0% found this document useful (0 votes)
395 views2 pagesANSYS Aluminum Beam Analysis Guide
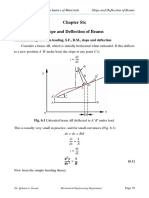
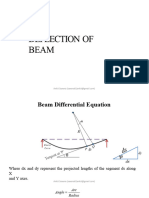
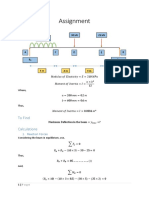
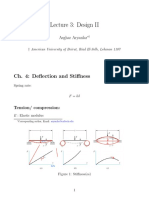
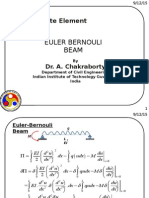
This document provides the problem description, nomenclature, theory, and geometry for modeling and analyzing an aluminum cantilever beam with a point load using one-dimensional elements in ANSYS. The beam has a length of 110m, cross section base of 10m, and height of 1m. It will be subjected to a 1000N point load. Beam theory equations are provided for von Mises stress, bending stress, and beam deflection. The maximum von Mises stress is calculated to be 66KPa and the maximum deflection at the loaded end is calculated to be 0.11m. Steps for opening ANSYS and beginning the geometry are outlined.
Uploaded by
Allan MarbaniangCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
395 views2 pagesANSYS Aluminum Beam Analysis Guide
This document provides the problem description, nomenclature, theory, and geometry for modeling and analyzing an aluminum cantilever beam with a point load using one-dimensional elements in ANSYS. The beam has a length of 110m, cross section base of 10m, and height of 1m. It will be subjected to a 1000N point load. Beam theory equations are provided for von Mises stress, bending stress, and beam deflection. The maximum von Mises stress is calculated to be 66KPa and the maximum deflection at the loaded end is calculated to be 0.11m. Steps for opening ANSYS and beginning the geometry are outlined.
Uploaded by
Allan MarbaniangCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd