0% found this document useful (0 votes)
196 views2 pagesCentral Difference Interpolation
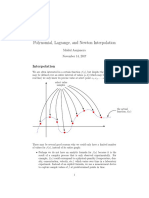
Central difference interpolation uses data points on both sides of the point being interpolated to estimate the value of the function at that point. It provides a more accurate interpolation than forward or backward difference methods alone. Some common central difference interpolation formulas include Gauss' formula, Bessel's formula, and Laplace's formula. Lagrange interpolation finds a polynomial that passes through the given data points by solving a system of linear equations. Spline interpolation uses piecewise polynomials joined at points to provide a smooth interpolation over an interval. Linear splines of order 0 simply connect the data points with straight line segments.
Uploaded by
Mengistu AbebeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
196 views2 pagesCentral Difference Interpolation
Central difference interpolation uses data points on both sides of the point being interpolated to estimate the value of the function at that point. It provides a more accurate interpolation than forward or backward difference methods alone. Some common central difference interpolation formulas include Gauss' formula, Bessel's formula, and Laplace's formula. Lagrange interpolation finds a polynomial that passes through the given data points by solving a system of linear equations. Spline interpolation uses piecewise polynomials joined at points to provide a smooth interpolation over an interval. Linear splines of order 0 simply connect the data points with straight line segments.
Uploaded by
Mengistu AbebeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd