Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Preparation of Catalysts 16
Preparation of Catalysts 16
Uploaded by
vahidOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Preparation of Catalysts 16
Preparation of Catalysts 16
Uploaded by
vahidCopyright:
Available Formats
What is a solid catalyst ?
Characteristics
• High surface area
• Low pressure drop
• High number of active sites
Classification of heterogeneous catalysts
Class Functions Examples
Metals, alloys hydrogenation Fe, Ni, Pd, Pt, Ag
conductors dehydrogenation
hydrogenolysis
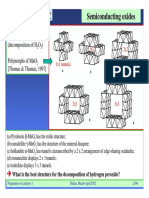
Oxides and sulphides block d oxidation NiO, ZnO, MnO2
Semiconductors dehydrogenation Cr2O3, Bi2O3-MoO3
desulphurization WS2
Insulator oxides blocks s and p dehydration Al2O3, SiO2, MgO
Acids, zeolites polymerization H3PO4, H2SO4
isomerization SiO2-Al2O3
cracking, alkylation
Preparation of catalysts 1 Dalian, March-April 2012 18/44
What is a solid catalyst ? The periodic table
18
1 2 H 13 14 15 16 17 He
Li Be B C N O F Ne
Na Mg 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Al Si P S Cl Ar
K Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr
Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te I Xe
Cs Ba Lu Hf Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg Tl Pb Bi Po At Rn
Fr Ra Lr
s block d block p block
lanthanides La Ce Pr Nd Pm Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb
actinides Ac Th Pa U Np Pu Am Cm Bk Cf Es Fm Md No
f block
Preparation of catalysts 1 Dalian, March-April 2012 19/44
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Orsi 2005Document10 pagesOrsi 2005vahidNo ratings yet
- US4072814Document6 pagesUS4072814vahidNo ratings yet
- Sure. in The Ideal Case This A Diabatic Process IsDocument2 pagesSure. in The Ideal Case This A Diabatic Process IsvahidNo ratings yet
- Inso نﺎﻣزﺎﺳ ﻲﻠﻣ ناﺮﻳا دراﺪﻧﺎﺘﺳا: ناﺮﻳا ﻲﻠﻣ دراﺪﻧﺎﺘﺳا 14607 14607 لوا پﺎﭼ 1st. EditionDocument8 pagesInso نﺎﻣزﺎﺳ ﻲﻠﻣ ناﺮﻳا دراﺪﻧﺎﺘﺳا: ناﺮﻳا ﻲﻠﻣ دراﺪﻧﺎﺘﺳا 14607 14607 لوا پﺎﭼ 1st. EditionvahidNo ratings yet
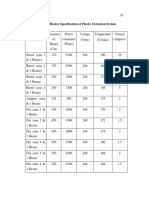
- Table 3.1 Heater Specification of Plastic Extrusion SystemDocument2 pagesTable 3.1 Heater Specification of Plastic Extrusion SystemvahidNo ratings yet
- 08 - Chapter 3Document2 pages08 - Chapter 3vahidNo ratings yet
- 4.1.2 Steel Casing - LQ DesignDocument2 pages4.1.2 Steel Casing - LQ DesignvahidNo ratings yet
- Cacl2 Concntrating - 1 PDFDocument2 pagesCacl2 Concntrating - 1 PDFvahidNo ratings yet
- Equipment Description: 4.1 CasingDocument2 pagesEquipment Description: 4.1 CasingvahidNo ratings yet
- 10 Runkel - Sulphuric 2009 - Pyrite Roasting - Runkel Sturm - OUTOTEC JH - 1Document2 pages10 Runkel - Sulphuric 2009 - Pyrite Roasting - Runkel Sturm - OUTOTEC JH - 1vahidNo ratings yet
- 10 Runkel - Sulphuric 2009 - Pyrite Roasting - Runkel Sturm - OUTOTEC JH - 6Document2 pages10 Runkel - Sulphuric 2009 - Pyrite Roasting - Runkel Sturm - OUTOTEC JH - 6vahidNo ratings yet
- 10 Runkel - Sulphuric 2009 - Pyrite Roasting - Runkel Sturm - OUTOTEC JH - 5Document2 pages10 Runkel - Sulphuric 2009 - Pyrite Roasting - Runkel Sturm - OUTOTEC JH - 5vahidNo ratings yet
- 10 Runkel - Sulphuric 2009 - Pyrite Roasting - Runkel Sturm - OUTOTEC JHDocument26 pages10 Runkel - Sulphuric 2009 - Pyrite Roasting - Runkel Sturm - OUTOTEC JHvahidNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Catalysts 19Document2 pagesPreparation of Catalysts 19vahidNo ratings yet
- Methylated Mesoporous SnsiDocument2 pagesMethylated Mesoporous SnsivahidNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Catalysts 10Document2 pagesPreparation of Catalysts 10vahidNo ratings yet
- TST Company Profile 2013 - 1Document2 pagesTST Company Profile 2013 - 1vahidNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Catalysts 17Document2 pagesPreparation of Catalysts 17vahidNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Catalysts 8Document2 pagesPreparation of Catalysts 8vahidNo ratings yet