Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Medcoro
Medcoro
Uploaded by
Vhinny Macabontoc0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageOriginal Title
medcoro.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageMedcoro
Medcoro
Uploaded by
Vhinny MacabontocCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
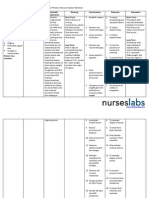
Ineffective peripheral tissue perfusion:
1. Check for pallor, cyanosis, mottling, cool or clammy skin. Assess quality of every pulse.
2. Monitor for oxygen saturation
3. Assist with position changes.
4. Promote active/passive ROM exercises.
5. Provide oxygen therapy as necessary.
6. Position patient properly in a semi-Fowler’s to high-Fowler’s as tolerated.
Fluid volume excess:
1. Monitor input and output
2. Monitor fluid intake.
3. Monitor vital signs: noting BP, HR
4. Assess for bounding peripheral pulses
5. Assess for crackles in the lungs, changes in respiratory pattern, shortness of breath, and
orthopnea.
6. Note for presence of edema by palpating
7. Limit sodium intake as prescribed.
8. Elevate edematous extremities, and handle with care.
9. Aid with repositioning every 2 hours if the patient is not mobile.
10. Instruct patient, caregiver, and family members regarding fluid restrictions, as appropriate.
You might also like
- Excess Fluid VolumeDocument3 pagesExcess Fluid VolumeStephanie Joy Escala100% (1)
- Fluids and Electrolytes ExamDocument3 pagesFluids and Electrolytes Exammonmon100% (3)
- Fluid Volume ExcessDocument4 pagesFluid Volume ExcessTamil Villardo100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan 1Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan 1gagandipkS100% (1)
- NCP - Fluid RetentionDocument3 pagesNCP - Fluid RetentionMichelle Teodoro100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plans For Burned PatientDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plans For Burned PatientJunah Marie Rubinos Palarca85% (26)
- Nursing Care Plan: DiagnosisDocument11 pagesNursing Care Plan: DiagnosisCharmaine100% (1)
- Pediatric Nursing Care Plan Impaired Physical MobilityDocument5 pagesPediatric Nursing Care Plan Impaired Physical Mobilityapi-3077327050% (1)
- Orthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingFrom EverandOrthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingNo ratings yet
- HypernatremiaDocument2 pagesHypernatremiaAliyah PundagNo ratings yet
- ARDSDocument18 pagesARDSChurrizo IslamiNo ratings yet
- Lifestyle Modification: Asterlyn T. Coniendo Bsn-IvDocument4 pagesLifestyle Modification: Asterlyn T. Coniendo Bsn-IvAsterlyn ConiendoNo ratings yet
- Lifestyle Modification: Asterlyn T. Coniendo Bsn-IvDocument4 pagesLifestyle Modification: Asterlyn T. Coniendo Bsn-IvAsterlyn ConiendoNo ratings yet
- n360 Concept Map Care Plan Week 3 Sheryl SatoDocument15 pagesn360 Concept Map Care Plan Week 3 Sheryl Satoapi-283363983No ratings yet
- Oxygen Administration ScriptDocument2 pagesOxygen Administration ScriptTyn TynNo ratings yet
- Risk For AspirationDocument9 pagesRisk For AspirationFerreze AnnNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation Subjective DataDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation Subjective DataCheila CruzNo ratings yet
- Impaired Skin Integrity Related To Pruritus From Jaundice and EdemaDocument6 pagesImpaired Skin Integrity Related To Pruritus From Jaundice and EdemaDwi Kurnia SariNo ratings yet
- Core PulmunaleDocument1 pageCore PulmunaleJuvick Lopez DionsonNo ratings yet
- Ncp'sDocument8 pagesNcp'sDuchess Kleine RafananNo ratings yet
- Postoperative PhaseDocument8 pagesPostoperative PhasereymarhayNo ratings yet
- Lahore School of Nursing 9Document4 pagesLahore School of Nursing 9Ayesha ImtiazNo ratings yet
- Collaborative Problems ChartDocument4 pagesCollaborative Problems ChartninaNo ratings yet
- Nursing InterventionsDocument1 pageNursing InterventionsdyiselaNo ratings yet
- Conceptmaptext For EpDocument9 pagesConceptmaptext For Epapi-272402391No ratings yet
- Fluid Electrolytes and Acid-Base BalanceDocument12 pagesFluid Electrolytes and Acid-Base BalanceHajra Al-Khuwaitem100% (1)
- Activity Intolerance NCPDocument6 pagesActivity Intolerance NCPDoo NahNo ratings yet
- Overhydration Nursing Care Plan: Wong, Karl Michael PDocument8 pagesOverhydration Nursing Care Plan: Wong, Karl Michael PMikaela Wong50% (2)
- Deficit Knowledge Related To Less Nutrition IntakeDocument3 pagesDeficit Knowledge Related To Less Nutrition IntakealifazranshahNo ratings yet
- Nursing InterventionsDocument2 pagesNursing InterventionsAaron Paul Romualdez100% (4)
- NCPDocument15 pagesNCPCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Skills Lab Day 13.1 Arterial Blood Gas Abg22Document38 pagesNCM 109 Skills Lab Day 13.1 Arterial Blood Gas Abg22Sheena Patricia ArasulaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management For Acute Respiratory FailureDocument7 pagesNursing Management For Acute Respiratory FailureEvolynNo ratings yet
- NCP For HHSDocument1 pageNCP For HHSLizzuly Galindo100% (1)
- Name: FRANCHIE M. HSU Score: - I. Interpret The Following: 1Document7 pagesName: FRANCHIE M. HSU Score: - I. Interpret The Following: 1FranchieNo ratings yet
- Nclex Questions - Medical Surgical NursingDocument15 pagesNclex Questions - Medical Surgical NursingRegine Gozo100% (1)
- Group 5 - Hemodialysis - Chronic Kidney FailureDocument31 pagesGroup 5 - Hemodialysis - Chronic Kidney FailureKimberly Abella CabreraNo ratings yet
- Pre-Lab Questions:: Deep Breathing & Coughing Exercises Oxygen TherapyDocument3 pagesPre-Lab Questions:: Deep Breathing & Coughing Exercises Oxygen TherapyaliNo ratings yet
- Actual NCPDocument3 pagesActual NCPMabz BoholNo ratings yet
- NCP Liver CirrhosisDocument7 pagesNCP Liver CirrhosisIris Jimenez-BuanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Nursing TestDocument4 pagesEndocrine Nursing TestAaron Carlos100% (2)
- Postural DrainageDocument6 pagesPostural DrainageKit Alizon Barredo0% (1)
- Snake Bites MainDocument6 pagesSnake Bites MainElvisNo ratings yet
- Chronic BronchitisDocument2 pagesChronic BronchitisEimhie Lee CasiNo ratings yet
- Osteomalacia Care Plan/OthersDocument11 pagesOsteomalacia Care Plan/OthersJill Jackson, RNNo ratings yet
- Carlo Fluid and ElectrolyteDocument22 pagesCarlo Fluid and ElectrolyteJem PantigNo ratings yet
- NCP - Pulmonary TuberculosisDocument6 pagesNCP - Pulmonary TuberculosisastrijuNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Excess CRFDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Excess CRFDana Fajardo RezanoNo ratings yet
- Dialysis ReviewerDocument16 pagesDialysis ReviewerlarraNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances: Nursing Management Nursing Care Plan Discharge Planning Core CompetenciesDocument40 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Imbalances: Nursing Management Nursing Care Plan Discharge Planning Core Competenciesayazafra100% (1)
- Agn Diagnosis and InterventionsDocument2 pagesAgn Diagnosis and InterventionsKristine JamilleNo ratings yet
- Advanced Clinical Concepts QuestionsDocument10 pagesAdvanced Clinical Concepts QuestionsMelissa BuckNo ratings yet
- NCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Document4 pagesNCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Jessamine EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Concept On Surgery: Postoperative CareDocument44 pagesConcept On Surgery: Postoperative CareMelisa ClaireNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis 1. Fluid Volume Deficit Related To Vaginal BleedingDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis 1. Fluid Volume Deficit Related To Vaginal BleedingNica Gaborne NavarroNo ratings yet
- Laryngopharyngeal Reflux, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandLaryngopharyngeal Reflux, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Fluid and Electrolytes for Nursing StudentsFrom EverandFluid and Electrolytes for Nursing StudentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (12)
- Diseases of Poultry - How to Know Them, Their Causes, Prevention and Cure - Containing Extracts from Livestock for the Farmer and Stock OwnerFrom EverandDiseases of Poultry - How to Know Them, Their Causes, Prevention and Cure - Containing Extracts from Livestock for the Farmer and Stock OwnerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)