Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2017-2018 Surveying I UT3
2017-2018 Surveying I UT3
Uploaded by
Makesh KumarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2017-2018 Surveying I UT3
2017-2018 Surveying I UT3
Uploaded by
Makesh KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
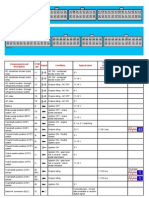
CIVIL ENGINEERING A III SEMESTER UNIT TEST III Date: 07.11.
2017
TIME: 90 MINS 16CPC05 –Surveying I MAX. MARKS: 50
Part A (Answer all the questions) 5 x 2 = 10
1. What is advantages and disadvantages of plane table surveying. L2 CO2
2. List the accessories of plane table surveying. L2 CO2
3. What is meant by a transition curve? L3 CO3
4. List the instrumental methods commonly used for setting out a circular curve. L2 CO3
5. Define Degree of curve? L2 CO3
CIVIL ENGINEERING A III SEMESTER UNIT TEST II Date: 11.06.2017
TIME: 90 MINS 16CPC05 –Surveying I MAX. MARKS: 50
Part A (Answer all the questions) 5 x 2 = 10
1. What is advantages and disadvantages of plane table surveying. L2 CO2
2. List the accessories of plane table surveying. L2 CO2
3. What is meant by a transition curve? L3 CO3
4. List the instrumental methods commonly used for setting out a circular curve. L2 CO3
5. Define Degree of curve? L2 CO3
CIVIL ENGINEERING A III SEMESTER UNIT TEST III Date: 11.06.2017
TIME: 90 MINS 16CPC05 –Surveying I MAX. MARKS: 50
Part A (Answer all the questions) 5 x 2 = 10
1. What is advantages and disadvantages of plane table surveying. L2 CO2
2. List the accessories of plane table surveying. L2 CO2
3. What is meant by a transition curve? L3 CO3
4. List the instrumental methods commonly used for setting out a circular curve. L2 CO3
5. Define Degree of curve? L2 CO3
CIVIL ENGINEERING B III SEMESTER UNIT TEST III Date: 11.06.2017
TIME: 90 MINS 16CPC05 –Surveying I MAX. MARKS: 50
Part A (Answer all the questions) 5 x 2 = 10
1. What is advantages and disadvantages of plane table surveying. L2 CO2
2. List the accessories of plane table surveying. L2 CO2
3. What is meant by a transition curve? L3 CO3
4. List the instrumental methods commonly used for setting out a circular curve. L2 CO3
5. Define Degree of curve? L2 CO3
CIVIL ENGINEERING B III SEMESTER UNIT TEST III Date: 11.06.2017
TIME: 90 MINS 16CPC05 –Surveying I MAX. MARKS: 50
Part A (Answer all the questions) 5 x 2 = 10
1. What is advantages and disadvantages of plane table surveying. L2 CO2
2. List the accessories of plane table surveying. L2 CO2
3. What is meant by a transition curve? L3 CO3
4. List the instrumental methods commonly used for setting out a circular curve. L2 CO3
5. Define Degree of curve? L2 CO3
Part B (Answer all the questions) 4 x 10 = 40
6. Briefly explain the methods of plane table. L4 CO2
7. Two straights AB and BC are intersected by a line D1 D2. The angles BD1 D2 and BD2 D1 are 40° 30’ and
36° 24’ respectively. The radius of the first arc is 600m and that of second arc is 800m. If the chainage of
intersection point B is 8248.1 m. Find the chainages of the tangent points and the point of compound
curvature. L 4 CO3
8. Explain linear methods of setting out a simple curve. L4 CO3
9. Explain two point problem. L4 CO2
Part B (Answer all the questions) 4 x 10 = 40
6. Briefly explain the methods of plane table. L4 CO2
7. Two straights AB and BC are intersected by a line D1 D2. The angles BD1 D2 and BD2 D1 are 40° 30’ and
36° 24’ respectively. The radius of the first arc is 600m and that of second arc is 800m. If the chainage of
intersection point B is 8248.1 m. Find the chainages of the tangent points and the point of compound
curvature. L 4 CO3
8. Explain linear methods of setting out a simple curve. L4 CO3
9. Explain two point problem. L4 CO2
Part B (Answer all the questions) 4 x 10 = 40
6. Briefly explain the methods of plane table. L4 CO2
7. Two straights AB and BC are intersected by a line D1 D2. The angles BD1 D2 and BD2 D1 are 40° 30’ and
36° 24’ respectively. The radius of the first arc is 600m and that of second arc is 800m. If the chainage of
intersection point B is 8248.1 m. Find the chainages of the tangent points and the point of compound
curvature. L 4 CO3
8. Explain linear methods of setting out a simple curve. L4 CO3
9. Explain two point problem. L4 CO2
Part B (Answer all the questions) 4 x 10 = 40
6. Briefly explain the methods of plane table. L4 CO2
7. Two straights AB and BC are intersected by a line D1 D2. The angles BD1 D2 and BD2 D1 are 40° 30’ and
36° 24’ respectively. The radius of the first arc is 600m and that of second arc is 800m. If the chainage of
intersection point B is 8248.1 m. Find the chainages of the tangent points and the point of compound
curvature. L 4 CO3
8. Explain linear methods of setting out a simple curve. L4 CO3
9. Explain two point problem. L4 CO2
Part B (Answer all the questions) 4 x 10 = 40
6. Briefly explain the methods of plane table. L4 CO2
7. Two straights AB and BC are intersected by a line D1 D2. The angles BD1 D2 and BD2 D1 are 40° 30’ and
36° 24’ respectively. The radius of the first arc is 600m and that of second arc is 800m. If the chainage of
intersection point B is 8248.1 m. Find the chainages of the tangent points and the point of compound
curvature. L 4 CO3
8. Explain linear methods of setting out a simple curve. L4 CO3
9. Explain two point problem. L4 CO2
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- 323 BA 2-0 94-98 (ECU Pinout)Document5 pages323 BA 2-0 94-98 (ECU Pinout)TimSmith76% (17)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Surveying UNIT II ProblemsDocument3 pagesSurveying UNIT II ProblemsMakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Concrete Structures ObjectiveDocument3 pagesConcrete Structures ObjectiveMakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 SurveyDocument1 pageAssignment 3 SurveyMakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- A Simple Two-Stage PCR Based Method To Construct Gene Disruption CassetteDocument4 pagesA Simple Two-Stage PCR Based Method To Construct Gene Disruption CassetteMakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Tamil Nadu Fire & Rescue Services - Licence Application FormDocument3 pagesTamil Nadu Fire & Rescue Services - Licence Application FormMakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- L2 Co2 L2 Co2 L3 Co3 4. L2 Co3 5 L2 Co3: Part A (Answer All The Questions) 5 X 2 10 1. 2. 3Document1 pageL2 Co2 L2 Co2 L3 Co3 4. L2 Co3 5 L2 Co3: Part A (Answer All The Questions) 5 X 2 10 1. 2. 3Makesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Two Point Problem Survey LabDocument2 pagesTwo Point Problem Survey LabMakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Government College of Technology, Coimbatore - 641013: Continuous Assessment Record For Laboratory CoursesDocument4 pagesGovernment College of Technology, Coimbatore - 641013: Continuous Assessment Record For Laboratory CoursesMakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Surveying I Unit I ProblemsDocument2 pagesSurveying I Unit I ProblemsMakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Method-Elements of Elasticity: BY ANJALI A (1211108) JEYAGOMATHI (1211136)Document23 pagesFinite Element Method-Elements of Elasticity: BY ANJALI A (1211108) JEYAGOMATHI (1211136)Makesh Kumar100% (1)
- Guyons End BlockDocument71 pagesGuyons End BlockMakesh Kumar80% (5)
- Chemical Analysis of CementDocument45 pagesChemical Analysis of CementElango Paulchamy100% (2)
- Bending and Vibration of Functionally Graded Material Sandwich Plates Using An Accurate TheoryDocument2 pagesBending and Vibration of Functionally Graded Material Sandwich Plates Using An Accurate TheoryMakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Technology Hype and IOT PDFDocument3 pagesTechnology Hype and IOT PDFKriti DixitNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Guide For Build ConstDocument72 pagesCurriculum Guide For Build ConstLuis VasquezNo ratings yet
- JZ-500 / OZ-500: Technical DataDocument3 pagesJZ-500 / OZ-500: Technical Datademetrio lopezNo ratings yet
- Seam 3 Prelim2022 2023Document3 pagesSeam 3 Prelim2022 2023John Lloyd AquinoNo ratings yet
- ZetCode Java TutorialDocument683 pagesZetCode Java Tutorialg_teodorescuNo ratings yet
- Astronomy Education Around The WorldDocument4 pagesAstronomy Education Around The Worldhipoteticamente.contactoNo ratings yet
- Success Factors in Mergers and Acquisitions - Complexity Theory ADocument158 pagesSuccess Factors in Mergers and Acquisitions - Complexity Theory AMohamed Aly100% (1)
- SL-70W Series: Operating InstructionsDocument19 pagesSL-70W Series: Operating InstructionsMohamad BarakatNo ratings yet
- Ses 2000Document46 pagesSes 2000Omeerul Rafie100% (1)
- Unit - V Analysis of Pipe Flow and Laminar and Turbulent Flow in PipesDocument6 pagesUnit - V Analysis of Pipe Flow and Laminar and Turbulent Flow in PipesajaythermalNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Food: Proposed Sabbatical Program For Hwa Chong Institution (Year 2)Document2 pagesThe Chemistry of Food: Proposed Sabbatical Program For Hwa Chong Institution (Year 2)chuasioklengNo ratings yet
- Summary Arena Mathematics f5 KSSMDocument8 pagesSummary Arena Mathematics f5 KSSMFAZLINA BINTI MUSTAFA KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Telkom Internet Educational Product SheetDocument4 pagesTelkom Internet Educational Product SheetJustin NicklinNo ratings yet
- La Quinta Columna - Analysis of Vaccination Vial Confirms Presence of Graphene Nanoparticles - ORWELL CITYDocument20 pagesLa Quinta Columna - Analysis of Vaccination Vial Confirms Presence of Graphene Nanoparticles - ORWELL CITYnionmaNo ratings yet
- Feature Extraction Gabor FiltersDocument2 pagesFeature Extraction Gabor FiltersZeeshan AslamNo ratings yet
- Blake NRL Report 7098 AD709897Document58 pagesBlake NRL Report 7098 AD709897randy-j-jost-5054No ratings yet
- Dasa Bukthi Anthara Pala PDFDocument18 pagesDasa Bukthi Anthara Pala PDFsarathNo ratings yet
- Earnings Price Anomaly (Ray Ball, 1992)Document27 pagesEarnings Price Anomaly (Ray Ball, 1992)jeetNo ratings yet
- USC Application For RecordsDocument1 pageUSC Application For RecordsfortunecNo ratings yet
- (A) Morse Code and International Code of Flag SignalsDocument63 pages(A) Morse Code and International Code of Flag SignalsJohn Rey CastillanoNo ratings yet
- E1390-12 Standard Specification For Illuminators Used For Viewing Industrial RadiographsDocument3 pagesE1390-12 Standard Specification For Illuminators Used For Viewing Industrial RadiographsMuhammed Abo-FandoodNo ratings yet
- Seduction Warfare Author No Bullsht Seduction (NBS)Document12 pagesSeduction Warfare Author No Bullsht Seduction (NBS)Silly BearNo ratings yet
- Dr. Vandana Gupta: EducationDocument3 pagesDr. Vandana Gupta: EducationMadhu DatarNo ratings yet
- Egypt Biosimilar Guidline Biologicals RegistrationDocument54 pagesEgypt Biosimilar Guidline Biologicals Registrationshivani hiremathNo ratings yet
- My Revised Thesis Chapter 1 3.editedDocument49 pagesMy Revised Thesis Chapter 1 3.editedJeriel Baton SeguidoNo ratings yet
- Marine CatalogueDocument43 pagesMarine Cataloguefarhan_82No ratings yet
- Scientific Management TheoryDocument11 pagesScientific Management TheorySaf Tanggo Diampuan100% (1)
- VeraCrypt - Begginer's TutorialDocument18 pagesVeraCrypt - Begginer's TutorialjpNo ratings yet
- Data Lakehouse As A Service For Vmware Sovereign Clouds Solution BriefDocument2 pagesData Lakehouse As A Service For Vmware Sovereign Clouds Solution Briefdicruz81No ratings yet