0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views6 pagesFinancial Adjustments Analysis
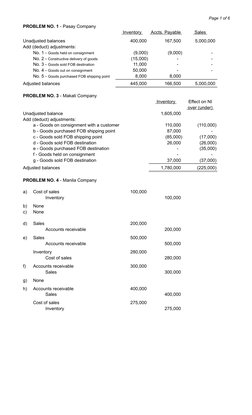
The document contains accounting problems and solutions for multiple companies (Pasay, Makati, Manila, Taguig, Mandaluyong, and Muntinlupa). For Pasay Company, the adjustments to inventory, accounts payable and sales are provided. For Makati Company, the adjustments to inventory and their impact on net income are listed. Multiple transactions are presented for the companies to be solved.
Uploaded by
James PaulCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as XLS, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views6 pagesFinancial Adjustments Analysis
The document contains accounting problems and solutions for multiple companies (Pasay, Makati, Manila, Taguig, Mandaluyong, and Muntinlupa). For Pasay Company, the adjustments to inventory, accounts payable and sales are provided. For Makati Company, the adjustments to inventory and their impact on net income are listed. Multiple transactions are presented for the companies to be solved.
Uploaded by
James PaulCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as XLS, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Problem No. 4 - Manda Company
- Problem No. 3 - Makati Company
- Problem No. 1 - Pasay Company
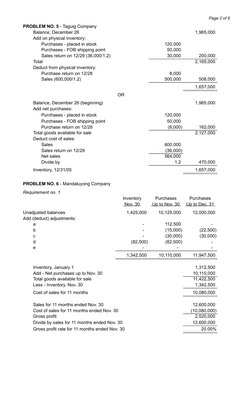
- Problem No. 5 - Taguig Company
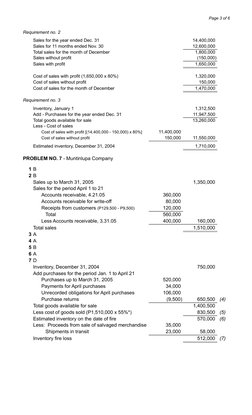
- Problem No. 6 - Mandaluyong Company
- Problem No. 7 - Muntilupa Company
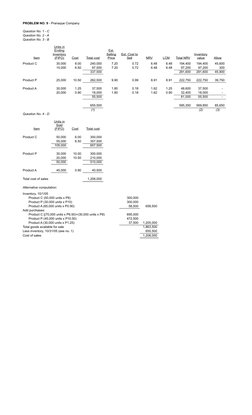
- Problem No. 8 - Parañaque Company
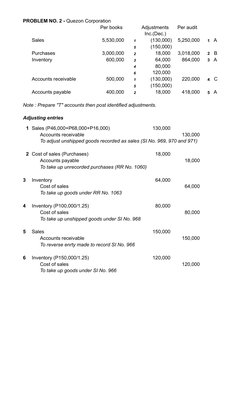
- Problem No. 2 - Quezon Corporation
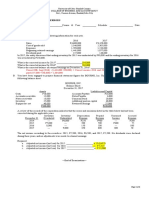
- Problem No. 9 - Primexage Company