Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(Personal Notes) Broad Spectrum Antibiotics
(Personal Notes) Broad Spectrum Antibiotics
Uploaded by
AmniAzmi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pagebroad spectrum antibiotics
Original Title
[Personal Notes] Broad Spectrum Antibiotics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentbroad spectrum antibiotics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 page(Personal Notes) Broad Spectrum Antibiotics
(Personal Notes) Broad Spectrum Antibiotics
Uploaded by
AmniAzmibroad spectrum antibiotics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
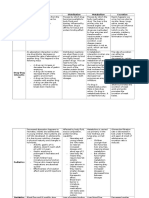
BROAD SPECTRUM ANTIBIOTICS
TETRACYCLIN MACROLIDES CHLORAMPHENICOL SULFONAMIDE TRIMETHOPRIM QUINOLONE
Mechanis - Bacteriostatic - Bacteriostatic - Bacteriostatic - Bacteriostatic - Bacteriostatic - Bactericial
m - Effective against G+ - Actively against many - Protein synthesis inhibitors - Act as competitive - Chemotherapeutic agent - Inhibit DNA replication
& G- G+ - Active against bacterial cause inhibitors of enzyme (dihydrofolate reductase & transcription
- Act by inhibiting protein meningitis (N. meningitides, S. DHPS (needed for folate inhibitor) - Enter cells via porin
synthesis of bacteria by pneumonia, H. influenza) synthesis – folate for cell - Act by interfering with the
binding to the 50S - Excellent CSF penetration) division) action of DHFR – inhibit
ribosomal element synthesis of
tetrahydrofolate reductase
- Precursor in DNA
nucleotide & thymidine
Indication - Treat mild to moderate - Typhoid - Pneumonia - Prophylaxis - Pt with infection of
infections - Multi-drug resistant salmonella - Urinary tract infection - Urinary tract infections intracellular pathogen
typhi - Shigellosis such as Mycoplasma
- 2nd line agent in treatment of - Certain protozoa pneumonia
tetracyclin-resistant chorela infections
- Brain abscess (staphylococcal or
mixed organism)
- Meningitis (for pt with severe
penicillin & cephalosporin allergy)
Contra- 1) Pregnant women - Interaction with digoxin Control the dosage for 1) Neonates Enchance toxicity
indication 2) Breast feeding may occur in some pt. 1) Neonates 2) Infant <2 months 1) Caffeine
/ women 2) Pt with abnormal liver function 3) Pregnant women 2) NSAID
interaction 3) Children <8 yrs old 3) Thephylline
4) Renal impairment Monitor plasma level for 4) Corticosteroid
pt. 1) Children <4 yrs old Drug interacton:
2) Elderly Antacid, cimetidine,
3) Pt with renal failure warfarin, phenytoin,
cyclosporine & rifampin
Adverse Serious effect on - Cholestatic jaundice - Aplastic anaemia - Crystalluria
effect calcified tissues, it - Ototoxicity - Bone marrow suppression - Hypersensitivity
can be deposit in - Accumulate in liver - Leukemia - Hemolytic anemia
bone, cause (inhibit hepatic - Gray baby syndrome
discoloration & metabolism)
hypoplasia of the
teeth
Dosage 750mg (4x daily)
Resistance 1) Reduced membrane permeability
2) Mutation of 50S ribosomal unit
3) Elaboration of chloramphenicol
acetyltransferase
Example / Erythromycin,
types Azithromycin,
Chlarithromycin
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Textbook of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics5eDocument476 pagesA Textbook of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics5ekuldip.biotechNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Introduction To PathologyDocument12 pagesIntroduction To PathologyAmniAzmi100% (1)
- Biopharmaceutics Answer Key-BLUE PACOPDocument48 pagesBiopharmaceutics Answer Key-BLUE PACOPChengD100% (5)
- Soldering, Brazing and Welding in DentistryDocument36 pagesSoldering, Brazing and Welding in DentistryAmniAzmiNo ratings yet
- Dental PolymerDocument36 pagesDental PolymerAmniAzmi100% (2)
- Clinical Pharmacy: Definition, Scope and ActivitiesDocument18 pagesClinical Pharmacy: Definition, Scope and ActivitiesSachin MishraNo ratings yet
- Rational Use of DrugsDocument2 pagesRational Use of DrugsRajan Manandhar ShambhavNo ratings yet
- Prosthetic Rehabilitation of Severe Hypodontia: A Clinical ReportDocument12 pagesProsthetic Rehabilitation of Severe Hypodontia: A Clinical ReportAmniAzmiNo ratings yet
- Prostho Rehabilitation - HypodontiaDocument24 pagesProstho Rehabilitation - HypodontiaAmniAzmiNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System PharmacologyDocument7 pagesAutonomic Nervous System Pharmacologydonordarah93No ratings yet
- Impression MaterialsDocument35 pagesImpression MaterialsAmniAzmi100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyLuriel BancasoNo ratings yet
- Denture Lining MaterialsDocument28 pagesDenture Lining MaterialsAmniAzmi100% (2)
- Denture Cleansers: A Material For Removing Deposits From A DentureDocument14 pagesDenture Cleansers: A Material For Removing Deposits From A DentureAmniAzmiNo ratings yet
- Non-Elastic Impression MaterialDocument24 pagesNon-Elastic Impression MaterialAmniAzmi100% (1)
- RASPRODocument36 pagesRASPROVera Yulianti100% (2)
- Glass Ionomer CementDocument57 pagesGlass Ionomer CementAmniAzmi100% (1)
- Amyloidosis: Dr. Ung Pathology Year 2Document18 pagesAmyloidosis: Dr. Ung Pathology Year 2AmniAzmiNo ratings yet
- Cast Dental Alloys - Wrought AlloysDocument50 pagesCast Dental Alloys - Wrought AlloysAmniAzmiNo ratings yet
- Defect in CastingDocument13 pagesDefect in CastingAmniAzmiNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Intracellular DepositionsDocument20 pagesAbnormal Intracellular DepositionsAmniAzmiNo ratings yet
- Tarnish - CorrosionDocument18 pagesTarnish - CorrosionAmniAzmiNo ratings yet
- Investment Materials 1 - 2Document53 pagesInvestment Materials 1 - 2AmniAzmiNo ratings yet
- Casting: DR Thulfiqar Dental Material Block 3Document24 pagesCasting: DR Thulfiqar Dental Material Block 3AmniAzmiNo ratings yet
- Dentifrice: A Semi-Aqueous Material For Removing Naturally-Occuring Deposits From The TeethDocument11 pagesDentifrice: A Semi-Aqueous Material For Removing Naturally-Occuring Deposits From The TeethAmniAzmiNo ratings yet
- Denture AdhesiveDocument11 pagesDenture AdhesiveAmniAzmiNo ratings yet
- Full Periodontal ChartDocument4 pagesFull Periodontal ChartAmniAzmiNo ratings yet
- Review Nur Atiqah HassanDocument2 pagesReview Nur Atiqah HassanAmniAzmiNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Mechanical Instrumentation EditedDocument15 pagesGroup 4 Mechanical Instrumentation EditedAmniAzmiNo ratings yet
- Esmo Course Medical Student Motivation Course-NUR ATIQAH HASSANDocument2 pagesEsmo Course Medical Student Motivation Course-NUR ATIQAH HASSANAmniAzmiNo ratings yet
- Ortho SurgeryDocument2 pagesOrtho SurgeryAmniAzmiNo ratings yet
- Amni Balik Kelate Yeay YeayDocument2 pagesAmni Balik Kelate Yeay YeayAmniAzmiNo ratings yet
- Drotaverine: Solution For Injection - 40 MG / 2 MLDocument1 pageDrotaverine: Solution For Injection - 40 MG / 2 MLZarbakht AliNo ratings yet
- Biopharmaceutics Classification System-The Scientific Basis PDFDocument5 pagesBiopharmaceutics Classification System-The Scientific Basis PDFtrianawidiacandra100% (1)
- Daftar Obat High Alert Royal MaternityyDocument1 pageDaftar Obat High Alert Royal Maternityydiffa rahmaNo ratings yet
- Drug To Drug InteractionDocument47 pagesDrug To Drug InteractionMannan SokaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics For Test 1Document3 pagesPharmacokinetics For Test 1KaitlynNo ratings yet
- Insomnia and CanabisDocument10 pagesInsomnia and CanabisEbetWasuwayNo ratings yet
- Sat, Jun 25, 2022 062-0002719-22 0105 35001: MSP Hart Post OceanaDocument3 pagesSat, Jun 25, 2022 062-0002719-22 0105 35001: MSP Hart Post OceanaFergus BurnsNo ratings yet
- Đề mẫu Dược VB2-2016Document9 pagesĐề mẫu Dược VB2-2016Hoài LinhNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic IndexDocument8 pagesTherapeutic IndexMary Jennel RosNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotic AgentsDocument18 pagesAntipsychotic AgentsmengakuNo ratings yet
- 0007PNTDocument11 pages0007PNTPau Lo JakobyNo ratings yet
- Unit#01 Pharma II MCqs Provided by MirhaDocument6 pagesUnit#01 Pharma II MCqs Provided by MirhaShayan Shayan100% (1)
- Stock AbstractDocument113 pagesStock AbstractsriramNo ratings yet
- Geri ScriptDocument172 pagesGeri Scriptmmeisels257100% (1)
- Syringe Driver ChartDocument1 pageSyringe Driver ChartThananjayanNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting Renal SystemDocument58 pagesDrugs Affecting Renal SystemDaniel OkakaNo ratings yet
- Conflict of Interest Disclosures: Patient Case # 1Document28 pagesConflict of Interest Disclosures: Patient Case # 1Chirac OanaNo ratings yet
- Common Medical AbbreviationsDocument2 pagesCommon Medical AbbreviationsShahad HakimuddinNo ratings yet
- Etest Reading 2Document68 pagesEtest Reading 2Anan ChongthaleongNo ratings yet
- Narce, Almera Rose F. Pharmacology BSN-2A Instructor: Ms. Kenvyne Quides-Calugay, RN, Man Drug Study 2 FinalsDocument1 pageNarce, Almera Rose F. Pharmacology BSN-2A Instructor: Ms. Kenvyne Quides-Calugay, RN, Man Drug Study 2 FinalsAlmera Rose NarceNo ratings yet
- StemBook 2011 FinalDocument187 pagesStemBook 2011 Finalskeebs23No ratings yet
- MCH IV Solution Recipes - New PDFDocument1 pageMCH IV Solution Recipes - New PDFSyrelle DeiparineNo ratings yet
- Essential Medicine List (Updated) (Medex - Com.bd)Document5 pagesEssential Medicine List (Updated) (Medex - Com.bd)Daak ChattalaNo ratings yet