDH over optical fiber, E1 (sometimes
referred to as PDH) - over a copper wire or microwave radio. Several E1s can be bundled to form
an IMA Group. Since the interfaces are logical, many interfaces can be multiplexed onto the
same transmission line. The actual implementation depends on the network topology; examples
are chain, distant star,mesh and loop configurations.
You might also like
- SIP Report Sarit Das 404Document70 pagesSIP Report Sarit Das 404shripalNo ratings yet
- 4G Commands in EricssonDocument2 pages4G Commands in Ericssonshripal0% (1)
- Troubleshoot and upgrade Ericsson router software remotelyDocument2 pagesTroubleshoot and upgrade Ericsson router software remotelyshripalNo ratings yet
- SW Upgrade From USB - SelfDocument1 pageSW Upgrade From USB - SelfshripalNo ratings yet
- 2G Command in EricssonDocument2 pages2G Command in EricssonshripalNo ratings yet
- Add On Packs 2018 01 30Document3 pagesAdd On Packs 2018 01 30shripalNo ratings yet
- 3g Umts Originating CallDocument5 pages3g Umts Originating CallshripalNo ratings yet
- Rahul RessumeDocument2 pagesRahul RessumeshripalNo ratings yet
- 3G Command in EricssonDocument2 pages3G Command in EricssonshripalNo ratings yet
- Add On Packs 2018 01 30 PDFDocument1 pageAdd On Packs 2018 01 30 PDFshripalNo ratings yet
- 1552 Link Calculator V1Document26 pages1552 Link Calculator V1shripalNo ratings yet
- What is a cell site and its componentsDocument10 pagesWhat is a cell site and its componentsshripalNo ratings yet
- RF Plan.Document1 pageRF Plan.shripalNo ratings yet
- 3g Umts Originating CallDocument6 pages3g Umts Originating Callk.naveedNo ratings yet
- Site AnalyserDocument1 pageSite AnalysershripalNo ratings yet
- Shelter and Tower Layout: Bts 1 Bts 2 PIUDocument1 pageShelter and Tower Layout: Bts 1 Bts 2 PIUshripalNo ratings yet
- Shripal Singh (Site Engineer)Document2 pagesShripal Singh (Site Engineer)shripalNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Shiv Prakash YadavDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Shiv Prakash YadavshripalNo ratings yet
- MW Communication System in UMTS NetworksDocument84 pagesMW Communication System in UMTS NetworksshripalNo ratings yet
- Document On 2G GSM ConfigurationDocument19 pagesDocument On 2G GSM ConfigurationAnonymous 6Wo8gboGWd100% (3)
- Rfi Checklist NokiaDocument4 pagesRfi Checklist NokiashripalNo ratings yet
- Installation and Commissioning of Ceragon MW IP10 and IP 20Document1 pageInstallation and Commissioning of Ceragon MW IP10 and IP 20shripalNo ratings yet
- What is a cell site and its componentsDocument10 pagesWhat is a cell site and its componentsshripalNo ratings yet
- Telecom Engineer Resume - 14+ Months ExperienceDocument2 pagesTelecom Engineer Resume - 14+ Months ExperienceshripalNo ratings yet
- Tems ParametersDocument2 pagesTems ParametersshripalNo ratings yet
- 2g Drive AnalysisDocument26 pages2g Drive AnalysisshripalNo ratings yet
- Document On 2G GSM ConfigurationDocument19 pagesDocument On 2G GSM ConfigurationAnonymous 6Wo8gboGWd100% (3)
- MW QuestionDocument4 pagesMW QuestionshripalNo ratings yet
- 202 Software Testing Interview Questions and Answers PDFDocument25 pages202 Software Testing Interview Questions and Answers PDFSanalMohanNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)