0% found this document useful (0 votes)
411 views41 pagesIntroduction & Sketching
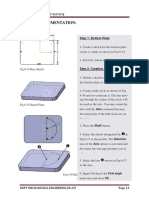
The document provides an overview of CATIA V5, which is an integrated computer-aided engineering tool incorporating CAD, CAM, CAE, and other applications. It discusses the sketcher tool, which is used to create 2D sketches and apply constraints. The sketcher provides a flexible environment for designing and modifying 2D profiles that will be used to build solid models. The document also outlines how to interact with CATIA, including selecting applications, working with files, manipulating views, and using common commands such as copy/paste.
Uploaded by
Murali SiddarthCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
411 views41 pagesIntroduction & Sketching
The document provides an overview of CATIA V5, which is an integrated computer-aided engineering tool incorporating CAD, CAM, CAE, and other applications. It discusses the sketcher tool, which is used to create 2D sketches and apply constraints. The sketcher provides a flexible environment for designing and modifying 2D profiles that will be used to build solid models. The document also outlines how to interact with CATIA, including selecting applications, working with files, manipulating views, and using common commands such as copy/paste.
Uploaded by
Murali SiddarthCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd