Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Orbital Degeneracy, Orbital Ordering: Problem
Uploaded by
Ketan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageThe document discusses orbital degeneracy and orbital ordering in transition metal compounds. It focuses on a simple model with two sites, each having two-fold degenerate orbitals (eg states). The one-electron part of the Hamiltonian includes separate hopping terms for each orbital. Interactions include Hubbard-like repulsion energies that depend on the occupied orbitals, and the possibility of spin singlet or triplet states when electrons occupy different orbitals on the same site. This model aims to identify terms in an effective Hamiltonian and possibilities for novel ordering behaviors arising from orbital degeneracy.
Original Description:
General Document 128
Original Title
00242___bae84534eb5f3550a5559ceb8f959320
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses orbital degeneracy and orbital ordering in transition metal compounds. It focuses on a simple model with two sites, each having two-fold degenerate orbitals (eg states). The one-electron part of the Hamiltonian includes separate hopping terms for each orbital. Interactions include Hubbard-like repulsion energies that depend on the occupied orbitals, and the possibility of spin singlet or triplet states when electrons occupy different orbitals on the same site. This model aims to identify terms in an effective Hamiltonian and possibilities for novel ordering behaviors arising from orbital degeneracy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageOrbital Degeneracy, Orbital Ordering: Problem
Uploaded by
KetanThe document discusses orbital degeneracy and orbital ordering in transition metal compounds. It focuses on a simple model with two sites, each having two-fold degenerate orbitals (eg states). The one-electron part of the Hamiltonian includes separate hopping terms for each orbital. Interactions include Hubbard-like repulsion energies that depend on the occupied orbitals, and the possibility of spin singlet or triplet states when electrons occupy different orbitals on the same site. This model aims to identify terms in an effective Hamiltonian and possibilities for novel ordering behaviors arising from orbital degeneracy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
226 Ch.
5 Mott Transition and Hubbard Model
Problem 5.3 What kind of correlations does the X-term “want” to induce
in the system? You can try to find this out by considering the eigenstates
of N = 2 electrons on a linear chain, described by the truncated operator
3Cu +RX.
Problem 5.4. Use the Hubbard operators to express the non-diagonal terms
of the generalized Hubbard model given in (5.71). Is there anything
special about the point X = t ?
Problem 5.5. Derive the effective Hamiltonian for the half-filled extended
Hubbard model! Take 3Cu + 3Cv as the large term of the Hamiltonian. Discuss
the condition for a ferromagnetic effective exchange coupling!
5.4 Orbital Degeneracy, Orbital Ordering
The orbital degeneracy of the d-shell makes the physics of transition
metal compounds much richer than our previous experience with the
oon-degenerate Hubbard model would lead us to guess. At the same
time, our understanding of these complex phenomena is less detailed
than what we described in the foregoing text. We will confine ourselves
to simple arguments to identify pieces of an effective Hamiltonian, and to
characterize the ensuing novel possibilities of ordering. Our discussion is
based on [76] and [206], and on the short review [207]. A more complete
calculation of the same kind (applied to V203) was given in [SO].
For the sake of simplicity, let us consider two sites, each with a two-
fold degenerate orbital (we may think of eg states). The orbitals are
denoted by (pa and Yb, and the corresponding Wannier operators are
t where j = 1 , 2 is the site index and c the spin. Assuming
t and Cjb,,,
cia,,
that the hopping does not mix cpo with pb, the one-electron part of the
Hamiltonian is
%hop = -ta x ( C l at u % u + H-c.) - t b x ( C l btu C 2 b u + H-c-)- (5.72)
u u
Putting two electrons on the same site costs a Hubbard-like repulsion
energy which depends on which orbitals are occupied; these will be
denoted by U,, ub, and Uab. Furthermore, if one electron is in the a
state, and the other in the b state, they can form either a spin singlet
You might also like
- Problems in Quantum Mechanics: Third EditionFrom EverandProblems in Quantum Mechanics: Third EditionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Introduction to Non-Linear Mechanics. (AM-11), Volume 11From EverandIntroduction to Non-Linear Mechanics. (AM-11), Volume 11No ratings yet
- 23 - Fine Structure in Hydrogen and Alkali Atoms PDFDocument15 pages23 - Fine Structure in Hydrogen and Alkali Atoms PDFUltrazordNo ratings yet
- Energy Band TheoryDocument17 pagesEnergy Band Theorylalithamsc2004No ratings yet
- 8.321 Quantum Theory-I Fall 2016: Final Exam Dec 19, 2016Document4 pages8.321 Quantum Theory-I Fall 2016: Final Exam Dec 19, 2016bahadoor22i5583No ratings yet
- S.A. Kivelson Et Al - 2e or Not 2e: Flux Quantization in The Resonating Valence Bond StateDocument6 pagesS.A. Kivelson Et Al - 2e or Not 2e: Flux Quantization in The Resonating Valence Bond StatePo48HSDNo ratings yet
- KohmotoDocument12 pagesKohmotobiprajit mondalNo ratings yet
- Berry Phase Q.NiuDocument26 pagesBerry Phase Q.Niuhc690232985No ratings yet
- Feynman PaperDocument4 pagesFeynman PaperJun Rey LincunaNo ratings yet
- Dirac Cone in Lieb LatticeDocument29 pagesDirac Cone in Lieb LatticevanalexbluesNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh Physics Olympiad 2016Document9 pagesBangladesh Physics Olympiad 2016Science Olympiad Blog88% (8)
- The Theory of Alpha Decay: Tristan H UbschDocument15 pagesThe Theory of Alpha Decay: Tristan H Ubschlokpati22mishra4134No ratings yet
- The Hubbard Model and Its PropertiesDocument24 pagesThe Hubbard Model and Its PropertiesTùng Danh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Atomic Physics: Questions:, ~ and c. Evaluate αDocument10 pagesAtomic Physics: Questions:, ~ and c. Evaluate αvasudevan m.vNo ratings yet
- Electron States in A Crystal: Solid State PhysicsDocument23 pagesElectron States in A Crystal: Solid State PhysicsXylarNo ratings yet
- Huckel Molecular Orbital Theory: Sapan Kumar Jain Assistant Professor, JMIDocument45 pagesHuckel Molecular Orbital Theory: Sapan Kumar Jain Assistant Professor, JMIMayank GuptNo ratings yet
- Two-Band Electronic Metal and Neighboring Spin Liquid (Spin Bose-Metal) On A Zigzag Strip With Longer-Ranged RepulsionDocument12 pagesTwo-Band Electronic Metal and Neighboring Spin Liquid (Spin Bose-Metal) On A Zigzag Strip With Longer-Ranged RepulsionLomewcxNo ratings yet
- 1D LuttingerDocument9 pages1D LuttingerTonmoy DharNo ratings yet
- 7 - The MethodsDocument14 pages7 - The MethodsludihemicarNo ratings yet
- Exactly Ground: Proven Cases of High-Spin StatesDocument1 pageExactly Ground: Proven Cases of High-Spin StatesSupriyaNo ratings yet
- FOL Unit 1Document17 pagesFOL Unit 1syed1188No ratings yet
- Fermi Math - Proc.cambridge - Phil.soc.1930Document11 pagesFermi Math - Proc.cambridge - Phil.soc.1930leendert_hayen7107No ratings yet
- Magnetic Materials Assignment HelpDocument15 pagesMagnetic Materials Assignment HelpEdu Assignment Help100% (1)
- ArXivMOND10 16 06Document5 pagesArXivMOND10 16 06Dr. Harry RIngermacherNo ratings yet
- Separacao Spin CargaDocument12 pagesSeparacao Spin CargaMatheus MendesNo ratings yet
- PhysRevA 70 042308Document8 pagesPhysRevA 70 042308Micael AndradeNo ratings yet
- Solutions The Problems: 2L/3 CZ:CDocument1 pageSolutions The Problems: 2L/3 CZ:CKetanNo ratings yet
- F. D. M. Haldane PDFDocument4 pagesF. D. M. Haldane PDFHamid iqbalNo ratings yet
- Quantum Waves-The Proper Basis For Low Dissipation Quantum Computing (Microelectronic Engineering, Vol. 63, Issue 1-3) (2002)Document5 pagesQuantum Waves-The Proper Basis For Low Dissipation Quantum Computing (Microelectronic Engineering, Vol. 63, Issue 1-3) (2002)sepot24093No ratings yet
- Standard Model Higgs Physics at CollidersDocument16 pagesStandard Model Higgs Physics at CollidersMariangela Diaz DesposorioNo ratings yet
- Sebastiano Sonego - Ultrastatic SpacetimesDocument12 pagesSebastiano Sonego - Ultrastatic SpacetimesOllo43No ratings yet
- Vibrational and Rotational Spectroscopy of Diatomic MoleculesDocument6 pagesVibrational and Rotational Spectroscopy of Diatomic MoleculesBharathiNo ratings yet
- Vasili Perebeinos and Philip B. Allen - Toward A Theory of Orbiton Dispersion in LaMnO3Document8 pagesVasili Perebeinos and Philip B. Allen - Toward A Theory of Orbiton Dispersion in LaMnO3SaqqerNo ratings yet
- Fault-Tolerant Quantum Computation by Anyons: A.Yu. KitaevDocument29 pagesFault-Tolerant Quantum Computation by Anyons: A.Yu. KitaevNomentsuNo ratings yet
- A Mechanism of The Large-Scale Damping in The CMB AnisotropyDocument31 pagesA Mechanism of The Large-Scale Damping in The CMB AnisotropyFlori Rodriguez HernandezNo ratings yet
- Hamse Y. Mussa and Jonathan Tennyson - Calculating Quasi-Bound Rotation-Vibrational States of HOCl Using Massively Parallel ComputersDocument9 pagesHamse Y. Mussa and Jonathan Tennyson - Calculating Quasi-Bound Rotation-Vibrational States of HOCl Using Massively Parallel ComputersKmaxx2No ratings yet
- Guocai Liu Et Al - Spin Hall Effect On The Kagome Lattice With Rashba Spin-Orbit InteractionDocument7 pagesGuocai Liu Et Al - Spin Hall Effect On The Kagome Lattice With Rashba Spin-Orbit InteractionYamcsaNo ratings yet
- Miller Indices & Bragg LawDocument4 pagesMiller Indices & Bragg LawSayan KarNo ratings yet
- Vortices and The Berezinskii Kosterlitz Thouless TransitionDocument9 pagesVortices and The Berezinskii Kosterlitz Thouless TransitionAdam AhmedNo ratings yet
- Cold Atoms in Double-Well Optical Lattices V.I. Yukalov and E.P. YukalovaDocument24 pagesCold Atoms in Double-Well Optical Lattices V.I. Yukalov and E.P. YukalovaArturo CamachoNo ratings yet
- Hari Shanker Gupta and Phoolan Prasad - A Bicharacteristic Formulation of The Ideal MHD EquationsDocument25 pagesHari Shanker Gupta and Phoolan Prasad - A Bicharacteristic Formulation of The Ideal MHD EquationsHimaszNo ratings yet
- Ch4 - Chapter 4. Bra-Ket FormalismDocument68 pagesCh4 - Chapter 4. Bra-Ket FormalismdomeleuNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-To-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: Ikn A IkxDocument7 pages2.57 Nano-To-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: Ikn A IkxcaptainhassNo ratings yet
- Brian T. Sutcliffe and Jonathan Tennyson - Variational Methods For The Calculation of Rovibrational Energy Levels of Small MoleculesDocument12 pagesBrian T. Sutcliffe and Jonathan Tennyson - Variational Methods For The Calculation of Rovibrational Energy Levels of Small MoleculesTreaxmeANo ratings yet
- Holes in A Two-Dimensional Quantum AntiferromagnetDocument38 pagesHoles in A Two-Dimensional Quantum AntiferromagnetsantoshkudNo ratings yet
- Quantum Rotor Theory of Spinor Condensates in Tight TrapsDocument9 pagesQuantum Rotor Theory of Spinor Condensates in Tight TrapsgenhyinNo ratings yet
- Identical Particles PDFDocument31 pagesIdentical Particles PDFHồng NhânNo ratings yet
- Decoherence of An Exchange Qubit by Hyperfine Interaction: PACS Numbers: 03.67.Lx 73.21.la 03.65.yz 85.35.beDocument15 pagesDecoherence of An Exchange Qubit by Hyperfine Interaction: PACS Numbers: 03.67.Lx 73.21.la 03.65.yz 85.35.becrocoaliNo ratings yet
- Awake!, Jul 2011Document4 pagesAwake!, Jul 2011emediageNo ratings yet
- Aspects of 3d N 2 Chern-Simons-Matter Theories-LibreDocument77 pagesAspects of 3d N 2 Chern-Simons-Matter Theories-LibreRichard ZhuNo ratings yet
- LCAO MO Theory Illustrated by Its Application To H2Document8 pagesLCAO MO Theory Illustrated by Its Application To H2maugonzalezsuarezNo ratings yet
- Alexander Burinskii - Two Stringy Systems of The Kerr Spinning ParticleDocument22 pagesAlexander Burinskii - Two Stringy Systems of The Kerr Spinning ParticleSteam29No ratings yet
- Kalin Vetsigian - Chern-Simons Theory of Fractional Quantum Hall E EctDocument7 pagesKalin Vetsigian - Chern-Simons Theory of Fractional Quantum Hall E EctGreamxxNo ratings yet
- Bonding in Molecules 2019 2nd Yr Michaelmas TermDocument71 pagesBonding in Molecules 2019 2nd Yr Michaelmas Termtresa.george27No ratings yet
- Zheng-Cheng Gu and Xiao-Gang Wen - A Lattice Bosonic Model As A Quantum Theory of GravityDocument4 pagesZheng-Cheng Gu and Xiao-Gang Wen - A Lattice Bosonic Model As A Quantum Theory of GravityKiomaxNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Monopoles, Fiber BundlesDocument11 pagesMagnetic Monopoles, Fiber BundlesMojano De la MagdalenaNo ratings yet
- The Band: HubbardDocument1 pageThe Band: HubbardKetanNo ratings yet
- The Royal SocietyDocument18 pagesThe Royal Society2ymmgNo ratings yet
- Atomic and Laser Physics: PH-102 (Physics) : B. Tech. - I Year Spring Semester: 2006-07 Tutorial Sheet No. 3Document2 pagesAtomic and Laser Physics: PH-102 (Physics) : B. Tech. - I Year Spring Semester: 2006-07 Tutorial Sheet No. 3Tegar Wicaksana AdiansyachNo ratings yet
- Cond Mat9806216Document28 pagesCond Mat9806216fghsda123000No ratings yet
- Digression: Symmetry Breaking (Or The Lack It) : (17, 3821: As We 1,2,. ADocument1 pageDigression: Symmetry Breaking (Or The Lack It) : (17, 3821: As We 1,2,. AKetanNo ratings yet
- 31 JLSL: 5 Mott InsulatorsDocument1 page31 JLSL: 5 Mott InsulatorsKetanNo ratings yet
- Ofa As: !hasition andDocument1 pageOfa As: !hasition andKetanNo ratings yet
- Solutions: ProblemsDocument1 pageSolutions: ProblemsKetanNo ratings yet
- '&xisition Metals: and AlloysDocument1 page'&xisition Metals: and AlloysKetanNo ratings yet
- Ch. 5 Mott Insulators: (Cfatcfalcf6tcfblDocument1 pageCh. 5 Mott Insulators: (Cfatcfalcf6tcfblKetanNo ratings yet
- G1, Glj2 Where ?-Spins Igl,. G L / 2) : 6.3 For EvenDocument1 pageG1, Glj2 Where ?-Spins Igl,. G L / 2) : 6.3 For EvenKetanNo ratings yet
- Itinerant Electron Magnetism: 1 of Is A A AsDocument1 pageItinerant Electron Magnetism: 1 of Is A A AsKetanNo ratings yet
- The Problems: SolutionsDocument1 pageThe Problems: SolutionsKetanNo ratings yet
- Psat (442) (290) 1751: I Cannot Be The BareDocument1 pagePsat (442) (290) 1751: I Cannot Be The BareKetanNo ratings yet
- I To A: Zlansition Metals and AlloysDocument1 pageI To A: Zlansition Metals and AlloysKetanNo ratings yet
- 396 7 Itinerant Electron Magnetism: A So Pro-IsDocument1 page396 7 Itinerant Electron Magnetism: A So Pro-IsKetanNo ratings yet
- So We: ShouldDocument1 pageSo We: ShouldKetanNo ratings yet
- So Go: Itinerant Electron MagnetismDocument1 pageSo Go: Itinerant Electron MagnetismKetanNo ratings yet
- 7.7 Zhnsition Metals and Alloys 1 Also: So The Stoner Theory Is Not Valid in Its Original NaiveDocument1 page7.7 Zhnsition Metals and Alloys 1 Also: So The Stoner Theory Is Not Valid in Its Original NaiveKetanNo ratings yet
- 7.7 Tkansition Metals and AlloysDocument1 page7.7 Tkansition Metals and AlloysKetanNo ratings yet
- 7.6 Spin: Problem 7.6Document1 page7.6 Spin: Problem 7.6KetanNo ratings yet
- 7.7 Transition Metals and AlloysDocument1 page7.7 Transition Metals and AlloysKetanNo ratings yet
- Tiansition Metals and AlloysDocument1 pageTiansition Metals and AlloysKetanNo ratings yet
- 33meaning The Nearest-Neighbour Hopping Model On A Hypercubic LatticeDocument1 page33meaning The Nearest-Neighbour Hopping Model On A Hypercubic LatticeKetanNo ratings yet
- 7.7.2 LSDA Versus Lattice Fermion Models: Is ofDocument1 page7.7.2 LSDA Versus Lattice Fermion Models: Is ofKetanNo ratings yet
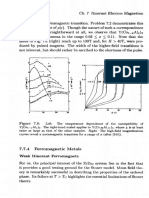
- 7 Itinerant Electron Magnetism: (166) Felt Compelled To Conjecture That Any Ordering Away FromDocument1 page7 Itinerant Electron Magnetism: (166) Felt Compelled To Conjecture That Any Ordering Away FromKetanNo ratings yet
- Ch. 7 Itinerant Electron Magnetism: T,, U, U. TDocument1 pageCh. 7 Itinerant Electron Magnetism: T,, U, U. TKetanNo ratings yet
- L'Kansition Metals Alloys: &F-PKJDocument1 pageL'Kansition Metals Alloys: &F-PKJKetanNo ratings yet
- Pm-Pi: Away From Half-FillingDocument1 pagePm-Pi: Away From Half-FillingKetanNo ratings yet
- 00396Document1 page00396KetanNo ratings yet
- 7.6 Spin Density: SDW MottDocument1 page7.6 Spin Density: SDW MottKetanNo ratings yet
- 7.6 Spin Density Waves: (SDWI)Document1 page7.6 Spin Density Waves: (SDWI)KetanNo ratings yet
- 7.6.3 Strong Coupling LimitDocument1 page7.6.3 Strong Coupling LimitKetanNo ratings yet
- 382 Ch. 7 Itinerant Electron Magnetism: RNQ (A) CosDocument1 page382 Ch. 7 Itinerant Electron Magnetism: RNQ (A) CosKetanNo ratings yet