Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thermodynamics of Solutions
Uploaded by
api-4124153560 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageOriginal Title
thermodynamics of solutions
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageThermodynamics of Solutions
Uploaded by
api-412415356Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
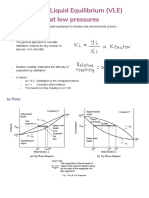
Thermodynamics of solutions
Figure taken from: https://www.thoughtco.com/definition-of-solution-604650
o
μi − μi = Δμi = RT ln(ai ) The acitivity ai of a solution @ constant pressure (P) and
temperature (T).
The activity of a liquid we could say stands for the fugacity in gases. This comes into
the picture when we deviate from our ideality inside solutions.
The activity of a pure component is defined as follows:
︿L
f
a = ︿ iO -------> a = γ i xi
fi
We can say that γ acts as the activity coefficient, similar to the φ fugacity coefficient.
as:
γ = ax also γ = ffugacity
ugacity in real mixture
in ideal solution
i
You might also like
- Assignment3Document3 pagesAssignment3Ashwin IndwarNo ratings yet
- Properties of Gibbs Free Energy KBDocument2 pagesProperties of Gibbs Free Energy KBapi-412415356No ratings yet
- Introductory Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics: Chapter 9 - Introduction To Multicomponent SystemsDocument14 pagesIntroductory Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics: Chapter 9 - Introduction To Multicomponent SystemsHarshil TejaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Week 4 - Chemical Potential and Fugacity PDFDocument24 pagesLecture - Week 4 - Chemical Potential and Fugacity PDFfNo ratings yet
- Key Points: B B B X XDocument5 pagesKey Points: B B B X XSIDDHANT KATARIANo ratings yet
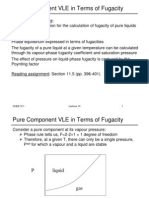
- Pure Component VLE in Terms of Fugacity: LiquidsDocument8 pagesPure Component VLE in Terms of Fugacity: Liquidsahad_shiraziNo ratings yet
- 6-3-Partial Fugacity in Liquid MixturesDocument9 pages6-3-Partial Fugacity in Liquid MixturesIkNo ratings yet
- Practice1 ConductimetricMethodDocument10 pagesPractice1 ConductimetricMethodHector LasluisaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Thermodynamics 2 Notes On Heterogeneous SystemsDocument5 pagesChemical Thermodynamics 2 Notes On Heterogeneous Systemsian tunanukyeNo ratings yet
- Liq Vap Phase 2Document11 pagesLiq Vap Phase 2Xedice MemmedyarovaNo ratings yet
- CES LogitDocument10 pagesCES LogitRundong WangNo ratings yet
- CHM 301 Note 1Document7 pagesCHM 301 Note 1Emmanuel JoyNo ratings yet
- Nonideal Soln: Activity & Activity CoefficientDocument13 pagesNonideal Soln: Activity & Activity Coefficientbits_who_am_iNo ratings yet
- Vapor-Liquid EquilibriumDocument2 pagesVapor-Liquid EquilibriumCornelius YudhaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2: Thermodynamics and Equilibrium: D RTDLNFDocument2 pagesLecture 2: Thermodynamics and Equilibrium: D RTDLNFRinaldi SaputraNo ratings yet
- Discrete Random VariableDocument53 pagesDiscrete Random VariableDanish NisarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 35: δ-functions, Eigenfunctions of X, and Discrete Variable RepresentationDocument9 pagesLecture 35: δ-functions, Eigenfunctions of X, and Discrete Variable RepresentationTui CohenNo ratings yet
- Pure Component VLE in Terms of Fugacity: CHEE 311 1Document8 pagesPure Component VLE in Terms of Fugacity: CHEE 311 1scienziatoNo ratings yet
- The Elasticities of Complementarity and Substitution: Peter BroerDocument13 pagesThe Elasticities of Complementarity and Substitution: Peter BroerDaniél CárdenasNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering - Section of The FE - Chemical Engineering - Section of The FE Supplied-Reference Handbook - NCEESDocument5 pagesChemical Engineering - Section of The FE - Chemical Engineering - Section of The FE Supplied-Reference Handbook - NCEESjazz fraire bernalNo ratings yet
- Ideal Dilute and Real SolutionsDocument9 pagesIdeal Dilute and Real SolutionsJksgNo ratings yet
- Chialvo Crisalle 2019Document20 pagesChialvo Crisalle 2019Tiên PhạmNo ratings yet
- ActivityDocument1 pageActivityDally Garnique CapuñayNo ratings yet
- Pelton Bale1986 ModifiedInteractionParameterFDocument5 pagesPelton Bale1986 ModifiedInteractionParameterFmanish pandeNo ratings yet
- Functions & Boolean ExpressionsDocument19 pagesFunctions & Boolean Expressionsabhijeetkumar7985No ratings yet
- The Phase-Equilibrium ProblemDocument13 pagesThe Phase-Equilibrium ProblemthchouNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Project-I: TopicDocument11 pagesChemical Engineering Thermodynamics Project-I: TopicRohit GuptaNo ratings yet
- PCRE 501 Module 4 Note 1 P 1-5Document5 pagesPCRE 501 Module 4 Note 1 P 1-5Abhijit NathNo ratings yet
- ML:Introduction: Week 1 Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesML:Introduction: Week 1 Lecture NotesShubhamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Chemical Reaction EquilibDocument41 pagesChapter 13 Chemical Reaction EquilibAhmed D. Jonjun100% (1)
- ElectrochemistryDocument31 pagesElectrochemistryzerathjanginNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document46 pagesChapter 13Khloud MadihNo ratings yet
- Fugacity & Fugacity Coefficient: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics - II (2150503)Document21 pagesFugacity & Fugacity Coefficient: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics - II (2150503)Laiba JanjuaNo ratings yet
- LIGSflashpointDocument2 pagesLIGSflashpointjonabelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15: Chemical and Phase Equilibrium: CH O N DCO ECO FO GHO BNDocument0 pagesChapter 15: Chemical and Phase Equilibrium: CH O N DCO ECO FO GHO BNAlex Samuel SilvaNo ratings yet
- TD BasicsDocument33 pagesTD BasicsKarthik SakthivelNo ratings yet
- 23 3 Even N Odd FuncnsDocument10 pages23 3 Even N Odd FuncnsEbookcrazeNo ratings yet
- Maths Notes: Matter If You Do Not Know Everything!Document40 pagesMaths Notes: Matter If You Do Not Know Everything!Rachel FangNo ratings yet
- Il ReconciliatioDocument37 pagesIl ReconciliatioIan BeardsleyNo ratings yet
- Activity in InfiniteDocument5 pagesActivity in InfiniteLelis Clemente FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Relation Between Equilibrium Constant and Free Energies: GibbsDocument3 pagesRelation Between Equilibrium Constant and Free Energies: GibbsjhalendrafbNo ratings yet
- Regression in Modal LogicDocument21 pagesRegression in Modal LogicIvan José Varzinczak100% (1)
- Thermodynamic Modelling of Solid Solutions: J GangulyDocument33 pagesThermodynamic Modelling of Solid Solutions: J GangulytazuddinNo ratings yet
- The Derivative EnglishDocument35 pagesThe Derivative EnglishAlfia MagfiraNo ratings yet
- 13 GroupsDocument50 pages13 Groupsapi-3808925No ratings yet
- (Machine Learning Coursera) Lecture Note Week 1Document8 pages(Machine Learning Coursera) Lecture Note Week 1JonnyJackNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Equilibrium in Open Chemical Systems.: The R-Modynamics of Chemical EquilibriaDocument10 pagesThermodynamic Equilibrium in Open Chemical Systems.: The R-Modynamics of Chemical EquilibriayeshiduNo ratings yet
- Flash CalculationDocument12 pagesFlash CalculationHamidreza HasaniNo ratings yet
- C02 Part 2 PDFDocument28 pagesC02 Part 2 PDFSyahmiNo ratings yet
- Reconciling Quantum Mechanics With RelativityDocument22 pagesReconciling Quantum Mechanics With RelativityIan BeardsleyNo ratings yet
- Math 1201 Learning Journal Unit 4.Document4 pagesMath 1201 Learning Journal Unit 4.Khomani MwewaNo ratings yet
- Whole PacketDocument396 pagesWhole PacketHenry DunaNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry - 102: IISER Pune, Spring 2014 March 28, 2014Document2 pagesPhysical Chemistry - 102: IISER Pune, Spring 2014 March 28, 2014Aakash VermaNo ratings yet
- CH 6Document30 pagesCH 6tamay 95No ratings yet
- Fe Chemical EngineeringDocument5 pagesFe Chemical EngineeringJudith LugoNo ratings yet
- Non IdealDocument29 pagesNon IdealAmin SyazrinNo ratings yet
- Strong Rigidity of Locally Symmetric Spaces. (AM-78), Volume 78From EverandStrong Rigidity of Locally Symmetric Spaces. (AM-78), Volume 78No ratings yet
- Vapour Pressure Calculation 2Document2 pagesVapour Pressure Calculation 2api-412415356No ratings yet
- Gibbs Free EnergyDocument1 pageGibbs Free Energyapi-412415356No ratings yet
- Raoult's LawDocument2 pagesRaoult's Lawapi-412415356No ratings yet
- EosDocument3 pagesEosapi-412415356No ratings yet
- Vapour Liquid EquilibriumDocument1 pageVapour Liquid Equilibriumapi-412415356No ratings yet
- Fundamental ConceptsDocument3 pagesFundamental Conceptsapi-412415356No ratings yet
- Multicomponent SystemDocument3 pagesMulticomponent Systemapi-412415356No ratings yet
- Fugacity - Fundamentals and CalculationsDocument3 pagesFugacity - Fundamentals and Calculationsapi-412415356No ratings yet
- Henrys ConstantDocument1 pageHenrys Constantapi-412415356No ratings yet
- Phase Transition Phase DiagramDocument5 pagesPhase Transition Phase Diagramapi-412415356No ratings yet
- Simplest Phase Equilibrium Pure Component 2fmulticomponentDocument3 pagesSimplest Phase Equilibrium Pure Component 2fmulticomponentapi-412415356No ratings yet
- Fugacity in LiquidsDocument4 pagesFugacity in Liquidsapi-412415356No ratings yet
- Physical Transformations of Pure Substances 1Document3 pagesPhysical Transformations of Pure Substances 1api-412415356No ratings yet
- EquilibriumDocument3 pagesEquilibriumapi-412415356No ratings yet