Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GACE Mathematics Notations, Definitions, and Formulas PDF
Uploaded by
lolhaha321Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GACE Mathematics Notations, Definitions, and Formulas PDF
Uploaded by
lolhaha321Copyright:
Available Formats
NOTATIONS
(a, b) {x : a < x < b}
[ a, b ) {x : a £ x < b}
( a, b ] {x : a < x £ b}
[ a, b ] {x : a £ x £ b}
gcd (m, n ) greatest common divisor of two integers m and n
lcm (m, n ) least common multiple of two integers m and n
[ x] greatest integer m such that m £ x
m ∫ k (mod n ) m and k are congruent modulo n (m and k have the same remainder
when divided by n, or equivalently, m - k is a multiple of n)
-1 1
f inverse of an invertible function f (not the same as )
f
lim f ( x ) right-hand limit of f ( x ) ; limit of f ( x ) as x approaches a from the right
xÆ a+
lim f ( x ) left-hand limit of f ( x ) ; limit of f ( x ) as x approaches a from the left
xÆ a-
∆ the empty set
x ŒS x is an element of set S
SÃT set S is a proper subset of set T
SÕT either set S is a proper subset of set T or S = T
S »T union of sets S and T
S «T intersection of sets S and T
DEFINITIONS
A relation ¬ on a set S is
reflexive if x  x for all x ΠS
symmetric if x  y fi y  x for all x, y ΠS
transitive if ( x  y and y  z ) fi x  z for all x, y, z ΠS
antisymmetric if ( x  y and y  x ) fi x = y for all x, y ΠS
An equivalence relation is a reflexive, symmetric, and transitive relation.
FORMULAS
Sum
sin(x ± y) = sin x cos y ± cos x sin y
cos( x ± y) = cos x cos y ∓ sin x sin y
tan x ± tan y
tan(x ± y) =
1 ∓ tan x tan y
(
Half-angle sign depends on the quadrant of
q
2 )
q 1 - cos q
sin =±
2 2
q 1 + cos q
cos =±
2 2
Range of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
sin -1 x È- p , p ˘
ÎÍ 2 2 ˙˚
cos -1 x [0, p ]
tan -1 x (- p2 , p2 )
Law of Sines
B
sin A sin B sin C
= =
a b c
c a
Law of Cosines
A C
c = a + b - 2 ab (cos C )
2 2 2 b
DeMoivre’s Theorem
(cos q + i sin q ) k = cos (k q ) + i sin (k q )
Coordinate Transformation
y
Rectangular ( x, y ) to polar (r, q ) : r 2 = x 2 + y2 ; tan q = if x π 0
x
Polar (r, q ) to rectangular ( x, y ) : x = r cos q; y = r sin q
Distance from point ( x1 , y1 ) to line Ax + By + C = 0
Ax1 + By1 + C
d =
A2 + B2
Volume
4 3
Sphere with radius r : V = pr
3
1 2
Right circular cone with height h and base of radius r : V = pr h
3
Right circular cylinder with height h and base of radius r : V = p r 2h
1
Pyramid with height h and base of area B : V = Bh
3
Right prism with height h and base of area B : V = Bh
Surface Area
Sphere with radius r : A = 4 p r2
Right circular cone with radius r and slant height s : A = p rs + p r 2
Differentiation
( f ( x ) g ( x ) )¢ = f ¢ ( x ) g ( x ) + f ( x ) g ¢ ( x )
( f ( g ( x ) ) )¢ = f ¢ ( g ( x ) ) g ¢ ( x )
Ê f ( x) ˆ ¢ f ¢ ( x ) g ( x ) - f ( x ) g ¢( x )
= if g( x ) π 0
ËÁ g ( x ) ¯˜ ( g ( x ) )2
Integration by Parts
Ú u dv = uv - Ú v du
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- King's Air Raid OffenseDocument13 pagesKing's Air Raid Offenselolhaha321100% (1)
- King's Air Raid OffenseDocument13 pagesKing's Air Raid Offenselolhaha321100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Dual-Clutch Transmission: Scalable HybridDocument4 pagesDual-Clutch Transmission: Scalable HybridSamadNo ratings yet
- Training Sinal PDFDocument15 pagesTraining Sinal PDFlobitoferoz81No ratings yet
- PAMDocument14 pagesPAMRashed IslamNo ratings yet
- FCE Reading and Use of English - Practice Test 14Document13 pagesFCE Reading and Use of English - Practice Test 14Andrea LNo ratings yet
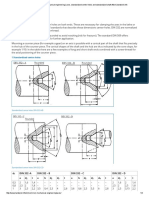
- Din332 PDFDocument4 pagesDin332 PDFmateo100% (2)
- Practice Writing Effective SentencesDocument5 pagesPractice Writing Effective SentencesHaekal FarabyNo ratings yet
- Linda Bloomberg: Certified Elementary School Teacher (Grades K 6)Document2 pagesLinda Bloomberg: Certified Elementary School Teacher (Grades K 6)lolhaha321No ratings yet
- Chris Black: New York State-Certified Special Education Teacher - Grades K-12Document1 pageChris Black: New York State-Certified Special Education Teacher - Grades K-12lolhaha321No ratings yet
- Country Item Name Litre Quart Pint Nip 700 ML IndiaDocument17 pagesCountry Item Name Litre Quart Pint Nip 700 ML Indiajhol421No ratings yet
- January 2005 6677 Mechanics M1: Mark SchemeDocument7 pagesJanuary 2005 6677 Mechanics M1: Mark SchemeWael TareqNo ratings yet
- Geographic Information Systems and Science-GoodchildDocument8 pagesGeographic Information Systems and Science-GoodchildChoc OlateNo ratings yet
- Mono and DicotDocument3 pagesMono and Dicotlady chaseNo ratings yet
- 15b. FANC - Focused Antenatal Care - Koros E.KDocument71 pages15b. FANC - Focused Antenatal Care - Koros E.KMercy KeruboNo ratings yet
- Baremos Sexual Desire Inventory MEN WomenDocument1 pageBaremos Sexual Desire Inventory MEN WomenGabriNo ratings yet
- Case Report - Anemia Ec Cervical Cancer Stages 2bDocument71 pagesCase Report - Anemia Ec Cervical Cancer Stages 2bAnna ListianaNo ratings yet
- Example Lab ReportDocument12 pagesExample Lab ReportHung Dang QuangNo ratings yet
- Jotafloor: Traffic Deck SystemDocument12 pagesJotafloor: Traffic Deck SystemUnited Construction Est. TechnicalNo ratings yet
- SGK Tieng Anh 9 Thi Diem Tap 1Document73 pagesSGK Tieng Anh 9 Thi Diem Tap 1Nhu NguyenNo ratings yet
- Ps 0412 0612obh WDocument1 pagePs 0412 0612obh WHunterNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Codes and Standards Workshop: Naser ChowdhuryDocument24 pagesHydrogen Codes and Standards Workshop: Naser ChowdhuryDiana DhominicNo ratings yet
- PIA Rivalry Strategy MapDocument16 pagesPIA Rivalry Strategy MapRomeo KhanNo ratings yet
- Installiation of Automatic Fire Sprinkler System and Design CalculationDocument8 pagesInstalliation of Automatic Fire Sprinkler System and Design CalculationSat AungNo ratings yet
- Fra Assignment 1Document11 pagesFra Assignment 1Ruchi SambhariaNo ratings yet
- Optoelectronics Circuit CollectionDocument18 pagesOptoelectronics Circuit CollectionSergiu CristianNo ratings yet
- 2005 Removing Aland RegeneratingDocument6 pages2005 Removing Aland RegeneratingHebron DawitNo ratings yet
- Recognizing and Classifying Daily Human Activities: Group-22Document23 pagesRecognizing and Classifying Daily Human Activities: Group-22Divyam GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ste FannyDocument17 pagesSte FannyElmer DE LA CruzNo ratings yet
- International StandardDocument8 pagesInternational Standardnazrul islamNo ratings yet
- SEC - Connection Guidelines - v3 - CleanDocument54 pagesSEC - Connection Guidelines - v3 - CleanFurqan HamidNo ratings yet
- Sa 387Document6 pagesSa 387ismaelarchilacastilloNo ratings yet
- Mesoamerica: Where Civilizations Flourished, and Crashed, RepeatedlyDocument8 pagesMesoamerica: Where Civilizations Flourished, and Crashed, RepeatedlyEnvyAmarr •No ratings yet
- MAIN Electrical Parts List: Design LOC Sec-Code DescriptionDocument12 pagesMAIN Electrical Parts List: Design LOC Sec-Code DescriptionAndroid Schematics and CircuitsNo ratings yet